10th Standard CBSE Social Science Subjects Question Paper Software Subscription
QB365 covers complete information about 10th Standard CBSE Social Science Subject for 2024-2025 Exam. Question Bank includes 10th Standard CBSE Social Science Subjects Book back, exercise, Updated Question types MCQ, Case Study , Assertion and reason with solution, Previous year asked questions, all possible questions and other key points also. All question with detailed answers are readily available for preparting Maths question papers.
All Chapters Covered

Create Unlimited Question Papers

Access anywhere anytime
Multiple Pattern Question Papers
Share your Question Paper
Font size, line spacing, watermark etc,
10th Standard CBSE Social Science Chapters / Lessons
HIS - The Rise of Nationalism in Europe
The Nationalist Movement in Indo-China
HIS - Nationalism in India
GEO - Minerals and Energy Resources
GEO - Manufacturing Industries
GEO - Life Lines of National Economy
Popular Struggles and Movements
PS - Political Parties
PS - Outcomes of Democracy
Challenges to Democracy
ECO - Money and Credit
ECO - Globalisation and the Indian Economy
ECO - Consumer Rights
HIS - The Making of a Global World
HIS - The Age of Industrialization
Work, Life and Leisure
HIS - Print Culture and Modern World
Novels, Society and History
GEO - Resources and Development
GEO - Forest and Wildlife Resources
GEO - Water Resources
GEO - Agriculture
PS - Power Sharing
PS - Federalism
Democracy and Diversity
PS - Gender, Religion and Caste
The Story of Development
ECO - Sectors of the Indian Economy
ECO - Development
10th Standard CBSE Social Science Chapters / Lessons Syllabus
India and the Contemporary World-II
The Rise of Nationalism in Europe:
(a) The growth of nationalism in Europe after the 1830s. (b) The ideas of Giuseppe Mazzini, etc. (c) General characteristics of the movements in Poland, Hungary, Italy, Germany and Greece.
The Nationalist Movement in Indo - China:
Factors Leading to Growth of Nationalism in Indo-China
a)French colonialism in Indo-China. (b) Phases of struggle against the French. (c) The ideas of Phan Chu Trinh, Phan Boi Chau, HO Chi Minh (d) The Second World War and the liberation struggle. (e) America and the Vietnam war.
Nationalism in India:
(a) Impact of First world war, Khilafat, NonCooperation and Differing Strands within the Movement. (b) Salt Satyagraha. (c) Movements of peasants, workers, tribals. (d) Limits of Civil Disobedience. (e) The Sense of Collective Belonging.
The making of a Global World:
(a) The Pre-modern world (b) The Nineteenth Century global economy, colonialism) (c) The Inter war Economy (Great Depression) (d) Rebuilding the World Economy
The Age of Industrialization :
(a) Proto-industrialization and pace of industrial change (b) Life of workers (c) Industrialization in the colonies (d) Early Entrepreneurs & workers (e) The Peculiarities of Industrial Growth (f) Market for Goods.
Work, Life & Leisure :
(a) Development of modern cities due to Industrialization in London & Bombay
(b) Housing and Land Reclamation (c) Social Changes in the cities (d) Cities and the challenge of the Environment
Print Culture and the Modern World:
(a) The history of print in Europe. (b) The growth of press in nineteenth century India. (c) Relationship between print culture, public debate and politics.
Novels, Society and History:
(a) Emergence of the novel as a genre in the west. (b) The relationship between the novel and changes in modern society. (c) Early novels in nineteenth century India. (d) A study of two or three major writers.
Contemporary India - II
Resources and Development: Types - natural and human; Need for resource planning, natural resources, land as a resource, soil types and distribution; changing land-use pattern; land degradation and conservation measures
Water Resources: Sources, distribution, utilisation, multi-purpose projects, water scarcity, need for conservation and management, rainwater harvesting.
Agriculture: Types of farming, major crops, cropping pattern, technological and institutional reforms; their impact; contribution of Agriculture to national economy-employment and output.
Minerals and Energy Resources:
Types of minerals, distribution (Note : on map only) use and economic importance of minerals, conservation, types of power resources: conventional and nonconventional, distribution and utilization, and conservation.
Manufacturing Industries:
Types, spatial distribution (Note : on map only) contribution of industries to the national economy, industrial pollution and degradation of environment, measures to control degradation.
Life Lines of National Economy :
Importance of means of Communication and transportation, Trade & Tourism.
Democratic Politics - II
Power Sharing & Federalism: Why and how is power shared in democracies? How has federal division of power in India helped national unity? To what extent has decentralisation achieved this objective? How does democracy accommodate different social groups?
Democracy and Diversity & Gender, Religion and Caste:
Are divisions inherent to the working of democracy? What has been the effect of caste on politics and of politics on caste? How has the gender division shaped politics? How do communal divisions affect democracy?
Popular Struggles and Movements
Political Parties:What role do political parties play in competition and contestation? Which are the major national and regional parties in India?
Outcomes of Democracy:
Can or should democracy be judged by its outcomes? What outcomes can one reasonably expect of democracies? Does democracy in India meet these expectations? Has democracy led to development, security and dignity for the people? What sustains democracy in India?
Challenges to Democracy:
Is the idea of democracy shrinking? What are the major challenges to democracy in India? How can democracy be reformed and deepened? What role can an ordinary citizen play in deepening democracy
Understanding Economic Development
Development: The traditional notion of development; National Income and Percapita Income. Growth of National Income - critical appraisal of existing development indicators (PCI, IMR, SR and other income and health indicators) The need for health and educational development; Human Development Indicators (in simple and brief as a holistic measure of development.
Sectors of the Indian Economy: *Sectors of Economic Activities; Historical change in sectors; Rising importance of tertiary sector; Employment Generation; Division of Sectors- Organised and Unorganised; Protective measures for unorganised sector workers.
Money and Credit: Role of money in an economy: Formal and Informal financial institutions for Savings and Credit - General Introduction; Select one formal institution such as a nationalized commercial bank and a few informal institutions; Local money lenders, landlords, chit funds and private finance companies.
Globalisation and the Indian Economy: Production across countries, Foreign trade and Interaction of Markets, what is Globalization? Factors, WTO, Impact, Fair Globalization.
Consumer Rights: ***How consumer is exploited (one or two simple case studies) factors causing exploitation of consumers; Rise of consumer awareness; how a consumer should be in a market; role of government in consumer protection.
The Rise of Nationalism in Europe
The French Revolution and the Idea of the Nation-The Making of Nationalism in Europe-The Age of Revolutions: 1830-1848-The Making of Germany and Italy-Visualising the Nation-Nationalism and Imperialism
The Nationalist Movement in Indo-China
Emerging from the Shadow of China-The Dilemma of Colonial Education-Hygiene, Disease and Everyday Resistance-Religion and Anti-colonialism-The Vision of Modernisation-The Communist Movement and Vietnamese Nationalism-The Nation and Its Heroes-The End of the War
Nationalism in India
The First World War, Khilafat and Non-Cooperation-Differing Strands within the Movement-Towards Civil Disobedience-The Sense of Collective Belonging
The Making of a Global World
The Pre-modern World-The Nineteenth Century-The Inter-war Economy-Rebuilding a World Economy: The Post-war Era
The Age of Industrialisation
Before the Industrial Revolution-Hand Labour and Steam Power-Industrialisation in the Colonies-Factories Come Up-The Peculiarities of Industrial Growth-Market for Goods
Work, Life and Leisure Cities in the Contemporary World
Characteristics of the City-Social Change in the City-Politics in the City-The City in Colonial India-Cities and the Challenge of the Environment
Print Culture and the Modern World
The First Printed Books-Print Comes to Europe-The Print Revolution and Its Impact-The Reading Mania-The Nineteenth Century-India and the World of Print-Religious Reform and Public Debates-New Forms of Publication-Print and Censorship
Novels, Society and History
The Rise of the Novel-The Novel Comes to India-Novels in the Colonial World-Women and the Novel-The Nation and its History
Resource and Development
Introduction-Types Of Resources-Development Of Resources-Resource Planning-Land Resources-Land Utilisation Land Degradation And Conservation Measures-Soil As A Resource
Forest and Wildlife Resources
Flora and Fauna in India-Conservation of Forest and Wildlife in India-Types and Distribution of Forest and Wildlife Resources-Community and Conservation
Water Resources
Water Scarcity and the Need for Water Conservation and Management-Multi-Purpose River Projects and Integrated Water Resources Management-Rainwater Harvesting
Agriculture
Types of Farming-Cropping Pattern-Food Security
Minerals and Energy Resources
Mode of Occurrence of Minerals-Conservation of Minerals
Manufacturing Industries
Importance of Manufacturing-Contribution of Industry to National Economy-Industrial Location-Classification of Industries-Agro-based Industries-Industrial Pollution and Environmental Degradation
Lifelines of National Economy
Transport-Communication-International Trade-Tourism as a Trade
Power-Sharing
Overview-Belgium and Sri Lanka-Majoritarianism in Sri Lanka-Accommodation in Belgium-Forms of power-sharing
Federalism
Overview-What is federalism-What makes India a federal country-How is federalism practiced-Decentralisation in India
Democracy and Diversity
Overview-A Story from Mexico Olympics-Differences, similarities, divisions-Politics of social divisions
Gender, Religion and Caste
Overview-Gender and politics-Religion, communalism and politics-Caste and politics
Popular Struggles and Movements
Overview-Popular struggles in Nepal and Bolivia-Mobilisation and organizations-Pressure groups and movements
Political Parties
Overview-Why do we need political parties-How many parties should we have-National parties-State parties-Challenges to political parties-How can parties be reformed
Outcomes of Democracy
Overview-How do we assess democracy’s outcomes-Accountable, responsive and legitimate government-Economic growth and development-Reduction of inequality and poverty-Accommodation of social diversity-Dignity and freedom of the citizens
Challenges to Democracy
Overview-Thinking about challenges-Different contexts, different challenges-Different types of challenges-Thinking about political reforms-Redefining democracy
Development
What Development Promises Different People, Different Goals-Income And Other Goals-National Development-How To Compare Different Countries Or States-Income And Other Criteria-Public Facilities-Sustainability Of Development
Sectors of The Indian Economy
Sectors Of Economic Activities-Comparing The Three Sectors-Primary, Secondary And Tertiary Sectors In India-Division Of Sectors As Organised And Unorganised-Sectors In Terms Of Ownership: Public And Private Sectors
Money and Credit
Money as a Medium of Exchange-Modern Forms of Money-Loan Activities of Banks-Two Different Credit Situations-Terms of Credit-Formal Sector Credit In India-Self-Help Groups For The Poor-Summing Up
Globalisation and The Indian Economy
Production Across Countries-Interlinking Production Across Countries-Foreign Trade And Integration of Markets-What is Globalisation-Factors That Have Enabled Globalisation-World Trade Organisation-Impact of Globalisation in India-The Struggle For A Fair Globalisation
Consumer Rights
The Consumer in the Marketplace-Consumer Movement-Consumer Rights-Taking the Consumer Movement Forward
Features in Question Paper Preparation software

(or) type Question

Add or Remover

Sub Questions
Adding Notes

Multiple Pattern

All subjects available
How to Create 10th Standard CBSE Social Science Question Paper
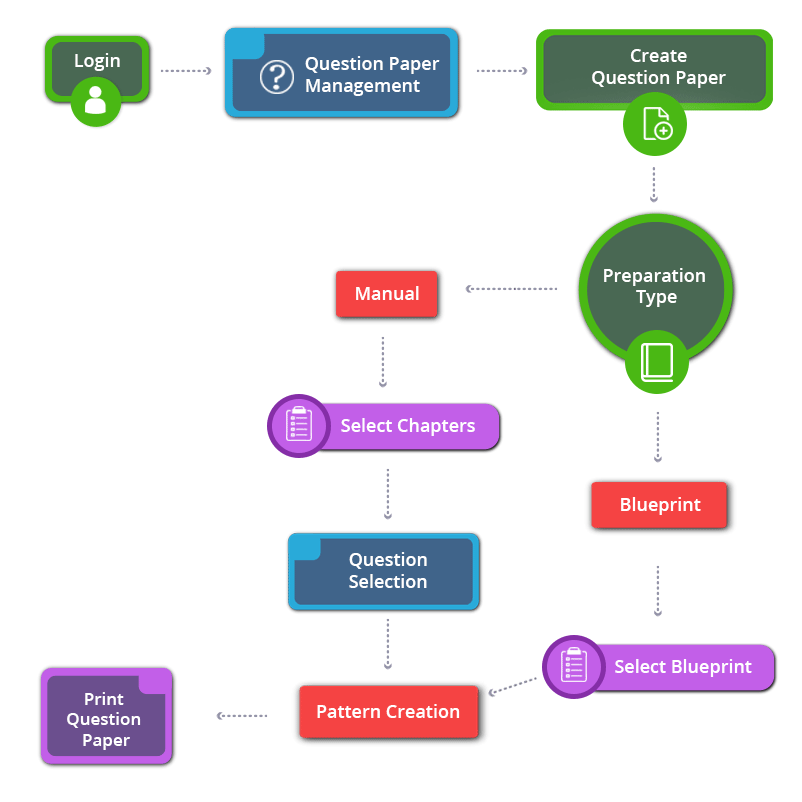

10th Standard CBSE Social Science
- Covers all chapters
- Unique Creative Questions
- Unlimited Question Paper
- Multiple Patterns & Answer keys
1943
1749


