CBSE 11th Standard Physics Subject Ncert Exemplar 3 Mark Questions With Solution 2021
By QB365
QB365 Provides the updated NCERT Exemplar Questions for Class
11, and also provide the detail solution for each and every NCERT Exemplar questions. NCERT Exemplar questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 11th Standard Physics Subject Ncert Exemplar 3 Mark Questions With Solution 2021
11th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Physics
-
A police van moving on a highway with a speed of 30 km h–1 fires a bullet at a thief’s car speeding away in the same direction with a speed of 192 km h–1. If the muzzle speed of the bullet is 150 m s–1, with what speed does the bullet hit the thief’s car ? (Note: Obtain that speed which is relevant for damaging the thief’s car).
(a) -
Two towns A and B are connected by a regular bus service witha bus leaving in either direction every t min. A man cycling with a speed of 20 km/h in the direction A to B notices that a bus goes past him every 18 min in the direction of his motion and every 6 min in the opposite direction .What is the period T of the bus servioce and with what speed ( assumed constant) do the buses ply on the road?
(a) -
A wheel in uniform motion about an axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to its plane is considered to be in mechanical (translation and rotational) equilibrium because no net external torque is required to sustain its motion.
However, the particles that constitute the wheel to experience a centripetal acceleration towards the centre. How do you reconcile this fact with the wheel begin in equilibrium?
How would you set a half wheel into uniform motion about an axis passing through the centre of mass of the wheel and perpendicular to its plane? Will you require external forces to sustain the motion?(a) -
A child stands at centre of a turntable with his arms out stretched. The turntable is set rotating with an angular speed of 40 rev/min.
Show that child's new kinetic energy of rotations is more than the initial kinetic energy. How do you account for this increase in kinetic energy?(a) -
A hoop of radius 2m weighs 100 kg. It rolls along a horizontal floor so that its centre of mass has a speed of 20 cm/s. How much work has to be done to stop it?
(a) -
A car weighs 1800 kg. The distance between its front and back axles is 1.8 m. Its centre of gravity is 1.05 m behind the front axle. Determine the force exerted by the level ground on each front wheel and each back wheel.
(a) -
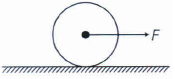
uniform disc of radius R is resting on a table on its rim. The coefficient of friction between disc and table is \(\mu \)(figure). Now, the disc is lled with a force F as shown in the figure. What is the maximum value of F for which the disc rolls without slipping?
 (a)
(a) -
An object if mass m is raised from the surface of the earth to a height equal to the radius of the earth, that is, taken from a distance R to 2R from the centre of the earth. What is the gain in its potential energy?
(a) -
Identical springs of steel and copper are equally stretched.On which, more work will have to be done?
(a) -
The container shown in figure has two chambers, separated by a partition of volumes V1=2.0 L and V2 =3.0 L. The chambers contain \({ \mu }_{ 1 }=4.0\ and\ { \mu }_{ 2 }=5.0\) moles of a gas at pressure p1=1.00 atm and p2= 2.00 atm. Calculate the pressure after the partition is removed and the mixtures attains equilibrium.
V1 V2 \({ \mu }_{ 1 }\) \({ \mu }_{ 2 }\) p1 p2 (a) -
The molecules of a given mass of a gas have root mean square speeds of 100 ms-1 at 270 C and 1.00 atm pressure. What will be the root mean square speeds of the molecules of the gas at 1270C and 2.0 atm pressure?
(a) -
An isolated container containing monatomic gas of molar mass m is moving with a velocity v0. If the container is suddenly stopped, find the change in temperature.
(a) -
Explain,
(i) why there is no atmosphere on moon.
(ii) there is fall in temperature with altitude(a) -
If C is rms speed of molecules in a gas and V is the speed of sound waves in the gas, show that c/v is constant and independent of temperature for all diatomic gases.
(a) -
A hoop of radius 2 m weighs 100 kg. It rolls along a horizontal floor so that its centre of mass has a speed of 20 cm/s. How much work has to be done to stop it?
(a)