- State Board
-
12th Standard
-

Biology
-

Computer Applications
-

Computer Science
-

Business Maths and Statistics
-

Commerce
-

Economics
-

Maths
-

Chemistry
-

Physics
-

Computer Technology
-

History
-

Accountancy
-

Tamil
-

Maths
-

Chemistry
-

Physics
-

Biology
-

Computer Science
-

Business Maths and Statistics
-

Economics
-

Commerce
-

Accountancy
-

History
-

Computer Applications
-

Computer Technology
-

English
12th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
11th Standard
-

Maths
-

Biology
-

உயிரியல் - தாவரவியல்
-

Economics
-

Physics
-

Chemistry
-

History
-

Business Maths and Statistics
-

Computer Science
-

Accountancy
-

Commerce
-

Computer Applications
-

Computer Technology
-

Tamil
-

Maths
-

Commerce
-

Economics
-

Biology
-

Business Maths and Statistics
-

Accountancy
-

Computer Science
-

Physics
-

Chemistry
-

Computer Applications
-

History
-

Computer Technology
-

Tamil
-

English
11th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
9th Standard
-

-

-

-

-

-

-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
9th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
6th Standard
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
6th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
10th Standard
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

Tamil
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

English
-

English
10th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
7th Standard
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
7th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
8th Standard
-

கணிதம் - old
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

கணிதம்
-

Maths
-

Science
-

Social Science
8th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் Subjects
English Subjects
-
-
12th Standard
- CBSE Board
-
12th Standard CBSE
-

Biology
-

Physics
-

Chemistry
-

Maths
-

Accountancy
-

Introductory Micro and Macroeconomics
-

Business Studies
-

Economics
-

Computer Science
-

Geography
-

English
-

History
-

Indian Society
-

Physical Education
-

Sociology
-

Tamil
-

Bio Technology
-

Engineering Graphics
-

Entrepreneurship
-

Hindi Core
-

Hindi Elective
-

Home Science
-

Legal Studies
-

Political Science
-

Psychology
12th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
-
11th Standard CBSE
-

Mathematics
-

Chemistry
-

Biology
-

Physics
-

Business Studies
-

Accountancy
-

Economics
-

Computer Science
-

Bio Technology
-

English
-

Enterprenership
-

Geography
-

Hindi
-

History
-

Home Science
-

Physical Education
-

Political Science
-

Psychology
-

Sociology
-

Applied Mathematics
11th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
- 10th Standard CBSE
-
9th Standard CBSE
-

Mathematics
-

Social Science
-

Science
-

English
-

Hindi
9th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
-
8th Standard CBSE
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

Mathematics
-

English
8th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
-
7th Standard CBSE
-

Mathematics
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

English
7th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
-
6th Standard CBSE
-

Mathematics
-

Science
-

Social Science
-

English
6th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material
-
-
12th Standard CBSE
- Free Online Test
- News
- Study Materials
-
Students
-

Stateboard Tamil Nadu
-

CBSE Board
-

Free Online Tests
-

Educational News
-

Scholarships
-

Entrance Exams India
-

Video Materials
Study Materials , News and Scholarships
-
-
Students

11th Standard Chemistry Thermodynamics and Gaseous State Important 3 Mark Questions Sep-30 , 2018
Important 3mark -chapter 7,8
Important 3mark -chapter 7,8
11th Standard
-
Reg.No. :
Chemistry
Use blue pen Only
Time :
00:50:00 Hrs
Total Marks :
90
-
Define the following terms
(a) isothermal process (b) adiabatic process
(c) isobaric process (d) isochoric process -
What are state and path functions? Give two examples
-
The equilibrium constant of a reaction is 10, what will be the sign of ΔG? Will this reaction be spontaneous?
-
Define the following terms.
-
Predict the change in internal energy for an isolated system at constant volume.
-
One mole of a gaseous system absorbs 100 J of heat and does work equivalent to 50 J. Calculate the change in the internal energy of the system.
-
Bring out the differences between extensive and intensive properties.
-
Identify processes under the following conditions
(i) dT = 0
(ii) dP = 0
(iii) dV = 0 -
Define Standard Entropy.
-
What is the nature of the reaction for the following?
(i) ΔG>0
(ii) ΔG<0
(iii) ΔG=0 -
5 moles of an ideal gas expand isothermally and reversibly from a pressure of 10 atm to 2 atm at 300K. Calculate the work done by the system.
-
Enthalpies of formation of CO(g),CO2(g), N2O(g) and N2O4(g) are -110, -393, + 81 and + 9.7 kJ mol respectively. Find the value of \(\Delta\)H for the reaction. N2O4(g) + 3CO(g) \(\rightarrow\) N2O(g) + 3CO2(g).
-
Urea on hydrolysis produces ammonia and carbon dioxide. The standard entropies of urea, H2O, CO2, NH3 are 173.8, 70, 213.5 and 192.5 J mole-1K-1 respectively. Calculate the entropy change for this reaction.
-
A gas contained in a cylinder fitted with a frictionless piston expands against a constant external pressure of 1 atm from a volume of 5 litres to a volume of 10 litres. In doing so it absorbs 400 J of thermal energy from its surroundings. Determine the change in internal energy of system.
-
The standard enthalpies of formation of \(C_2 H_5 OH_{I}, CO_{2{g}}\) and \(H_2 O(_{I})\) are -277, -393.5 and -285.5 kJ mol-1 respectively. Calculate the standard enthalpy change for the reaction \(C_2O_5 OH_{(I)}+3O_{2{g}} \rightarrow 2CO_{2{g}}+3 H_2 O_{(I)}\). The enthalpy of formation of O2(g) in the standard state is zero, by definition.
-
Calculate the value of \(\Delta\)U and \(\Delta\)H on heating 128 g of oxygen from O°C to 100°C. Cv and Cp on an average are 21 and 29 J mol-1 K-1. (The difference is 8 J mol-1 K-1 which is approximately equal to R)
-
The enthalpy of formation of methane at constant pressure and 300 K is - 78.84 k.l, What will be the enthalpy of formation at constant volume?
-
(a) Under what condition, the heat evolved or absorbed in a reaction is equal to its free energy change?
(b) Calculate the entropy change for the following reversible process.
\(H_2 O \rightleftharpoons H_2O_{I} \) Δfus H is 6 kJ mol-1 -
Prove that for an ideal gas, Cp is greater than Cv.
-
Calculate \(\triangle_r{G}^{\ominus}\) for conversion of oxygen to ozone, \({3\over 2}{O}_{{2}_{(g)}}\rightarrow{O}_{{3}_{(g)}}\) at 298 K. If Kp for this conversion is 2.47 X 10-29.
-
The value of Kc for the following reaction at 717 K is 48.
-
The value of Kc for the reaction
N2O2(g) \(\rightleftharpoons \) 2NO2(g) -
One mole of H2 and one mole of I2 are allowed to attain equilibrium in 1 lit container. If the equilibrium mixture contains 0.4 mole of HI. Calculate the equilibrium constant.
-
The equilibrium concentrations of NH3, N2 and H2 are 1.8 x 10-2 M, 1.2 x 10-2 M and 3 x 10-2 M respectively. Calculate the equilibrium constant for the formation of NH3 from N2 and H2. [Hint: M= mol lit-1]
-
The equilibrium constant at 298 K for a reaction is 100.
A + B \(\rightleftharpoons \) C + D
If the initial concentration of all the four species is 1 M, the equilibrium concentration of D (in mol lit-1) will be -
For an equilibrium reaction Kp = 0.0260 at 25° C ΔH= 32.4 kJmol-1, calculate Kp at 37° C
-
For the reaction,
A2(g) + B2(g) ⇌ 2AB(g) ; ΔH is –ve.
the following molecular scenes represent different reaction mixture (A – green, B – blue)
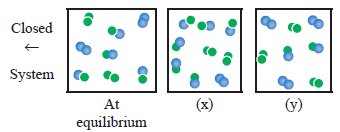
i) Calculate the equilibrium constant KP and (KC).
ii) For the reaction mixture represented by scene (x), (y) the reaction proceed in which directions?
iii) What is the effect of increase in pressure for the mixture at equilibrium. -
One mole of PCl5 is heated in one litre closed container. If 0.6 mole of chlorine is found at equilibrium, calculate the value of equilibrium constant.
-
For the reaction
SrCO3 (s) ⇌ SrO (s) + CO2(g),
the value of equilibrium constant KP = 2.2 x 10–4 at 1002 K. Calculate KC for the reaction. -
To study the decomposition of hydrogen iodide, a student fills an evacuated 3 litre flask with 0.3 mol of HI gas and allows the reaction to proceed at 500o C. At equilibrium he found the concentration of HI which is equal to 0.05 M. Calculate KC and KP for this reaction.
Answer all the questions
30 x 3 = 90






 11th Standard Chemistry Syllabus
11th Standard Chemistry Syllabus  11th Standard Chemistry Study Materials
11th Standard Chemistry Study Materials 11th Standard Chemistry MCQ Practise Tests
11th Standard Chemistry MCQ Practise Tests 

Reviews & Comments about 11th Standard Chemistry Thermodynamics and Gaseous State Important 3 Mark Questions
Write your Comment