9th Standard CBSE Social Science Subjects Question Paper Software Subscription
QB365 covers complete information about 9th Standard CBSE Social Science Subject for 2024-2025 Exam. Question Bank includes 9th Standard CBSE Social Science Subjects Book back, exercise, Updated Question types MCQ, Case Study , Assertion and reason with solution, Previous year asked questions, all possible questions and other key points also. All question with detailed answers are readily available for preparting Maths question papers.
All Chapters Covered

Create Unlimited Question Papers

Access anywhere anytime
Multiple Pattern Question Papers
Share your Question Paper
Font size, line spacing, watermark etc,
Our Other Subjects for 9th Standard CBSE
9th Standard CBSE Social Science Chapters / Lessons
The French Revolution
Socialism in Europe and the Russian Revolution
Nazism and the Rise of Hitler
India - Size and Location
Physical Features of India
Drainage
Democracy in the Contemporary World
What is Democracy? Why Democracy?
Constitutional Design
The Story of Village Palampur
People as Resource
Forest Society and Colonialism
Pastoralists in the Modern World
Peasants and Farmers
History and Sport: The Story of Cricket
Clothing : A Social History
Climate
Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
Population
Electoral Politics
Working of Institutions
Democratic Rights
Poverty as a Challenge
Food Security in India
9th Standard CBSE Social Science Chapters / Lessons Syllabus
India and the Contemporary World - I
I. The French Revolution:
(a)The Ancient Regime and its crises. (b) The social forces that led to the revolution. (c) The different revolutionary groups and ideas of the time. (d) The legacy.
II. Socialism in Europe and the Russian Revolution:
(a)The crises of Tzarism. (b) The nature of social movements between 1905 and 1917. (c) The First World War and foundation of Soviet state. (d) The legacy.
III. Nazism and the Rise of Hitler:
(a)The growth of social democracy (b) The crises in Germany. (b) The basis of Hitler’s rise to power. (c) The ideology of Nazism. (d) The impact of Nazism.
Sub-unit 1.2: Livelihoods, Economies and Societies:
The themes in this section will focus on how different social groups grapple with the changes in the contemporary world and how these changes affect their lives.
IV. Forest Society and Colonialism:
(a) Relationship between forests and livelihoods. (b) Changes in forest societies under colonialism.
Case studies : Focus on two forest movements one in colonial India (Bastar) and one in Indonesia.
V. Pastoralists in the Modern World:
(a) Pastoralism as a way of life. (b) Different forms of pastoralism. (c) What happens to pastoralism under colonialism and modern states?
Case studies: Focus on two pastoral groups, one from Africa and one from India.
VI. Peasants and Farmers:
(a) Histories of the emergence of different forms of farming and peasant societies.
(b) Changes within rural economies in the modern world.
Case studies: focus on contrasting forms of rural change and different forms of rural societies (expansion of large-scale wheat and cotton farming in USA, rural economy and the Agricultural Revolution in England, and small peasant production in colonial India)
Contemporary India - I
India - Size and Location
Physical Features of India:relief, structure, major physiographic unit.
Drainage: Major rivers and tributaries, lakes and seas, role of rivers in the economy, pollution of rivers, measures to control river pollution.
Climate: Factors influencing the climate; monsoon- its characteristics, rainfall and temperature distribution; seasons; climate and human life.
Natural Vegetation and Wild Life: Vegetation types, distribution as well as altitudinal variation, need for conservation and various measures. Major species, their distribution, need for conservation and various measures.
Population: Size, distribution, agesex composition, population changemigration as a determinant of population change, literacy, health, occupational structure and national population policy : adolescents as under-served population group with special needs.
Democratic Politics – I
What is Democracy? Why Democracy?:
What are the different ways of defining democracy? Why has democracy become the most prevalent form of government in our times? What are the alternatives to democracy? Is democracy superior to its available alternatives? Must every democracy have the same institutions and values?
Constitutional Design:
How and why did India become a democracy? How was the Indian constitution framed? What are the salient features of the Constitution? How is democracy being constantly designed and redesigned in India?
Electoral Politics:
Why and how do we elect representatives? Why do we have a system of competition among political parties? How has the citizens’ participation in electoral politics changed? What are the ways to ensure free and fair elections?
Working of Institutions:
How is the country governed? What does Parliament do in our democracy? What is the role of the President of India, the Prime Minister and the Council of Ministers? How do these relate to one another?
Democratic Rights :
Why do we need rights in a constitution? What are the Fundamental Rights enjoyed by the citizen under the Indian constitution? How does the judiciary protect the Fundamental Rights of the citizen? How is the independence of the judiciary ensured?
Economics
The Story of Village Palampur:
Economic transactions of Palampore and its interaction with the rest of the world through which the concept of production (including three factors of production (land, labour and capital) can be introduced.
People as Resource: Introduction of how people become resource/asset; economic activities done by men and women; unpaid work done by women; quality of human resource; role of health and education; unemployment as a form of non utilisation of human resource; sociopolitical implication in simple form
Poverty as a Challenge: Who is poor (through two case studies: one rural, one urban); indicators; absolute poverty (not as a concept but through a few simple examples)-why people are poor ; unequal distribution of resources; comparison between countries; steps taken by government for poverty alleviation.
Food Security in India: Source of Foodgrains, variety across the nation, famines in the past, the need for self sufficiency, role of government in food security, procurement of foodgrains, overflowing of granaries and people without food, public distribution system, role of cooperatives in food security (foodgrains, milk and vegetables ration shops, cooperative shops, two-three examples as case studies).
The French Revolution
French Society During the Late Eighteenth Century-The Outbreak of the Revolution-France Abolishes Monarchy and Becomes a Republic-Did Women have a Revolution-The Abolition of Slavery-The Revolution and Everyday Life
Socialism in Europe and the Russian Revolution
The Age of Social Change-The Russian Revolution-The February Revolution in Petrograd-What Changed after October-The Global Influence of the Russian Revolution and the USSR
Nazism and the Rise of Hitler
Birth of the Weimar Republic-Hitler’s Rise to Power-The Nazi Worldview-Youth in Nazi Germany-Ordinary People and the Crimes Against Humanity
Forest Society and Colonialism
Why Deforestation-The Rise of Commercial Forestry-Rebellion in the Forest-Forest Transformations in Java
Pastoralists in the Modern World
Pastoral Nomads and their Movements-Colonial Rule and Pastoral Life-Pastoralism in Africa
Peasants and Farmers
The Coming of Modern Agriculture in England-Bread Basket and Dust Bowl-The Indian Farmer and Opium Production
History and Sport: The Story of Cricket
The Historical Development of Cricket as a Game in England-The Spread of Cricket-The Modern Transformation of the Game-Commerce, Media and Cricket Today
Clothing: A Social History
Sumptuary Laws and Social Hierarchy-Clothing and Notions of Beauty-New Times-Transformations in Colonial India-Designing the National Dress
India – Size and Location
Location-Size-India and The World-India’s Neighbours
Physical Features of India
Introduction-Major Physiographic Divisions
Drainage
Drainage Systems in India- Lakes-Role of Rivers in The Economy-River Pollution
Climate
Climatic Controls-Factors Affecting India’s Climate-The Indian Monsoon-The Onset Of The Monsoon And Withdrawal-The Seasons-Distribution Of Rainfall-Monsoon As A Unifying Bond
Natural Vegetation and Wild Life
Relief-Climate-Ecosystem-Types of Vegetation-Wild Life
Population
Population Size and Distribution-Population Growth and Processes of Population Change
Democracy in the Contemporary World
Two Tales of Democracy-The Changing Map of Democracy-Phases in the Expansion of Democracy-Democracy At The Global Level
What is Democracy? Why Democracy?
What Is Democracy-Features Of Democracy-Why Democracy-Broader Meanings Of Democracy
Constitutional Design
Democratic Constitution In South Africa-Why Do We Need A Constitution-Making Of The Indian Constitution-Guiding Values Of The Indian Constitution
Electoral Politics
Why Elections-What Is Our System Of Elections-What Makes Elections In India Democratic
Working of Institutions
How is a Major Policy Decision Taken-Parliament-Political Executive-The Judiciary
Democratic Rights
Life Without Rights-Rights In A Democracy-Rights In The Indian Constitution-Expanding Scope Of Rights
The Story of Village Palampur
Introduction-Organisation of Production-Farming in Palampur-Non Farm Activities in Palampur
People as Resource
Introduction-Economic Activities by Men and Women-Quality of Population-Health-Unemployment
Poverty as a Challenge
Introduction- Two Typical Cases of Poverty- Poverty as seen by social scientists- Poverty Line- Poverty Estimates- Vulnerable Groups- Inter State Disparities- Global Poverty Scenario- Causes of Poverty- Anti-Poverty Measures- The Challenges Ahead
Food Security in India
What is food security- Why food security- Who are food insecure- What is Buffer stock- What is the Public Distribution System- Current Status of Public Distribution System- Role of cooperatives in food security
Features in Question Paper Preparation software

(or) type Question

Add or Remover

Sub Questions
Adding Notes

Multiple Pattern

All subjects available
How to Create 9th Standard CBSE Social Science Question Paper
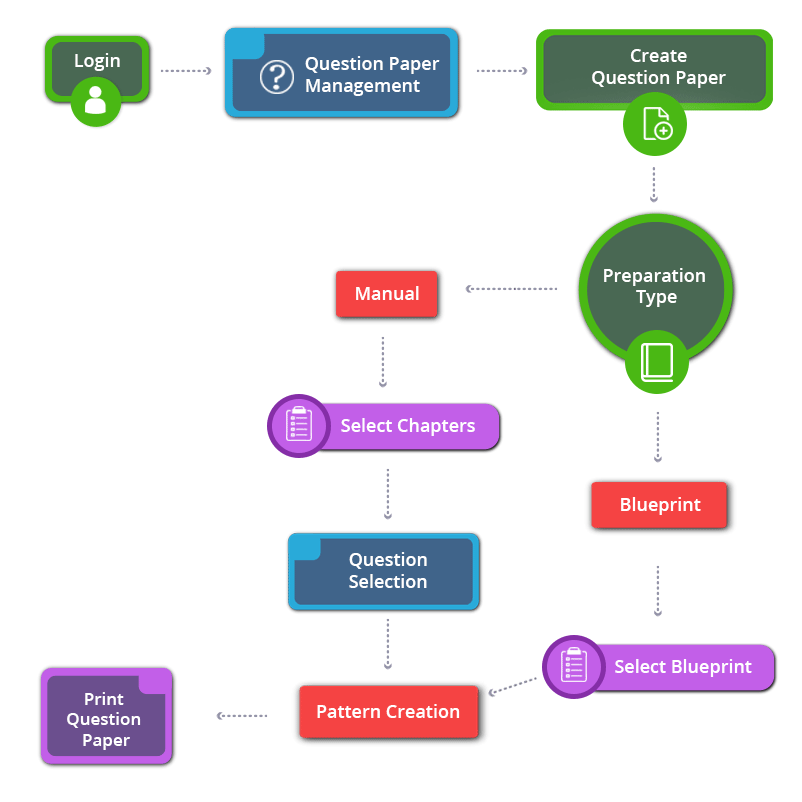

9th Standard CBSE Social Science
- Covers all chapters
- Unique Creative Questions
- Unlimited Question Paper
- Multiple Patterns & Answer keys
1943
1749


