9th Standard CBSE Science Subjects Question Paper Software Subscription
QB365 covers complete information about 9th Standard CBSE Science Subject for 2024-2025 Exam. Question Bank includes 9th Standard CBSE Science Subjects Book back, exercise, Updated Question types MCQ, Case Study , Assertion and reason with solution, Previous year asked questions, all possible questions and other key points also. All question with detailed answers are readily available for preparting Maths question papers.
All Chapters Covered

Create Unlimited Question Papers

Access anywhere anytime
Multiple Pattern Question Papers
Share your Question Paper
Font size, line spacing, watermark etc,
Our Other Subjects for 9th Standard CBSE
9th Standard CBSE Science Chapters / Lessons
Matter in Our Surroundings
Is Matter Around Us Pure
Atoms and Molecules
Structure of the Atom
The Fundamental Unit of Life
Tissues
Diversity in Living Organisms
Motion
Force and Laws of Motion
Gravitation
Work and Energy
Sound
Why Do We Fall Ill
Nature Resources
Improvement in Food Resources
9th Standard CBSE Science Chapters / Lessons Syllabus
Matter-Nature and Behaviour
Definition of matter; solid, liquid and gas; characteristics - shape, volume, density; change of state-melting (absorption of heat), freezing, evaporation (cooling by evaporation), condensation, sublimation.
Nature of matter : Elements, compounds and mixtures. Heterogeneous and homogenous mixtures, colloids and suspensions.
Particle nature, basic units : Atoms and molecules, Law of constant proportions, Atomic and molecular masses. Mole concept : Relationship of mole to mass of the particles and numbers.
Structure of atoms : Electrons, protons and neutrons, valency, chemical formula of common compounds. Isotopes and Isobars.
Organization in the Living World
Call - Basic Unit of life : Cell as a basic unit of life; prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, multicellular organisms; cell membrane and cell wall, cell organelles and cell inclusions; chloroplast, mitochondria, vacuoles, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus; nucleus, chromosomes - basic structure, number.
Tissues, Organs, Organ System, Organism : Structure and functions of animal and plant tissues (only four types of tissues in animals; Meristematic and Permanent tissues in plants).
Biological Diversity : Diversity of plants and animals - basic issues in scientific naming, basis of classification. Hierarchy of categories / groups, Major groups 64 of plants (salient features) (Bacteria, Thallophyta, Bryophyta, Pteridophyta, Gymnosperms and Angiosperms). Major groups of animals (salient features) (Nonchordates upto phyla and chordates upto classes).
Health and Diseases : Health and its failure. Infectious and Non-infectious diseases, their causes and manifestation. Diseases caused by microbes (Virus, Bacteria and Protozoans) and their prevention; Principles of treatment and prevention. Pulse Polio programmes.
Motion, Force and Work
Motion : Distance and displacement, velocity; uniform and non-uniform motion along a staight line; acceleration, distance-time and velocity-time graphs for uniform motion and uniformly accelerated motion, derivation of equations of motion by graphical method; elementary idea of uniform circular motion.
Force and Newton’s laws : Force and Motion, Newton’s Laws of Motion, Action and reaction forces, Inertia of a body, Inertia and mass, Momentum, Force and Acceleration. Elementary idea of conservation of Momentum.
Gravitation : Gravitation; Universal Law of Gravitation, Force of Gravitation of the earth (gravity), Acceleration due to Gravity; Mass and Weight; Free fall.
Floatation : Thrust and Pressure. Archimedes’ Principle; Buoyancy; Elementary Idea of Relative Density. Work, energy and power : Work done by a Force, Energy, Power; Kinetic and Potential energy; Law of conservation of energy.
Sound : Nature of sound and its propagation in various media, speed of sound, range of hearing in humans; ultrasound; reflection of sound; echo and SONAR. Structure of the Human Ear (Auditory aspect only).
Our Environment
Physical resources : Air, Water, Soil. Air for respiration, for combustion, for moderating temperatures; movements of air and its role in bringing rains across India. Air, Water and Soil pollution (brief introduction). Holes in ozone layer and the probable damages.
Bio-geo chemical cycles in nature : Water, Oxygen, Carbon and Nitrogen.
Food Production
Plant and animal breeding and selection for quality improvement and management; Use of fertilizers and manures; Protection from pests and diseases; Organic farming.
Matter in Our Surroundings
Physical Nature of Matter-Characteristics of Particles of Matter-States of Matter-Can Matter Change its State?-Evaporation
Is Matter Around Us Pure?
What is a Mixture?-What is a Solution?-Separating the Components of a Mixture-Physical and Chemical Changes-What are the Types of Pure Substances?
Atoms and Molecules
Laws of Chemical Combination-What is an Atom?-What is a Molecule?-Writing Chemical Formulae-Molecular Mass and Mole Concept
Structure of the Atom
Charged Particles in Matter-The Structure of an Atom-How are Electrons Distributed in Different Orbits (Shells)?-Valency-Atomic Number and Mass Number-Isotopes
The Fundamental Unit of Life
What are Living Organisms Made Up of?-What is a Cell Made Up of? What is the Structural Organisation of a Cell?
Tissues
Are Plants and Animals Made of Same Types of Tissues?-Plant Tissues-Animal Tissues
Diversity in Living Organisms
What is the Basis of Classification?-Classification and Evolution-The Hierarchy of Classification-Groups-Plantae-Animalia-Nomenclature
Motion
Describing Motion-Measuring the Rate of Motion-Rate of Change of Velocity-Graphical Representation of Motion-Equations of Motion by Graphical Method-Uniform Circular Motion
Force and Laws of Motion
Balanced and Unbalanced Forces-First Law of Motion-Inertia and Mass-Second Law of Motion-Third Law of Motion-Conservation of Momentum
Gravitation
Gravitation-Free Fall-Mass-Weight-Thrust and Pressure-Archimedes’ Principle-Relative Density
Work and Energy
Work-Energy-Rate of Doing Work
Sound
Production of Sound-Propagation of Sound-Reflection of Sound-Range of Hearing-Applications of Ultrasound-Structure of Human Ear
Why do we Fall Ill?
Health and its Failure-Disease and Its Causes-Infectious Diseases
Natural Resources
The Breath of Life: Air-Water: A Wonder Liquid-Mineral Riches in the Soil-Biogeochemical Cycles-Ozone Layer
Improvement in Food Resources
Improvement in Crop Yields-Animal Husbandry
Features in Question Paper Preparation software

(or) type Question

Add or Remover

Sub Questions
Adding Notes

Multiple Pattern

All subjects available
How to Create 9th Standard CBSE Science Question Paper
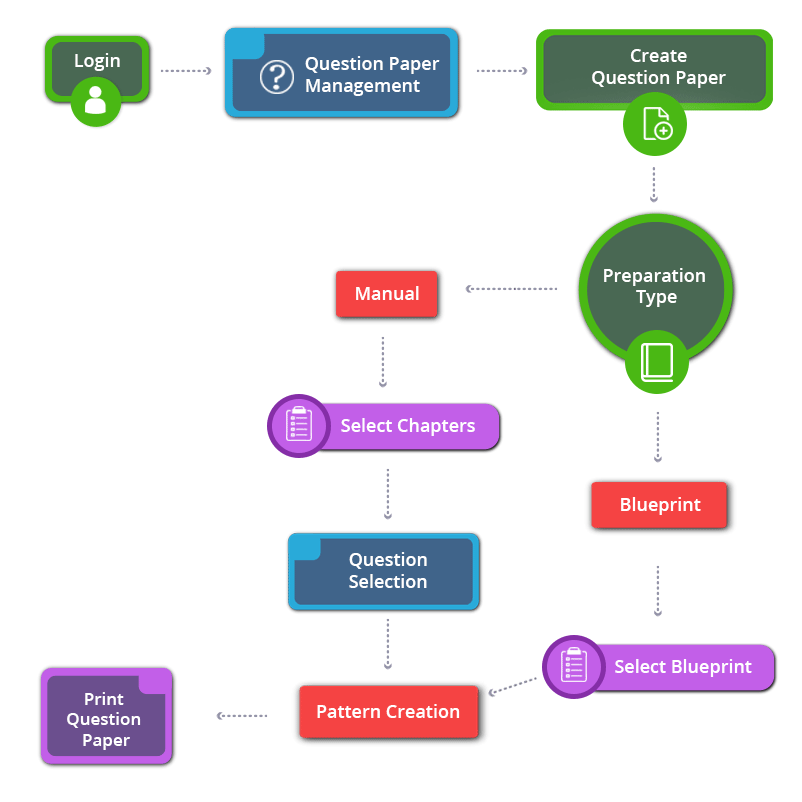

9th Standard CBSE Science
- Covers all chapters
- Unique Creative Questions
- Unlimited Question Paper
- Multiple Patterns & Answer keys
0


