12th Standard CBSE Biology Human Reproduction Important Questions
By QB365
12th Standard CBSE Biology Human Reproduction Important Questions
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Human Reproduction Important Questions
12th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Biology
-
Write two major functions each of testis and ovary.
(a) -
Define spermiogenesis and spermiation
(a) -
What is parturition? Which hormones are involved in induction of parturition?
(a) -
How many eggs do you think were released by the ovary of a female dog which gave birth to 6 puppies?
(a)Six eggs
-
What is menstrual cycle? Which hormones regulate menstrual cycle?
(a) -
Describe the structure of a seminiferous tubule.
(a) -
What are the major components of the seminal plasma?
(a) -
The secondary oocyte retains bulk of the nutrientrich cytoplasm ofthe primary oocyte. Can you think
or any advantage for this?(a) -
How many chromosomes will be there in the zygote (of human)?
(a) -
What do you think the doctor injects to induce delivery?
(a) -
Describe how the changing levels of FSH,LH and progesterone during mentrual cycle induce changes in the ovary and the uterus in human female.
(a) -
Name the hormones involved in the regulation of spermatogenesis.
(a) -
What are the major functions of male accessory ducts and glands?
(a) -
How many eggs are released by a human ovary in a month? How many eggs do you think would have been released if the mother gave birth to identical twins?Would your answer change,if the twins born were fraternal?
(a) -
Draw a labelled diagram of a section through ovary.
(a) -
In our society the women are often blamed for giving birth to daughters. Can you explain why this is not correct?
(a) -
Draw a labelled diagram of male reproductive system.
(a) -
Draw a labelled diagram of female reproductive system.
(a) -
Write two major functions each of testes and ovaries.
(a) -
What is spermatogenesis? Briefly describe the process of spermatogenesis.
(a) -
Draw a labelled diagram of a Graafian follicle?
(a) -
Name the functions of the following:
(a) Corpus luteum
(b) Endometrium
(c) Acrosome
(d) Sperm tail
(e) Fimbriae(a) -
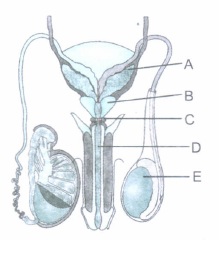
A diagrammatic sketch of the human male reproductive system is given above.
(a) Identify and name the three glands associated with the human male reproductive system. What is the term given to their secretions?
(b) Name the primary sex organ and the pouch in which it is located in human beings.(a) -
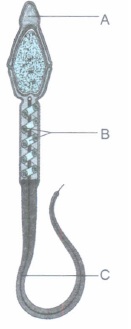
A Human Spermatozoan
A diagrammatic sketch of a human sperm is given. Identify the parts labelled A, Band C and mention their respective functions.(a) -
Study the following flow chart and answer the questions that follow:
 (a)
(a) -
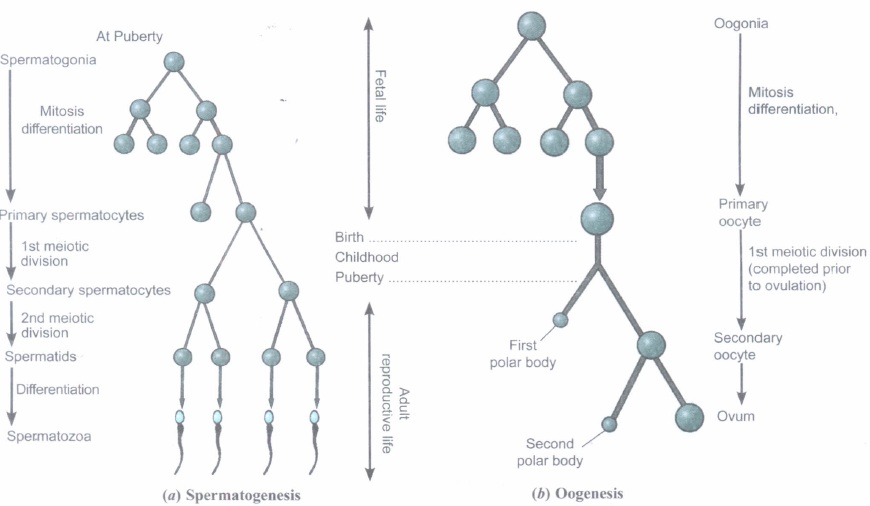
With reference to the above schematic diagram of (a) Spermatogenesis and (b) Oogenesis, answer the following questions.
(a) About 300 million spermatozoa may be present in a human male ejaculate at one time. Calculate how many primary spermatocytes will be involved to produce this number of spermatozoa .
(b) How many spermatids will be formed?
(c) How many chromatids are found during Oogenesis in
(i) Primary oocyte and
(ii) First polar body in a human female?(a) -
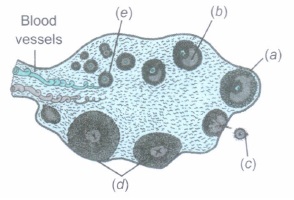
(A) In the diagrammatic sectional view of a human ovary, identify the following:
(i) Corpus luteum
(ii) Antrum
(iii) Secondary oocyte
(iv) Primary follicle
(B) Name the hormone that
(i) influences the formation of corpus luteum.
(ii) is secreted by corpus luteum.(a) -
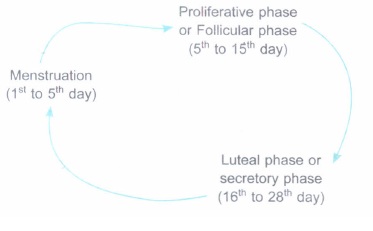
The events in a menstrual cycle are represented above. Answer the following questions based on that.
(a) Why is the phase between 5th and 15th day of menstrual cycle, called
(i) proliferative phase?
(ii) follicular phase?
(b) Mention the ovarian events during the luteal phase.(a) -
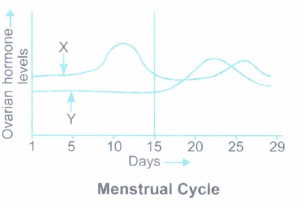
Read the graph given above and answer the following questions:
(a) Identify the ovarian hormones X and Y and name their respective sources in the ovary.
(b) Why does the hormone X peak before the hormone Y?(a) -
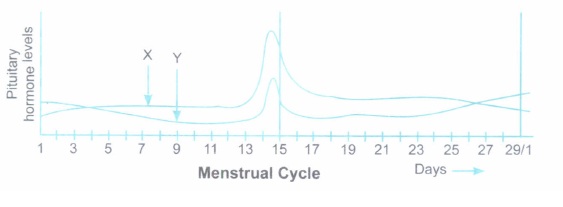
(a) Identify the pituitary hormones 'X' and 'Y' shown in the graph.
(b) Mention two functions each of X and Y in human females.(a) -
Study the flow chart given below and answer the questions that follow:
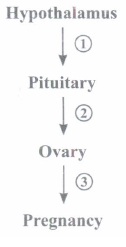
(a) Name the hormone(s) (in full form) involved in each of the stages,
(b) Specify the structure in the ovary that is the source of the hormone at stage (a)
(a) -
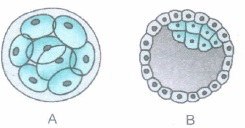
(a) Identify the human embryonic stages, A and B given.
(b) Write two differences between A and B.(a) -
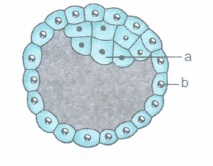
(a) Name the human embryonic stage shown above.
(b) Identify 'a' and 'b' in it.
(c) Where are stem cells located in it?
(d) Mention the role of 'b'.(a) -
Three of the steps in the neuro-endocrine mechanism of parturition are mentioned below. Write the other missing steps.
(a) Signals for parturition originate from the fullydeveloped foetus and placenta.
(b) _________________.
(c) _________________.
(d) Oxytocin causes stronger uterine contractions, which stimulate further secretion of oxytocin.
(e) __________________.
(f) ________________.(a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Human male reproductive system comprises of a pair of testes, primary sex organs associated with formation of gametes and production of sex hormone. Study the given figure of human male reproductive system and answer the following questions.
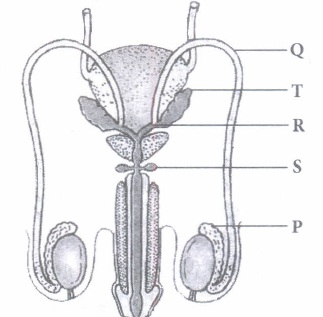
(i) Which of the following is correct for labelled part P?(a) P is rete testis which transports sperms to outside. (b) P is epididymis which secretes fluid that nourish the sperms (c) P is epididymis that carry sperms and secretion of seminal vesicles (d) P is rete testis which lies along inner side of each testis and stores the sperms (ii) Identify the correctly matched pair.
(a) Q - Vasa efferentia (b) R - Ejaculatory duct (c) S - Seminal vesicle (d) T - Cowper's gland (iii) Which statement is incorrect for Q?
(a) It carries spermatozoa from epididymis to ejaculatory duct (b) Q are only 2 in number. (c) It arises from rete testis. (d) It constitutes male sex accessory duct (iv) Which structure passes through the prostate gland and carries sperms and secretion of seminal vesicle?
(a) P (b) T (c) S (d) R (v) Assertion: Mucus present in secretion of bulbourethral gland decreases the number of sperms damaged during ejaculation
Reason: Mucus lubricates the end of penis and lining of the urethra.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false .(a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Oogenesis is the process of formation of ovum in ovaries. It consists of three phases : multiplication, growth and maturation. Oogenesis is controlled by hormones GnRH, LH, FSH. GnRH secreted by the hypothalamus stimulates the anterior lobe of pituitary gland to secrete LH and FSH.
(i) What is the function of hormone FSH?(a) It inhibits the formation of estrogen (b) It induces the release of secondary oocyte (c) It stimulates the growth of Graafian follicles (d) It causes ovulation. (ii) Which hormone induces the rupture of the mature Graafian follicle?
(a) Follicle stimulating hormone (b) Gonadotropin releasing hormone (c) Progesterone (d) Luteinising hormone (iii) Which cell division is involved in the formation of secondary oocyte?
(a) Mitosis (b) Meiosis I (c) Amitosis (d) Meiosis II (iv) Identify the function(s) of LH.
(A) Release of secondary oocyte from Graafian follicle.
(B) Stimulates corpus luteum to secrete progesterone.
(C) Stimulates estrogen formation.
(D) Promotes development of egg to form secondary oocyte.(a) (A) and (B) only (b) (B) and (C) only (c) (A), (C) and (D) only (d) (B) only (v) Assertion: The increase in progesterone level exerts positive feedback on GnRH
Reason: The rising level of progesterone stimulate production of FSH and LH.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.(a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
The first menstruation is called menarche, that usually occurs between 12 and 15 years. In human females, menstruation is repeated at an average interval of about 28129 days and is called menstrual cycle. It is regulated by certain hormones, as pituitary gland is stimulated by releasing factors produced in the hypothalamus. The hormones produced by pituitary gland influence the ovaries. The hormones secreted by the ovaries affect the walls of the uterus.
(i) The breakdown of endometrium is characteristic of(a) proliferative phase (b) luteal phase (c) ovulatory phase (d) menstrual phase (ii) Which days of the menstrual cycle marks the proliferative phase?
(a) 1-5 (b) 15-28 (c) 6-13 (d) 10-14 (iii) Which of the following occurs during secretory phase?
(a) Empty Graafian follicle changes into corpus luteum. (b) Primary follicle changes' into Graafian follicle. (c) Endometrium rebuilds and estrogen secretion increases (d) LH surge inducing release of an ovum. (iv) Identify the hormones that attain peak level during ovulatory phase
(a) FSH (b) Progesterone (c) LH (d) Both (a) and (c) (v) Withdrawal of which hormone causes degeneration of corpus luteum?
(a) FSH (b) LH (c) Progesterone (d) Estrogen (a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
A functional mammary gland is characteristic of all female mammals. Mammary glands are paired structures that contain glandular tissue and variable amount of fat. Refer to the given figure of a mammary gland and answer the following questions.
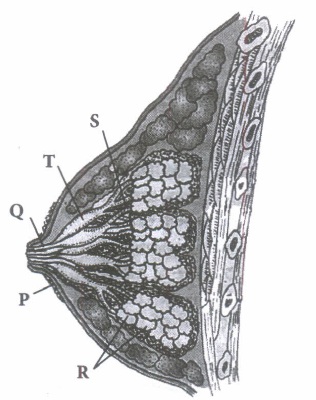
(i) Mammary glands are modified(a) sweat glands (b) sebaceous glands (c) sudoriferous glands (d) lacrimal glands. (ii) Identify the incorrectly matched pair.
(a) P - Areola (b) Q - Lactiferous duct (c) S - Mammary duct (d) T - Mammary alveoli (iii) Mammary ducts expand to form
(a) mammary alveoli (b) mammary ampullae (c) lactiferous ducts (d) mammary tubules. (iv) What is areola?
(a) Grape-like clusters of milk secreting structures (b) Fatty tissue between the mammary lobes (c) Circular pigmented area of skin around nipple (d) Connective tissue that supports the alveoli and ducts (v) Assertion: The size of breast depends on the amount of adipose tissue.
Reason: The adipose tissue supports the alveoli and the ducts.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.(a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
In testis, the immature male germ cells produce sperms by spermatogenesis that begins at puberty. It occurs in the seminifer.o•. us tubules of the testes. Seminiferous tubules are lined by germinal epithelium. Study the schematic representation of spermatogenesis and answer the following questions.
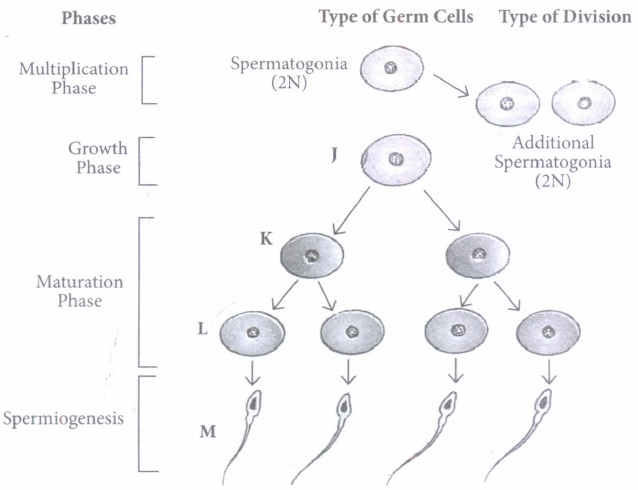
(i) Which cell division occurs during multiplication phase?(a) Mitosis (b) Meiosis I (c) Meiosis II (d) Both (b) and (c) (ii) How many chromosomes are present in secondary spermatocyte and spermatid respectively?
(a) 46,23 (b) 46,46 (c) 23,23 (d) 23, XY (iii) Transformation of L into M is known as
(a) spermiation (b) spermateliosis (c) spermatogenesis (d) none of these (iv) Select the correct option
(a) Type A spermatogonia grows to larger primary spermatocyte. (b) One spermatogonium forms two spermatids. (c) Spermiation is the release of sperms from seminiferous tubules. (d) Primary spermatocyte undergoes mitosis to form secondary spermatocytes. (v) Which hormone acts on spermatogonia to stimulate sperm production?
(a) LH (b) GnRE (c) ABP (d) FSH (a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Study the given table and answer the questions based on it.Hormone Source Function (A) Oxytocin W Ejection of milk (B) X Anterior lobe of pituitary gland Stimulates secretion of ABP from Sertoli cells (C) Y Placenta Maintains corpus luteum to secrete progesterone (D) Relaxin Ovary Z (i) Identify the hormones X and Y respectively
(a) Testosterone, FSH (b) LH, hPL (c) FSH, hCG (d) ICSH, hCG (ii) W in the given table is
(a) hypothalamus (b) posterior lobe of pituitary (c) placenta (d) ovary (iii) Which of the following is correct for Z?
(a) Dilation of uterine cervix during labour pains. (b) Stimulates the growth of the mammary glands during pregnancy (c) Supports the fetal growth and prevents desiccation. (d) Forms protective plug in cervix of uterus during pregnancy. (iv) Which set of hormones is secreted only during pregnancy?
(a) Human chorionic gonadotropin, relaxin and human placental lactogen
(b) Human placental lactogen, estrogen and chorionic thyrotropin
(c) Human chorionic gonadotropin, human placental lactogen and progesterone
(d) Chorionic thyrotropin, chorionic gonadotropin and estrogen
(v) Assertion: Follicle stimulating hormone controls the maintenance and functions of male reproductive organs.
Reason: FSH acts directly on spermatogonia to stimulate sperm production.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.(a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
During copulation, semen is released by the penis into the vagina. The motile sperms swim rapidly, fuse with ovum in the ampullary region, resulting in fertilisation. Haploid nucleus of sperm fuse with that of ovum to form diploid zygote.
(i) In female genital tract, sperms are made capable of fertilising the egg. This phenomenon of sperm activation is called(a) amphimixis (b) cortical reaction (c) capacitation (d) acrosomal reaction (ii) Select the correct sequence of various physical and chemical events that take place during fertilisation
P. Fusion of cortical granules with plasma membrane of secondary oocyte.
Q. Formation of fertilisation cone to receive sperm.
R. Release of sperm lysin from acrosome.
S. Mixing up of chromosomes of a sperm and an ovum.(a) R \(\to\)Q\(\to\) P\(\to\) S (b) Q\(\to\) S \(\to\)R\(\to\) P (c) Q\(\to\) R \(\to\)S \(\to\)P (d) R\(\to\) P \(\to\)Q\(\to\) S (iii) Assertion: Only one sperm can fertilise an ovum
Reason: The secretion of acrosome help the sperm to enter into cytoplasm of ovum through zona pellucida and plasma membrane.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false
(iv) What is the significance of fertilisation?(a) It restores haploid number of chromosomes. (b) It produces offspring genetically identical to parents. (c) It initiates cleavage (d) Both (b) and (c) (v) Site of fertilisation in humans is
(a) endometrium of uterine cavity (b) ampullary isthmic junction of oviduct (c) cervix of uterus (d) infundibulum of fallopian tube. (a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
The mature ovum or a female gamete is spherical in shape. The human ovum is almost free of yolk and is said to be alecithal. Human ovum loses its ability to be fertilised about 24 hours after ovulation. Refer to the given structure of ovum and answer the following questions.
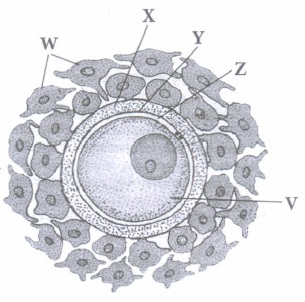
(i) Thick cellular layer formed of radially elongated follicular cells is(a) zona pellucida (b) plasma membrane (c) perivitelline membrane (d) corona radiata (ii) In humans, at which stage does ovum get released from ovary?
(a) Secondary oocyte (b) Oogonium (c) Primary oocyte (d) First polar body (iii) Cytoplasm of an ovum is enveloped by _________________ .
(a) zona pellucida (b) corona radiata (c) cell membrane (d) perivitelline space (iv) Select the correct option
V W X (a) Cytoplasm Zona pellucida Plasma membrane (b) Cortical granules Corona radiata Zona pellucida (c) Cortical granules Plasma membrane Corona radiata (d) Cytoplasm Corona radiata Zona pellucida (v) Which of the following is not a characteristic of an ovum?
(a) Nucleus of an ovum has prominent nucleolus (b) Only one ovum formed from one oogonium (c) It lacks centrioles (d) It has very small amount of ooplasm. (a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Each testicular lobule of testis contains .one to three highly coiled seminiferous tubules. Wall of each seminiferous tubule is formed of single layered germinal epithelium. Majority of cells in this epithelium are cuboidal called male germ cells. Study the transverse section of part of seminiferous tubule and answer the following questions.
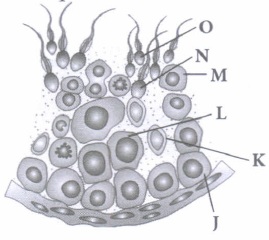
(i) What is the characteristic of K?(a) K is spermatogonium which grows into primary spermatocyte (b) K is Sertoli cell which provides nutrition to spermatids (c) K is secondary spermatocyte which undergo meiosis II to form spermatid (d) K is spermatid being converted into sperm. (ii) Which of the following cell undergo reduction division to form secondary spermatocyte?
(a) J (b) M (c) L (d) K (iii) How many among the following have 46 chromosomes?
J, K, L, M, N,O (a) 2 (b) 4 (c) 5 (d) 3 (iv) Select an option that correctly identifies different labels
(a) L - Primary spermatocyte, N - Spermatozoa, M - Secondary spermatocyte (b) J - Spermatogonium, K - Sertoli cell, O - Spermatozoa (c) L - Primary spermatocyte, M - Secondary spermatocyte, N - Spermatozoa (d) J - Spermatogonium, K - Primary spermatocyte, N - Spermatid (v) Which hormone initiates spermatogenesis at puberty?
(a) FSH (b) ICSH (c) ABP (d) GnRH (a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i)to (v) given below:
Cleavage is the series of rapid mitotic divisions in zygote and forms blastula. The 2, 4, 8, 16 daughter cells are called blastomeres. Embryo with 64 blastomeres is known as blastocyst and has blastocoel cavity. Blastocyst gets implanted in uterine wall and leads to pregnancy.
(i) Solid mass of cells with 16 blastomeres is called(a) morula (b) blastula (c) gastrula (d) zygote (ii) At which stage of embryonic development trophoectoderm develops?
(a) Zygote (b) Morula (c) Blastula (d) Gastrula (iii) Site of implantation is
(a) endometrium of uterus (b) cervix (c) uterine fundus (d) infundibulum of oviduct. (iv) Correct sequence of various structures formed during embryonic development is
(a) Morula\(\to\) Embryo \(\to\)Gastrula \(\to\)Blastula (b) Zygote\(\to\) Embryo \(\to\)Morula\(\to\) Blastula (c) Blastula \(\to\)Morula \(\to\)Gastrula\(\to\) Embryo (d) Zygote \(\to\)Morula \(\to\)Blastula\(\to\) Gastrula. (v) Assertion: Side of blastocyst with inner cell mass is called animal pole.
Reason: Inner cell mass gives rise to embryo.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.(a)