- State Board
-
12th Standard
-

Biology
-

Computer Applications
-

Computer Science
-

Business Maths and Statistics
-

Commerce
-

Economics
-

Maths
-

Chemistry
-

Physics
-

Computer Technology
-

History
-

Accountancy
-

Tamil
-

Maths
-

Chemistry
-

Physics
-

Biology
-

Computer Science
-

Business Maths and Statistics
-

Economics
-

Commerce
-

Accountancy
-

History
-

Computer Applications
-

Computer Technology
-

English
12th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
11th Standard
-

Maths
-

Biology
-

உயிரியல் - தாவரவியல்
-

Economics
-

Physics
-

Chemistry
-

History
-

Business Maths and Statistics
-

Computer Science
-

Accountancy
-

Commerce
-

Computer Applications
-

Computer Technology
-

Tamil
-

Maths
-

Commerce
-

Economics
-

Biology
-

Business Maths and Statistics
-

Accountancy
-

Computer Science
-

Physics
-

Chemistry
-

Computer Applications
-

History
-

Computer Technology
-

Tamil
-

English
11th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
9th Standard
-

-

-

-

-

-

-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
9th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
6th Standard
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
6th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
10th Standard
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

Tamil
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

English
-

English
10th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
7th Standard
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
7th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
8th Standard
-

கணிதம் - old
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

கணிதம்
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
8th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
12th Standard
- CBSE Board
-
12th Standard CBSE
-

Biology
-

Physics
-

Chemistry
-

Maths
-

Accountancy
-

Introductory Micro and Macroeconomics
-

Business Studies
-

Economics
-

Computer Science
-

Geography
-

English
-

History
-

Indian Society
-

Physical Education
-

Sociology
-

Tamil
-

Bio Technology
-

Engineering Graphics
-

Entrepreneurship
-

Hindi Core
-

Hindi Elective
-

Home Science
-

Legal Studies
-

Political Science
-

Psychology
12th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
-
11th Standard CBSE
-

Mathematics
-

Chemistry
-

Biology
-

Physics
-

Business Studies
-

Accountancy
-

Economics
-

Computer Science
-

Bio Technology
-

English
-

Enterprenership
-

Geography
-

Hindi
-

History
-

Home Science
-

Physical Education
-

Political Science
-

Psychology
-

Sociology
-

Applied Mathematics
11th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
- 10th Standard CBSE
-
9th Standard CBSE
-

Mathematics
-

Social Science
-

Science
-

English
-

Hindi
9th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
-
8th Standard CBSE
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

Mathematics
-

English
8th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
-
7th Standard CBSE
-

Mathematics
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

English
7th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
-
6th Standard CBSE
-

Mathematics
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

English
6th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
-
12th Standard CBSE
- Free Online Test
- News
- Study Materials
-
Students
-

Stateboard Tamil Nadu
-

CBSE Board
-

Free Online Tests
-

Educational News
-

Scholarships
-

Entrance Exams India
-

Video Materials
Study Materials , News and Scholarships
-
-
Students

11th Standard Business Maths Public Exam March 2019 Important One Mark Test Mar-15 , 2019
11th Public Exam March 2019 Important One Mark Test
11th Public Exam March 2019 Important One Mark Test
11th Standard
-
Reg.No. :
Business Maths
Time :
02:30:00 Hrs
Total Marks :
120
-
The value of \(\begin{vmatrix} 2x+y & x & y \\ 2y+z & y & z \\ 2z+x & z & x \end{vmatrix}\) is ________.
(a)xyz
(b)x+y+z
(c)2x+2y+2z
(d)0
-
If \(\triangle=\begin{vmatrix} 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 3 & 1 & 2 \\ 2 & 3 & 1 \end{vmatrix}\) then \(\begin{vmatrix} 3 & 1 & 2 \\ 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 2 & 3 & 1 \end{vmatrix}\) is ________.
(a)\(\triangle\)
(b)-\(\triangle\)
(c)3\(\triangle\)
(d)-3\(\triangle\)
-
The value of the determinant \({\begin{vmatrix} a & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & a & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & c \end{vmatrix}}^{2}\)is ________.
(a)abc
(b)0
(c)a2b2c2
(d)-abc
-
adj (AB) is equal to ________.
(a)adj A adj B
(b)adj AT adj BT
(c)adj B adj A
(d)adj BT adj AT
-
The inverse matrix of \(\begin{pmatrix} \frac { 1 }{ 5 } & \frac { 5 }{ 25 } \\ \frac { 2 }{ 5 } & \frac { 1 }{ 2 } \end{pmatrix}\) is ________.
(a)\({{7}\over{30}}\begin{pmatrix} \frac { 1 }{ 2 } & \frac { 5 }{ 12 } \\ \frac { 2 }{ 5 } & \frac { 4 }{ 5 } \end{pmatrix}\)
(b)\({{7}\over{30}}\begin{pmatrix} \frac { 1 }{ 2 } & \frac { -5 }{ 12 } \\ \frac { -2 }{ 5 } & \frac { 1 }{ 5 } \end{pmatrix}\)
(c)\({{30}\over{7}}\begin{pmatrix} \frac { 1 }{ 2 } & \frac { 5 }{ 12 } \\ \frac { 2 }{ 5 } & \frac { 4 }{ 5 } \end{pmatrix}\)
(d)\({{30}\over{7}}\begin{pmatrix} \frac { 1 }{ 2 } & \frac { -5 }{ 12 } \\ \frac { -2 }{ 5 } & \frac { 4 }{ 5 } \end{pmatrix}\)
-
The number of Hawkins-Simon conditions for the viability of an input - output analysis is ________.
(a)1
(b)3
(c)4
(d)2
-
The inventor of input-output analysis is ________.
(a)Sir Francis Galton
(b)Fisher
(c)Prof. Wassily W. Leontief
(d)Arthur Caylay
-
Which of the following matrix has no inverse.
(a)\(\begin{pmatrix} -1 & 1 \\ 1 &-4 \end{pmatrix}\)
(b)\(\begin{pmatrix} 2 & -1 \\ -4 &2 \end{pmatrix}\)
(c)\(\begin{pmatrix} cos\ a & sin\ a \\ -sin\ a & cos\ a \end{pmatrix}\)
(d)\(\begin{pmatrix} sin\ a & cos\ a \\ -cos\ a & sin\ a \end{pmatrix}\)
-
If A \(=\begin{pmatrix} -1 & 2 \\ 1 & -4 \end{pmatrix}\) then A (adj A) is ________.
(a)\(\begin{pmatrix} -4 & -2 \\ -1 & -1 \end{pmatrix}\)
(b)\(\begin{pmatrix} 4 & -2 \\ -1 & 1 \end{pmatrix}\)
(c)\(\begin{pmatrix} 2 & 0 \\ 0 & 2 \end{pmatrix}\)
(d)\(\begin{pmatrix} 0 & 2 \\ 2 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\)
-
If A is an invertible matrix of order 2, then det (A-1) be equal to ________.
(a)det (A)
(b)\({{1}\over{det(A)}}\)
(c)1
(d)0
-
If A is 3 \(\times\) 3 matrix and |A| = 4, then |A-1| is equal to ________.
(a)\({{1}\over{4}}\)
(b)\({{1}\over{16}}\)
(c)2
(d)4
-
If A is a square matrix of order 3 and IAI = 3 then | adj A| is equal to ________.
(a)81
(b)27
(c)3
(d)9
-
If A = \(\begin{vmatrix}cos \theta & sin \theta \\ -sin \theta&cons\theta \end{vmatrix},\) then |2A| is equal to ________.
(a)4 cos 2 \(\theta\)
(b)4
(c)2
(d)1
-
If \(\triangle=\begin{vmatrix} {a}_{11} & {a}_{12} & {a}_{13} \\ {a}_{21} & {a}_{22} & {a}_{23} \\ {a}_{31} & {a}_{32} & {a}_{33} \end{vmatrix}\) and Aij is cofactor of aij, then value of \(\triangle\) is given by ________.
(a)a11 A31 + a12 A32 + a13 A33
(b)a11 A11 + a12 A21 + a13 A31
(c)a21 A11 + a22 A12 + a23 A13
(d)a11 A11 + a21 A21 + a31 A31
-
If \(\begin{vmatrix} 4 & 3 \\ 3 & 1 \end{vmatrix}=-5\) then value of \(\begin{vmatrix} 20 & 15 \\ 15 & 5 \end{vmatrix}\) is ________.
(a)-5
(b)-125
(c)-25
(d)0
-
If nC3 = nC2, then the value of nC4 is _______.
(a)2
(b)3
(c)4
(d)5
-
The number of ways selecting 4 players out of 5 is _______.
(a)4!
(b)20
(c)25
(d)5
-
The greatest positive integer which divide n(n + 1) (n + 2) (n + 3) for n \(\in\) N is ________.
(a)2
(b)6
(c)20
(d)24
-
For all n > 0, nC1 + nC2 + nC3 + ... +nCn is equal to _______
(a)2n
(b)2n- 1
(c)n2
(d)n2 - 1
-
The constant term in the expansion of \({ \left( x+\frac { 2 }{ x } \right) }^{ 6 }\) is _______
(a)156
(b)165
(c)162
(d)160
-
If \(\frac { kx }{ (x+4)(2x-1) } =\frac { 4 }{ x+4 } +\frac { 1 }{ 2x-1 } \) then k is equal to _______.
(a)9
(b)11
(c)5
(d)7
-
The number of parallelograms that can be formed from a set of four parallel lines intersecting another set of three parallel lines is _________.
(a)18
(b)12
(c)9
(d)6
-
The total number of 9 digit number which have all different digit is ________.
(a)10!
(b)9!
(c)9\(\times\)9!
(d)10\(\times\)10!
-
Number of words with or without meaning that can be formed using letters of the word "EQUATION" , with no repetition of letters is _____.
(a)7!
(b)3!
(c)8!
(d)5!
-
The number of permutation of n different things taken r at a time, when the repetition is allowed is ________.
(a)rn
(b)nr
(c)\(\frac { n! }{ (n-r)! } \)
(d)\(\frac { n! }{ (n+r)! } \)
-
The angle between the pair of straight lines x2 - 7xy + 4y2 = 0 _______.
(a)\(tan^{-1}\left(1\over 3\right)\)
(b)\(tan^{-1}\left(1\over 2\right)\)
(c)\(tan^{-1}\left(\sqrt{33}\over 5\right)\)
(d)\(tan^{-1}\left(5\over\sqrt{33}\right)\)
-
If the lines 2x - 3y - 5 = 0 and 3x - 4y - 7 = 0 are the diameters of a circle, then its centre is _______.
(a)(-1, 1)
(b)(1,1)
(c)(1, -1 )
(d)(-1, -1)
-
The locus of the point P which moves such that P is at equidistance from their coordinate axes is _______.
(a)\(y={1\over x}\)
(b)y = -x
(c)y = x
(d)\(y=-{1\over x}\)
-
If kx2 + 3xy - 2y2 = 0 represent a pair of lines which are perpendicular then k is equal to _______.
(a)1/2
(b)-1/2
(c)2
(d)-2
-
The focus of the parabola x2 = 16y is _______.
(a)(4,0)
(b)(-4,0)
(c)(0,4)
(d)(0,-4)
-
The centre of the circle x2 + y - 2x + 2y - 9 = 0 is _______.
(a)(1,1)
(b)(-1,-1)
(c)(-1,1)
(d)(1, -1)
-
If the centre of the circle is (-a, -b) and radius is \(\sqrt{a^2-b^2}\), then the equation of circle is _______.
(a)x2+y2+2ax+2by+2b2 = 0
(b)x2+y2+2ax +2by-2b2 = 0
(c)x2 +y2 - 2ax - 2by - 2b2 = 0
(d)x2 + y - 2ax - 2by + 2b2 = 0
-
ax2 + 4xy + 2y2 = 0 represents a pair of parallel lines then 'a' is _______.
(a)2
(b)-2
(c)4
(d)-4
-
The equation of the circle with centre (3,-4) and touches the x - axis is _______.
(a)(x - 3)2 +(y - 4)2 = 4
(b)(x - 3)2 +(y + 4)2 = 16
(c)(x-3)2 + (y- 4)2 = 16
(d)x2+y2 = 16
-
The eccentricity of the parabola is _______.
(a)3
(b)2
(c)0
(d)1
-
The distance between directrix and focus of a parabola y2 = 4ax is _______.
(a)a
(b)2a
(c)4a
(d)3a
-
The degree measure of \(\frac{\pi}{8}\) is ______.
(a)20o60'
(b)22o30'
(c)20o60'
(d)20o30'
-
If \(\tan\theta=\frac{1}{\sqrt5}\) and \(\theta\) lies in the first quadrant, then \(\cos\theta\) is _______.
(a)\(\frac{1}{\sqrt6}\)
(b)\(\frac{-1}{\sqrt6}\)
(c)\(\frac{\sqrt5}{\sqrt6}\)
(d)\(\frac{-\sqrt5}{\sqrt6}\)
-
The value of \(\sin(-420^o)\) is _______.
(a)\(\frac{\sqrt3}{2}\)
(b)\(-\frac{\sqrt3}{2}\)
(c)\(\frac{1}{2}\)
(d)\(\frac{-1}{2}\)
-
The value of sin 15o cos 15o is ______.
(a)1
(b)\(\frac{1}{2}\)
(c)\(\frac{\sqrt3}{2}\)
(d)\(\frac{1}{4}\)
-
The value of cos245o - sin245o is_______.
(a)\(\frac{\sqrt3}{2}\)
(b)\(\frac{1}{2}\)
(c)0
(d)\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\)
-
The value of 1 - 2sin245o is _______.
(a)1
(b)\(\frac{1}{2}\)
(c)\(\frac14\)
(d)0
-
The value of \(\frac{2\tan30^o}{1+tan^230}\) is _____.
(a)\(\frac12\)
(b)\(\frac{1}{\sqrt3}\)
(c)\(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
(d)\(\sqrt3\)
-
The value of \(\frac{3 \tan 10^{\circ}-\tan ^3 10^{\circ}}{1-3 \tan ^2 10^{\circ}}\) is _______,
(a)\(\frac{1}{\sqrt3}\)
(b)\(\frac{1}{2}\)
(c)\(\frac{\sqrt3}2\)
(d)\(\frac{1}{\sqrt2}\)
-
If \(\alpha\) and \(\beta\) be between 0 and \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) and if \(\cos(\alpha+\beta)=\frac{12}{13}\) and \(\sin(\alpha-\beta)=\frac{3}{5}\) then \(\sin2\alpha\) is _____.
(a)\(\frac{16}{15}\)
(b)0
(c)\(\frac{56}{65}\)
(d)\(\frac{64}{65}\)
-
\(\tan\left(\frac{\pi}{4}-x\right)\) is _______.
(a)\(\left(\frac{1+\tan x}{1-\tan x}\right)\)
(b)\(\left(\frac{1-\tan x}{1+\tan x}\right)\)
(c)1-tan x
(d)1+tan x
-
\(\sin\left(\cos^{-1}\frac{3}{5}\right)\) is _____.
(a)\(\frac{3}{5}\)
(b)\(\frac{5}{3}\)
(c)\(\frac{4}{5}\)
(d)\(\frac{5}{4}\)
-
\(\left(\frac{\cos x}{cosec x}\right)-\sqrt{1-\sin^2x}\sqrt{1-\cos^2x}\) is _______.
(a)cos2x-sin2x
(b)sin2x-cos2x
(c)1
(d)0
-
If f(x) = x2 - x + 1, then f (x + 1) is _______.
(a)x2
(b)x
(c)1
(d)x2 + x + 1
-
If f(x) = \(\frac{1-x}{1+x}\) then f(-x) is equal to _______.
(a)-f(x)
(b)\(\frac{1}{f(x)}\)
(c)\(-\frac{1}{f(x)}\)
(d)f(x)
-
The graph of y = 2x2 is passing through _______.
(a)(0,0)
(b)(2,1)
(c)(2,0)
(d)(0,2)
-
If f(x) = 2x and get g(x) = \(\frac{1}{2^x}\) then (fg)(x) is ________.
(a)1
(b)0
(c)4x
(d)\(\frac{1}{4^x}\)
-
The range of f(x) = |x|, for all \(x\in R\), is ________.
(a)(0, \(\infty \))
(b)(0, \(\infty \))
(c)(-\(\infty \), \(\infty \))
(d)(1, \(\infty \))
-
\(\lim _{ x\rightarrow \infty }{ \frac { \tan { \theta } }{ \theta } } =\)________.
(a)1
(b)\(\infty\)
(c)\(-\infty\)
(d)\(\theta\)
-
For what value of x, f(x) = \(\frac{x+2}{x-1}\) is not continuous?
(a)-2
(b)1
(c)2
(d)-1
-
\(\frac{d}{dx}(\frac{1}{x})\) is equal to ________.
(a)\(-\frac{1}{x^2}\)
(b)\(-\frac{1}{x}\)
(c)log x
(d)\(\frac{1}{x^2}\)
-
If y = x and z = \(\frac{1}{x}\) then \(\frac{dy}{dz}=\)________.
(a)x2
(b)1
(c)-x2
(d)\(-\frac{1}{x^2}\)
-
\(\frac{d}{dx}(a^x)=\) ________.
(a)\(\frac { 1 }{ x\log e^a}\)
(b)aa
(c)x logea
(d)ax logea
-
Average fixed cost of the cost function C(x) = 2x3 +5x2 - 14x +21 is _______.
(a)\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \)
(b)\(\frac { 5}{ x } \)
(c)\(\frac { 14 }{ x } \)
(d)\(\frac { 21 }{ x } \)
-
Marginal revenue of the demand function p = 20–3x is _______.
(a)20–6x
(b)20–3x
(c)20+6x
(d)20+3x
-
If the demand function is said to be inelastic, then _______.
(a)|ηd| > 1
(b)|ηd| = 1
(c)|ηd| < 1
(d)|ηd| = 0
-
The elasticity of demand for the demand function x = \(\frac { 1 }{ p } \) is______.
(a)0
(b)1
(c)\(-\frac { 1 }{ p } \)
(d)\(\infty \)
-
Relationship among MR, AR and ηd is ______.
(a)\({ n }_{ d }=\frac { AR }{ AR-MR } \)
(b)ηd = AR - MR
(c)MR = AR = ηd
(d)\(AR=\frac { MR }{ {ηd } } \)
-
Instantaneous rate of change of y = 2x2 + 5x with respect to x at x = 2 is _________.
(a)4
(b)5
(c)13
(d)9
-
Profit P(x) is maximum when ________.
(a)MR = MC
(b)MR = 0
(c)MC = AC
(d)TR = AC
-
The maximum value of f(x) = sinx is ________.
(a)1
(b)\(\frac { \sqrt { 3 } }{ 2 } \)
(c)\(\frac { 1 }{ \sqrt { 2 } } \)
(d)\(-\frac { 1 }{ \sqrt { 2 } } \)
-
If f(x,y) is a homogeneous function of degree n, then \(x\frac { \partial f }{ \partial x } +y\frac { \partial f }{ \partial y } \) is equal to ________.
(a)(n–1)f
(b)n(n–1)f
(c)nf
(d)f
-
If u = \({ e }^{ { x }^{ 2 } }\) then \(\frac { \partial u }{ \partial x } \) is equal to _______.
(a)\({ 2x }e^{ { x }^{ 2 } }\)
(b)\({ e }^{ { x }^{ 2 } }\)
(c)\({2 e }^{ { x }^{ 2 } }\)
(d)0
-
A company begins to earn profit at _______.
(a)Maximum point
(b)Breakeven point
(c)Stationary point
(d)Even point
-
The demand function is always _______.
(a)Increasing function
(b)Decreasing function
(c)Non-decreasing function
(d)Undefined function
-
if q = 1000 + 8p1 - p2 then, \(\frac { \partial q }{ \partial { p }_{ 1 } } \) is _______.
(a)-1
(b)8
(c)1000
(d)1000 - p2
-
If R = 5000 units / year, C1 = 20 paise , C3 = Rs. 20 then EOQ is _______.
(a)5000
(b)100
(c)1000
(d)200
-
The dividend received on 200 shares of face value Rs.100 at 8% is ________.
(a)Rs. 1600
(b)Rs. 1000
(c)Rs. 1500
(d)Rs. 800
-
If a man received a total dividend of Rs. 25,000 at 10% dividend rate on a stock of face value Rs.100, then the number of shares purchased.
(a)3500
(b)4500
(c)2500
(d)300
-
The brokerage paid by a person on the sale of 400 shares of face value Rs.100 at 1% brokerage ________.
(a)Rs. 600
(b)Rs. 500
(c)Rs. 200
(d)Rs. 400
-
A person brought 100 shares of 9% stock of face value Rs. 100, at a discount of 10%, then the stock purchased is _______.
(a)Rs. 9000
(b)Rs. 6000
(c)Rs. 5000
(d)Rs. 4000
-
The annual income on 500 shares of face value Rs.100 at 15% is _______.
(a)Rs. 7,500
(b)Rs. 5,000
(c)Rs. 8,000
(d)Rs. 8,500
-
If ‘a’ is the annual payment, ‘n’ is the number of periods and ‘i’ is compound interest for Rs. 1 then future amount of the annuity is _______.
(a)A = \(\frac{a}{i}(1+i)(1+i)^n-1]\)
(b)A = \(\frac{a}{i}[(1+i)^n-1]\)
(c)P = \(\frac{a}{i}\)
(d)P = \(\frac{a}{i}(1+i)[1-(1+i)^{-n}]\)
-
An annuity in which payments are made at the beginning of each payment period is called _______.
(a)Annuity due
(b)An immediate annuity
(c)perpetual annuity
(d)none of these
-
The present value of the perpetual annuity of Rs. 2000 paid monthly at 10 % compound interest is _______.
(a)Rs. 2,40,000
(b)Rs. 6,00,000
(c)Rs. 20,40,000
(d)Rs. 2,00,400
-
Which of the following is positional measure?
(a)Range
(b)Mode
(c)Mean deviation
(d)Percentiles
-
When calculating the average growth of economy, the correct mean to use is?
(a)Weighted mean
(b)Arithmetic mean
(c)Geometric mean
(d)Harmonic mean
-
The best measure of central tendency is _________.
(a)Arithmetic mean
(b)Harmonic mean
(c)Geometric mean
(d)Median
-
The harmonic mean of the numbers 2,3,4 is _________.
(a)\(\frac { 12 }{ 13 } \)
(b)2
(c)\(\frac { 36 }{ 13 } \)
(d)\(\frac { 13 }{ 36 } \)
-
The geometric mean of two numbers 8 and 18 shall be _________.
(a)12
(b)13
(c)15
(d)11.08
-
The correct relationship among A.M.,G.M.and H.M.is: ________.
(a)A.M.
(b)G.M.≥A.M.≥H.M.
(c)H.M.≥G.M.≥A.M.
(d)A.M.≥G.M.≥H.M.
-
The median of 10,14,11,9,8,12,6 is _________.
(a)10
(b)12
(c)14
(d)9
-
If the mean of 1,2,3,.......n is\(\frac { 6n }{ 11 } \), then the value of n is _________.
(a)10
(b)12
(c)11
(d)13
-
The first quartile is also known as _________.
(a)median
(b)lower quartile
(c)mode
(d)third decile
-
If Q1 = 30 and Q3 = 50, the coefficient of quartile deviation is _________.
(a)20
(b)40
(c)10
(d)0.25
-
The two events A and B are mutually exclusive if _________.
(a)\(P\left( A\cap B \right) =0\)
(b)\(P\left( A\cap B \right) =1\)
(c)\(P\left( A\cup B \right) =0\)
(d)\(P\left( AUB \right) =1\)
-
If two events A and B are dependent then the conditional probability of P(B/A) is _________.
(a)\(P(A)P(B/A)\)
(b)\(\frac { P(A\cap B) }{ P(B) } \)
(c)\(\frac { P(A\cap B) }{ P(A) } \)
(d)\(P(A)P(A/B)\)
-
If the outcome of one event does not influence another event then the two events are _________.
(a)Mutually exclusive
(b)Dependent
(c)Not disjoint
(d)Independent
-
The probability of obtaining an even prime number on each die, when a pair of dice is rolled is _________.
(a)1/36
(b)0
(c)1/3
(d)1/6
-
Probability that at least one of the events A, B occur is _________.
(a)\(P(A\cup B)\)
(b)\(P(A\cap B)\)
(c)P(A/B)
(d)\((A\cup B)\)
-
Example for positive correlation is______.
(a)Income and expenditure
(b)Price and demand
(c)Repayment period and EMI
(d)Weight and Income
-
If the values of two variables move in opposite direction then the correlation is said to be ______.
(a)Negative
(b)Positive
(c)Perfect positive
(d)No correlation
-
If r(X,Y) = 0 the variables X and Y are said to be ______.
(a)Positive correlation
(b)Negative correlation
(c)No correlation
(d)Perfect positive correlation
-
The correlation coefficient from the following data N = 25, ΣX = 125, ΣY = 100, ΣX2 = 650, ΣY2 = 436, ΣXY = 520 ________.
(a)0.667
(b)-0.006
(c)-0.667
(d)0.70
-
The correlation coefficient is ________.
(a)r(X, Y) = \(\frac { { \sigma }_{ x }{ \sigma }_{ y } }{ cov(x,y) } \)
(b)r(X, Y) = \(\frac { cov(x,y) }{ { \sigma }_{ x }{ \sigma }_{ y } } \)
(c)r(X, Y) = \(\frac { cov(x,y) }{ { \sigma }_{ y } } \)
(d)r(X, Y) = \(\frac { cov(x,y) }{ { \sigma }_{ x } } \)
-
The variable whose value is influenced (or) is to be predicted is called ________.
(a)dependent variable
(b)independent variable
(c)regressor
(d)explanatory variable
-
The correlation coefficient ________.
(a)r = ±\(\sqrt { { b }_{ xy }\times { b }_{ yx } } \)
(b)r = \(\frac { 1 }{ { b }_{ xy }\times { b }_{ yx } } \)
(c)r = bxy x byx
(d)r = ±\(\sqrt { \frac { 1 }{ { b }_{ xy }\times { b }_{ yx } } } \)
-
The regression coefficient of X on Y ________.
(a)bxy = \(\frac { N\Sigma dxdy-(\Sigma dx)(\Sigma dy) }{ N\Sigma dy^{ 2 }-(\Sigma dy)^{ 2 } } \)
(b)byx = \(\frac { N\Sigma dxdy-(\Sigma dx)(\Sigma dy) }{ N\Sigma dy^{ 2 }-(\Sigma dy)^{ 2 } } \)
(c)bxy = \(\frac { N\Sigma dxdy-(\Sigma dx)(\Sigma dy) }{ N\Sigma dx^{ 2 }-(\Sigma dx)^{ 2 } } \)
(d)by =\(\frac { N\Sigma xy-(\Sigma x)(\Sigma y) }{ \sqrt { N\Sigma { x }^{ 2 }-(\Sigma x)^{ 2 }\times \sqrt { N\Sigma y^{ 2 }-(\Sigma y)^{ 2 } } } } \)
-
When one regression coefficient is negative, the other would be ________.
(a)Negative
(b)Positive
(c)Zero
(d)None of them
-
If X and Y are two variates, there can be atmost ________.
(a)One regression line
(b)two regression lines
(c)three regression lines
(d)more regression lines
-
Scatter diagram of the variate values (X,Y) give the idea about ________.
(a)functional relationship
(b)regression model
(c)distribution of errors
(d)no relation
-
If two variables moves in decreasing direction then the correlation is ________.
(a)positive
(b)negative
(c)perfect negative
(d)no correlation
-
The person suggested a mathematical method for measuring the magnitude of linear relationship between two variables say X and Y is ________.
(a)Karl Pearson
(b)Spearman
(c)Croxton and Cowden
(d)Ya Lun Chou
-
The term regression was introduced by ________.
(a)R.A Fisher
(b)Sir Francis Galton
(c)Karl Pearson
(d)Croxton and Cowden
-
The coefficient of correlation describes ________.
(a)the magnitude and direction
(b)only magnitude
(c)only direction
(d)no magnitude and no direction
-
If Cov(x, y) = –16.5, \({ \sigma }_{ x }^{ 2 }=2.89,{ \sigma }_{ y }^{ 2 }\) = 100. Find correlation coefficient ________.
(a)-0.12
(b)0.001
(c)-1
(d)-0.97
-
The critical path of the following network is________.
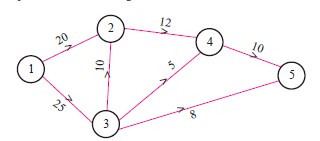 (a)
(a)1 – 2 – 4 – 5
(b)1 – 3 – 5
(c)1 – 2 – 3 – 5
(d)1 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 5
-
Maximize: z = 3x1 + 4x2 subject to 2x1 + x2 ≤ 40, 2x1+ 5x2 ≤ 180, x1, x2 ≥ 0. In the LPP, which one of the following is feasible corner point?
(a)x1 = 18, x2 = 24
(b)x1 = 15, x2 = 30
(c)x1 = 2.5, x2 = 35
(d)x1 = 20.5, x2 = 19
-
A solution which maximizes or minimizes the given LPP is called ______.
(a)a solution
(b)a feasible solution
(c)an optimal solution
(d)none of these
-
The maximum value of the objective function Z = 3x + 5y subject to the constraints x > 0 , y > 0 and 2x + 5y ≤ 10 is ______.
(a)6
(b)15
(c)25
(d)31
-
In the context of network, which of the following is not correct?
(a)A network is a graphical representation
(b)A project network cannot have multiple initial and final nodes
(c)An arrow diagram is essentially a closed network
(d)An arrow representing an activity may not have a length and shape
-
The objective of network analysis is to ________.
(a)Minimize total project cost
(b)Minimize total project duration
(c)Minimize production delays, interruption and conflicts
(d)All the above
-
Network problems have advantage in terms of project _______.
(a)Scheduling
(b)Planning
(c)Controlling
(d)All the above
-
In critical path analysis, the word CPM mean ______.
(a)Critical path method
(b)Crash project management
(c)Critical project management
(d)Critical path management
-
Given an L.P.P maximize Z = 2x1 + 3x2 subject to the constrains x1 + x2 ≤ 1, 5x1 + 5x2 ≥ 0 and x1 ≥ 0, x2 ≥ 0 using graphical method, we observe ______.
(a)No feasible solution
(b)unique optimum solution
(c)multiple optimum solution
(d)none of these
120 x 1 = 120
*****************************************
11th Standard Business Maths and Statistics Videos
TN 11th Maths Basic Algebra 50 Important 1 Marks Questions With Answers Book Back and Creative
TN Class 11 Maths Basic Algebra Study Materials TN State Board Samacheer / Matriculation 11th Maths Subject - Basic Algebra One Mark Question and Answers






 11th Standard Business Maths and Statistics Syllabus
11th Standard Business Maths and Statistics Syllabus  11th Standard Business Maths and Statistics Study Materials
11th Standard Business Maths and Statistics Study Materials 11th Standard Business Maths and Statistics MCQ Practise Tests
11th Standard Business Maths and Statistics MCQ Practise Tests 

Reviews & Comments about 11th Standard Business Maths Public Exam March 2019 Important One Mark Test
Write your Comment