8th Standard CBSE Social Science Subjects Question Paper Software Subscription
QB365 covers complete information about 8th Standard CBSE Social Science Subject for 2024-2025 Exam. Question Bank includes 8th Standard CBSE Social Science Subjects Book back, exercise, Updated Question types MCQ, Case Study , Assertion and reason with solution, Previous year asked questions, all possible questions and other key points also. All question with detailed answers are readily available for preparting Maths question papers.
All Chapters Covered

Create Unlimited Question Papers

Access anywhere anytime
Multiple Pattern Question Papers
Share your Question Paper
Font size, line spacing, watermark etc,
Our Other Subjects for 8th Standard CBSE
8th Standard CBSE Social Science Chapters / Lessons
HIS - How, When and Where
HIS - From Trade to Territory - Company Establishes Power
HIS - Ruling the Countryside
HIS - Tribals, Dikus and the Vision of a Golden Age
HIS - When People Rebel - 1857 and After
HIS - Colonialism and the City - Story of An Imperial Capital
HIS - Weavers, Iron Smelters and Factory Owners
HIS - Civilising the 'Native' - Educating the Nation
HIS - Women, Caste and Reform
HIS - The Changing World of Visual Arts
HIS - The Making of the National Movements - 1870s- 1947
HIS - India After Independence
GEO - Resources
GEO - Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resource
GEO - Mineral and Power
GEO - Agriculture
GEO - Industries
GEO - Human Resources
CIV - The Indian Constitution
CIV - Understanding Secularism
CIV - Why Do We Need a Parliament?
CIV - Understanding Laws
CIV - Judiciary
CIV - Understanding Our Criminal Justice System
CIV - Understanding Marginalisation
CIV - Confronting Marginalisation
CIV - Public Facilities
CIV - Law and Social Justice
Dis - Being Prepared-A Vital Part of Disaster Management
Dis - Earthquakes
Dis - Cyclones
Dis - Floods
Dis - Drought
Dis - Man-made Disasters - An Overview
8th Standard CBSE Social Science Chapters / Lessons Syllabus
Our Pasts III
Where, When, How - (a) An overview of the period. (b) Introduction to the new geographical categories. (c) An outline of the time frame. (d) An introduction to the sources.
The Establishment of Company Power- (a) Mercantilism and trade-wars. (b) Struggle for territory, wars with Indian rulers. (c) The growth of colonial army and civilian administration.
Rural Life and Society - (a) Colonial agrarian policies; their effect on peasants and landlords. (b) Growth of commercial crops. (c) Peasant revolts: focus on indigo rebellions.
Colonialism and Tribal Societies - (a) Changes within tribal economies and societies in the nineteenth century. (b) Tribal revolts: focus on Birsa Munda.
Crafts and Industries - (a) Decline of handicrafts in the nineteenth century. (b) Brief reference to growth of industries in the twentieth century
The Revolt of 1857-58 - (a) The rebellion in the army and the spread of the movement. (b) The nature of elite and peasant participation
Education and British rule - (a) The new education system – schools, syllabi, colleges, universities, technical training. (b) Changes in the indigenous systems. (c) Growth of ‘National education’.
Women and reform - (a) Debates around sati, widow remarriage, child marriage and age of consent. (b) Ideas of different reformers on the position of women and women’s education.
Challenging the Caste System - (a) Arguments for caste reform. The ideas of Phule, Veerasalingam, Sri Narayana Guru, Periyar, Gandhi, Ambedkar. (b) Consequences and implications of the activities of the reformers.
Colonialism and Urban Change - (a) De-urbanisation and emergence of new towns. (b) Implications of colonial policies and institutions – municipalities, public works, planning, railway links, police.
Changes in the Arts: Painting, Literature, architecture - (a) Impact of new technologies and institutions: art schools, printing press. (b) Western academic style and nationalist art. (c) Changes in performing arts – music and dance enter the public arena. (d) New forms of writing. (e) New architecture.
The Nationalist Movement - (a) Overview of the nationalist movement from the 1870s to the 1940s. (b) Diverse trends within the movement and different social groups involved. (c) Links with constitutional changes.
India after Independence - (a) National and regional developments since 1947. (b) Relations with other countries. (c) Looking to the future.
Resources and Development - III
Resources - Resources: resources and their types – natural and human. Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources
Natural resources: their distribution, utilisation and conservation, land and soil, water, natural vegetation, wildlife, mineral and power resources (world patterns with special reference to India).
Mineral & Power Resources - Agriculture - Agriculture: types of farming, major crops, food crops, fibres, beverages, agricultural development – two case studies – one from India and the other from a developed country/a farm in the US/ Netherlands/ Australia.
Industries - Industries: classification of industries based on size, raw material, ownership; major industries and distribution; infrastructure and development. Iron and Steel (a comparative study of Jamshedpur and a centre in USA e.g., Detroit). Textile Industry (Ahmedabad and Osaka). Information Technology (Bangalore and Silicon Valley).
Human Resources - Human Resources – composition, population change, distribution and density.
Social and Political Life - III
The Indian Constitution - On need for laws discussed through an example like dowry, Role of Constitution in determining the authority/legitimacy of the law, Laws and Dissent: Salt Satyagraha and a post-1947 example such as anti-liquor agitation. Vision set forth in the Indian Constitution with a focus on secularism. - On how an ideal of the Constitution translates into a law - On how ideals of secularism got translated into fundamental rights. - On Fundamental rights as human rights. - On Fundamental Duties.
UNIT 2: Parliamentary Government - Reasons why parliamentary form chosen in India. -Main features of composition of parliament and its role in debating a bill - Accountability of the government to the parliament - Role of President, PM and the Council of Ministers. Translation of felt need into law and the critical features of the legislation. - Implication of law.
UNIT 3: The Judiciary - The structure and process followed by the judiciary: Trace a case from lower to higher courts - Distinguish between civil and criminal cases - Indicate the rationale of the process Role of the Public Prosecutor - On an FIR: filing one, on the illegality of the police not accepting an FIR and the Supreme Court’s directive on this.
UNIT 4: Social Justice and the Marginalized
Forms of social inequality - Constitutional provisions relating to social justice - Effect of social inequalities on economic inequalities - On Reservations. The law on manual scavenging with reference to existing realities in rural and urban areas.
UNIT 5: Economic Presence of the Government
Introduction of various ways by which government is engaged in developmental activities, especially in infrastructure and social sectors.
History - How, When and Where
How Important are Dates-How do We know
History - From Trade to Territory The Company Establishes Power
East India Company Comes East-Company Rule Expands-Setting up a New Administration-Conclusion
History - Ruling the Countryside
The Company Becomes the Diwan-Crops for Europe-The Blue Rebellion and After
History - Tribes, Dikus and the Vision of a Golden Age
How did Tribal Groups Live-How did Colonial Rule Affect Tribal Lives-A Closer Look
History - When People Rebel 1857 and After
Policies and the People-Through the Eyes of the People-A Mutiny Becomes a Popular Rebellion-The Company Fights Back-Aftermath
History - Colonialism and the City The Story of an Imperial Capital
What Happened to Cities Under Colonial Rule-The Making of New Delhi-Inside the Old City
History - Weavers, Iron Smelters and Factory Owners
Indian Textiles and the World Market-The sword of Tipu Sultan and Wootz steel
History - Civilising the “Native”, Educating the Nation
How the British saw Education- What Happened to the Local Schools- The Agenda for a National Education
History - Women, Caste and Reform
Working Towards Change- Caste and Social Reform
History - The Changing World of Visual Arts
New Forms of Imperial Art-What Happened to the Court Artisrts-The New Popular Indian Art-The Search for a National Art
History - The Making of the National Movement: 1870s -1947
The Emergence of Nationalism- The Growth of Mass Nationalism- The March to Dandi- Quit India and Later
History - India After Independence
A New and Divided Nation-A Constitution is Written-How were States to be Formed-Planning for Development-The Nation, Sixty Years On
Geography - Resources
Introduction- Types Of Resources- Conserving Resources
Geography - Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources
Land- Land Use- Conservation Of Land Resource- Soil- Factors Of Soil Formation- Degradation Of Soil And Conservation Measures- Water- Problems Of Water Availability- Conservation Of Water Resources- Natural Vegetation And Wildlife-Distribution Of Natural Vegetation- Conservation Of Natural Vegetation And Wildlife
Geography - Mineral and Power Resources
Types Of Minerals- Distribution Of Minerals- Europe- North America- South America- Africa- Australia- Antarctica- Distribution In India- Uses Of Minerals- Conservation Of Minerals- Power Resources- Non-Conventional Sources Of Energy- Tidal Energy- Biogas
Geography - Agriculture
Farm System- Types Of Farming
Geography - Industries
Classification Of Industries- Factors Affecting Location Of Industries- Industrial System- Industrial Regions- Distribution Of Major Industries- Tata Iron And Steel Company, Jamshedpur- Cotton Textile Industry- Information Technology
Geography - Human Resources
Distribution Of Population- Density Of Population- Factors Affecting Distribution Of Population- Population Change- Patterns Of Population Change- Population Composition
Civics - The Indian Constitution
Why Does a Country Need a Constitution- The Indian Constitution: Key Features
Civics - Understanding Secularism
What is Secularism- Why is it Important to Separate Religion from the State- What is Indian Secularism
Civics - Why Do We Need a Parliament
Why should People Decide- People and their Representatives- The Role of the Parliament- Who are the People in Parliament
Civics - Understanding Laws
Do Laws Apply to All- How Do New Laws Come About- Unpopular and Controversial Laws
Civics - Judiciary
What is the Role of the Judiciary- What is an Independent Judiciary- What is the Structure of Courts in India- What are the Different Branches of the Legal System- Does Everyone Have Access to the Courts
Civics - Understanding Our Criminal Justice System
What is the Role of the Police in Investigating a Crime- What is the Role of the Public Prosecutor- What is the Role of the Judge- What is a Fair Trial
Civics - Understanding Marginalisation
What Does it Mean to be Socially Marginalised- Who are Adivasis- Adivasis and Stereotyping- Adivasis and Development- Minorities and Marginalisation- Muslims and Marginalisation- Conclusion
Civics - Confronting Marginalisation
Invoking Fundamental Rights- Laws for the Marginalised- Protecting the Rights of Dalits and Adivasis- Adivasi Demands and the 1989 Act- Conclusion
Civics - Public Facilities
Water and the People of Chennai- Water as Part of the Fundamental Right to Life- Public Facilities- The Government’s Role- Water Supply to Chennai: Is it Available to All- In Search of Alternatives- Conclusion
Civics - Law and Social Justice
What is a Worker’s Worth- Enforcement of Safety Laws- New Laws to Protect the Environment- Conclusion
Features in Question Paper Preparation software

(or) type Question

Add or Remover

Sub Questions
Adding Notes

Multiple Pattern

All subjects available
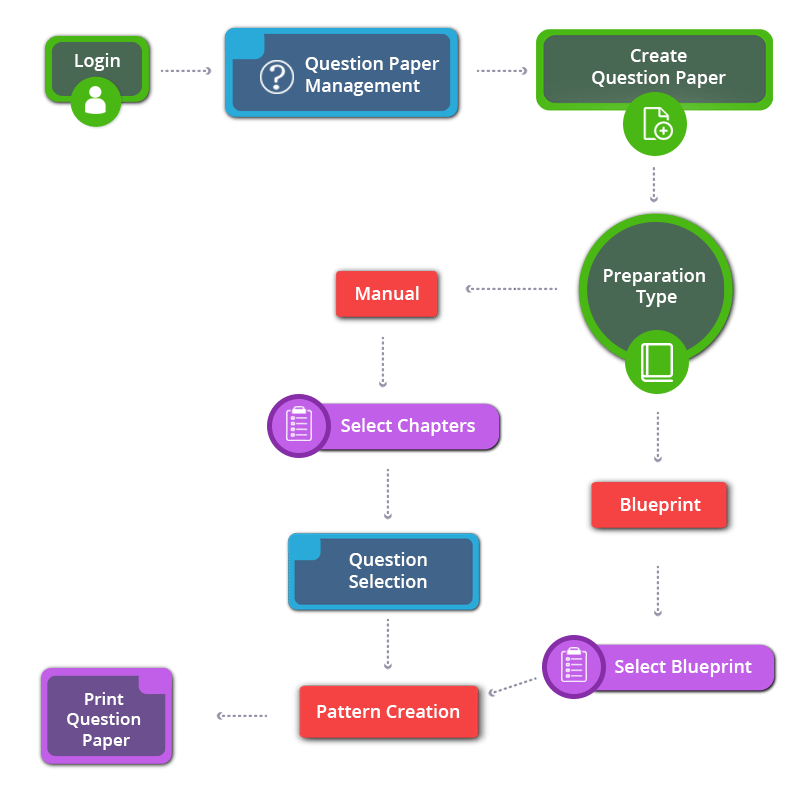
How to Create 8th Standard CBSE Social Science Question Paper

8th Standard CBSE Social Science
- Covers all chapters
- Unique Creative Questions
- Unlimited Question Paper
- Multiple Patterns & Answer keys
3888
3499



