CBSE 10th Standard Maths Subject Introduction to Trigonometry Ncert Exemplar 2 Marks Questions With Solution 2021
By QB365 on 26 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated NCERT Examplar Questions for Class 10 Maths, and also provide the detail solution for each and every ncert examplar questions , QB365 will give all kind of study materials will help to get more marks
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 10th Standard Maths Subject Introduction to Trigonometry Ncert Exemplar 2 Marks Questions With Solution 2021
10th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Maths
-
Name the type of triangle formed by the points A(-5, 6), B(-4, 2) and C(7, 5).
(a) -
Find the value of m if the points (5, 1), (-2, -3) and (8, 2m) are collinear.
(a) -
The points A(2, 9), B(a, 5) and C(5, 5) Are the vertices of \(\triangle ABC\) right angled at B. Find the value of a and hence the area of \(\triangle ABC\).
(a) -
Name the type of triangle PQR formed by the points \(P(\sqrt { 2 } ,\sqrt { 2 } ),Q(-\sqrt { 2 } ,-\sqrt { 2 } )\) and \(R(-\sqrt { 6 } ,\sqrt { 6 } )\)
(a) -
Show that \(\Delta \)ABC with vertices A(-2, 0), B(0, 2) and C(2,0) is similar to \(\Delta \)DFE with vertices D(- 4, 0), E(4, 0) and F(0, 4).
(a)
2 Marks
*****************************************
CBSE 10th Standard Maths Subject Introduction to Trigonometry Ncert Exemplar 2 Marks Questions With Solution 2021 Answer Keys
-
scalene triangle
-
\(m=\frac { 19 }{ 14 } \)
-
\(a=2,\ OR\ \left( \triangle ABC \right) =6\ sq.units\)
-
We have P(\(\sqrt{2}\) , \(\sqrt{2}\)) , Q(-\(\sqrt{2}\),-\(\sqrt{2}\)) and R(-\(\sqrt{6}\),\(\sqrt{6}\))
\(\therefore\) PQ = \(\sqrt { \left( \sqrt { 2 } +\sqrt { 2 } \right) ^{ 2 }+\left( \sqrt { 2 } +\sqrt { 2 } \right) ^{ 2 } } \)
\(=\sqrt { \left( 2\sqrt { 2 } \right) ^{ 2 }+\left( 2\sqrt { 2 } \right) ^{ 2 } } \)
\(=\sqrt { 4\times 2+4\times 2 } =\sqrt { 8+8 } \)
\(=\sqrt { 16 } \)=4 units
PR = \(\sqrt { \left( \sqrt { 2 } +\sqrt { 6 } \right) ^{ 2 }+\left( \sqrt { 2 } +\sqrt { 6 } \right) ^{ 2 } } \)
\(=\sqrt { 2+6+2\sqrt { 2 } +2+6-2\sqrt { 2 } } \)
\(=\sqrt { 2+6+2+6 } \)
\(=\sqrt { 16 } \) = 4 units
RQ = \(\sqrt { [(-\sqrt { 2 } )+\sqrt { 6 } ^{ 2 }+\left( -\sqrt { 2 } -\sqrt { 6 } \right) ^{ 2 } } \)
\(=\sqrt { 2+6-2\sqrt { 2 } +2+6+2\sqrt { 2 } } \)
\(=\sqrt { 2+6+2+6 } \)
\(=\sqrt { 16 } \) =4 units
Since PQ=PR=RQ = 4 units
∴ PQR is an equilateral triangle. -
Given, vertices of \(\Delta \)ABC are A(-2, 0), B(0, 2) and C(2,0) and D(- 4, 0), E(4, 0) and F(0, 4).
Now, AB = \(\sqrt { { (0+2) }^{ 2 }+{ (2-0) }^{ 2 } } =\sqrt { 4+4 } =2\sqrt { 2 } \) units [\(\because \) distance=\(\sqrt { { \left( { x }_{ 2 }-{ x }_{ 1 } \right) }^{ 2 }-{ \left( { y }_{ 2 }-{ y }_{ 1 } \right) }^{ 2 } } \)]
BC = \(\sqrt { { (2-0) }^{ 2 }+{ (0-2) }^{ 2 } } \) \( =\sqrt { 4+4 } =2\sqrt { 2 } \) units
CA = \(\sqrt { { (-2-2) }^{ 2 }+{ (0-0) }^{ 2 } } \) = \(\sqrt { { (-4) }^{ 2 }+0 } \)= 4 units
FD = \(\sqrt { { (0+4) }^{ 2 }+{ (4-0) }^{ 2 } } \) = \(\sqrt { { (4) }^{ 2 }+{ (-4) }^{ 2 } } \) = \(4\sqrt { 2 } \) units
FE = \(\sqrt { { (4-0) }^{ 2 }+{ (0-4) }^{ 2 } } \) = \(\sqrt { { (4) }^{ 2 }+{ (-4) }^{ 2 } } \) = \(4\sqrt { 2 } \) units
and ED = \(\sqrt { { (-4-4) }^{ 2 }+{ (0-0) }^{ 2 } } \) = \(\sqrt { { (-8) }^{ 2 }} \) = \(\sqrt { {64} }\) = 8 units
Here, we see that sides of \(\Delta \) DEF are twice the sides of \(\Delta \)ABC.
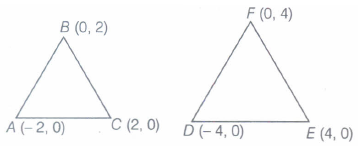
Hence, both the triangle are similar.
Hence proved.
2 Marks

























