CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Carbon and Its Compounds Ncert Exemplar 5 Mark Questions 2021
By QB365 on 26 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated NCERT Exemplar Questions for Class
10, and also provide the detail solution for each and every NCERT Exemplar questions. NCERT Exemplar questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Carbon and Its Compounds Ncert Exemplar 5 Mark Questions 2021
10th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Science
-
A salt X is formed and a gas is evolved when ethanoic acid reacts with sodium hydrogen carbonate. Name the salt X and the gas evolved. Describe an activity and draw the diagram of the apparatus to prove that the evolved gas is the one which you have named. Also, write chemical equation of the reaction involved.
(a) -
a) What are hydrocarbons? Give examples
b) Give the structural differences between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons with two example each.
c) What is a functional group? Give example of four different functional groups.(a) -
Name the reaction which is commonly used in the conversion of vegetable oils to fats. Explain the reaction involved in detail.
(a) -
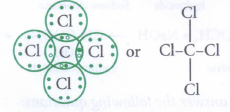
a) Write the formula and draw electron dot structure of carbon tetrachloride?
b) What is saponification? Write the reaction involved in this process.(a) -
Esters are sweet-smelling substances and are used in making perfumes. Suggest some activity and the reaction involved for the preparation of an ester with well labeled diagram.
(a)
*****************************************
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Carbon and Its Compounds Ncert Exemplar 5 Mark Questions 2021 Answer Keys
-
\(\underset{Ethanoic\ acid}{CH_3COOH} + \underset {Sodium\ hydrogen\\ Carbonate}{NaHCO_3} \rightarrow \underset{sodium\ ethanoate}{CH_3COONa}+ \underset{Cabon\ dioxide}{CO_2} + \underset{Water}{H_2O}\)
Activity to show that ethanoic acid reacts with metal hydrogen carbonate to liberate carbon dioxide.
Procedure:
i) Take two test tubes and label them as A and B.
ii) Now, take few grams of sodium carbonate in test tube A.
iii) Take few grams of sodium hydrogen carbonate in test tube B.
iv) Now, add ethanoic acid to both the test tubes.
v) Note your observation.
vi) Pass the gas liberated in test tube A and B through lime water or calcium hydroxide solution.
vii) Record your observation.
Observation
a) A brisk effervescence is formed.
b) The lime water turns milky in both the test tubes.
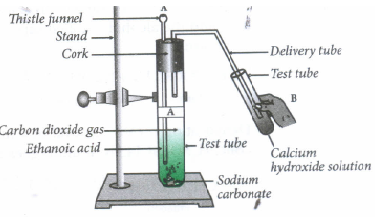
When carboxylic acids react with sodium carbonate or sodium bicarbonates, it liberates carbon dioxide gas which turns lime water milky.
\(\underset{Calcium\ hydroxide\\ (Lime\ wate)}{Ca(OH)_2(aq)}+\underset{Carbon\ dioxide}{CO_2(g)}\rightarrow \underset{Calcium\ carbonate\\ (White \ ppt)}{CaCO_3(s)\downarrow}+\underset{Water}{H_2O(l)}\) -
a) Compounds of carbon and hydrogen only are called hydrocarbons. For example
methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), ethene (C2H4), ethyne (C2H2), cydohexane
(C6H12), benzene (C6H6) etc.
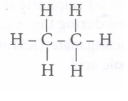
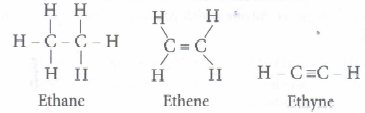
b) Saturated hydrocarbons contains only C - C and C - H single covalent bonds while
unsaturated hydrocarbons contain at least one C = C double bond (besides C - C
and C - H single covalent bonds) or one triple bond.
c) That portion of the organic molecule which largely determine its chemical properties is called the functional group. For example, -OH (alcoholic group),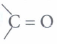 (keto group) - CHO (aldehyde group), -COOH (carboxyl group).
(keto group) - CHO (aldehyde group), -COOH (carboxyl group). -
Addition of hydrogen to understand hydrocarbons in presence of a catalyst such as nickel or palladium to form saturated hydrocarbons is called hydrogenation. For example,
\(\underset { Ethyne }{ CH } \equiv CH+{ H }_{ 2 }\xrightarrow [ ]{ Ni/473K} \underset { Ethene }{ { CH }_{ 2 } } ={ CH }_{ 2 }+{ H }_{ 2 }\xrightarrow [ ]{Ni/473K } { CH }_{ 3 }-\underset { Ethane }{ { CH }_{ 3 } } \) -
\(\underset{Carbon}{C}+\underset{Chlorine}{2Cl_2}\xrightarrow{Heat}\underset{Carbon\ tetrachloridse}{CCl_4}\)
Its electron dot structure and structural formulae are:
b) Saponification - Alkaline hydrolysis of an ester to give the salt of the corresponding
acid and the alcohol is called saponification. It is reverse of esterification reaction.
For example.
\(\underset{Ester}{CH_3COOC_2H_5}+\underset{sodium\ hydroxide}{NaOH}\xrightarrow{Heat}\underset{Sodium\ acetate}{CH_3COONa}+\underset{Ethanol}{CH_3CH_2OH}\)
Dehydration means removal of a molecule of water. When ethanol is heated with
conc. H2SO4 at 443 K, it undergoes dehydration to form ethene.
\(\underset{Ethanol}{CH_3CH_2OH}\xrightarrow{Conc. H_2SO_4,443K}\underset{Ethene}{CH_2=CH_2+H_2O}\) -
Carboxylic acid reacts with alcohols to form ester. For example, when ethanoic acid is warmed with ethanol in presence of a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid as catalyst, an ester (ethyl ethanoate, commonly called ethyl acetate) and water are formed.
\(\underset{Acetic\ or\ ethanoic\ acid}{CH_COOH}+\underset{Ethanol}{C_2H_5OH}\xrightarrow{Conc. H_2SO_4}\underset{Ethyl\ ethanoate}{CH_3COOC_2H_5}+\underset{Water}{H_2O)}\)
Ester are sweet -smelling substances. So they are widely used in making perfumes and flavoring agents. Further, the reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol to form a sweet ester is used as a test for alcohols as well as carboxylic acids.

























