CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Heredity and Evolution Chapter Case Study Questions 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Heredity and Evolution Case Study Questions 2021
10th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Science
-
Purebred pea plant with smooth seeds (dominated characteristic) were crossed with purebred pea plant with wrinkled seeds (recessive characteristic). The F1 generation was self pollinated to give rise to the F2 generation.
(i) What is the expected observation of the F1 generation of plants?
(a) 1/2 of them have smooth seeds and 1/2 of the have wrinkled seeds.
(b) 1/4 of them have wrinkled seeds and 3/4 of them have smooth seeds.
(c) 3/4 of them have wrinkled seeds and 1/4 of them have smooth seeds.
(d) All of them have smooth seeds.
(ii) What is the expected observation of the F2 generation of plants?
(a) 1/2 of them have smooth seeds and 1/2 of them have wrinkled seeds.
(b) 1/4 of them have wrinkled seeds and 3/4 of them have smooth seeds.
(c) 3/4 of them have wrinkled seeds and 1/4 of them have smooth seeds.
(d) All of them have smooth seeds.
(iii) If a genotype consists of different types of alleles, it is called(a) homozygous (b) heterozygous (c) monoallelic (d) uniallelic (iv) The alternative form of gene is called
(a) dominant character (b) recessive character (c) alternative genes (d) allele. (v) Which of the following will be the genotypic ratio of given F2 generation?
(a) 1: 3 (b) 3: 1 (c) 1: 2 : 1 (d) 1: 1 : 1 (a) -
In fruittlies, the gene for wing shape has two alleles, an unusual allele for curled wings (c) and the normal allele for straight wings (C). The given phenotypes are observed for each genotype.
Genotype Phenotype CC Normal, straight wings Cc Wings curled up at the ends, has difficulty flying cc Unable to hatch from egg (i) Which of the following crosses would produce live offspring from 50% of the eggs?
(a) CC x Cc (b) CC x CC (c) CC x cc (d) Cc x cc (i) (d)
(ii) (a)
(iii) (a): 25% of the total number of eggs will not
hatch (genotype cc). 50% of the offspring will be curlywinged
(Cc) and 25% of the offspring are straightwinged
(CC).
(iv) (c)
(v) (b)(ii) Which of the following crosses would be able to produce offspring that would fly normally from 50% of the egg?
(a) CC x Cc (b) Cc x Cc (c) CC x cc (d) Cc x cc (iii) Two curly winged flies are crossed, and they produce 150 eggs. What is the proportion of straight-winged flies expected among the live offspring?
(a) 25% (b) 33% (c) 50% (d) 75% (iv) Normal straight winged flies are self crossed and they produce 120 eggs. What is the proportion of curly winged flies expected among the live offspring?
(a) 25% (b) 75% (c) 0% (d) 100% (v) Which of the following crosses would be able to produce offspring that has curled wings only?
(a) CC x Cc (b) CC x cc (c) Cc x Cc (d) Cc x cc (a) -
Refer to the schematic representation of the albinism that is an inherited condition caused by recessive allele (a). 'A' is the dominant allele for the normal condition. The inheritance of certain genetic traits for two or more generations is represented in a pedigree or family tree. Study the given pedigree chart and answer the following questions.
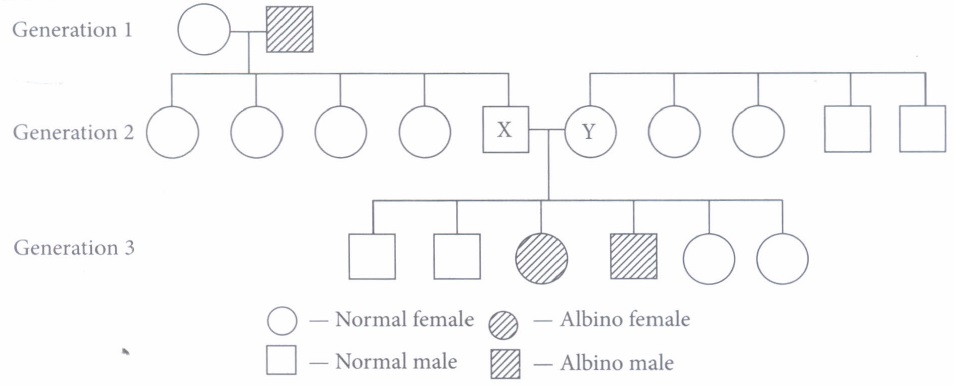
(i) Which of the following could be the genotypes of X and Y?X Y (a) AA AA (b) AA Aa (c) Aa Aa (d) aa aa (ii) Which of the following could be the genotype of generation - 1 male and female?
Male Female (a) AA aa (b) aa AA (c) Aa aa (d) AA AA (iii) If X married an albino female, then what is the probability that their children would be albino?
(a) 0 (b) 0.125 (c) 0.25 (d) 0.5 (iv) If Y married a normal homozygous male, then what is the probability that their children would be albino?
(a) 0 (b) 0.125 (c) 0.25 (d) 0.5 (v) Which of the following could be the genotype of offsprings produced by cross of X and Y?
(a) AA, Aa, aa (b) aa, aa (c) Aa, Aa (d) AA, AA (a) -
Refer to the given table regarding results of F2 generation of Mendelian cross.
Plants with round and yellow coloured seeds (P) 315 Plants with round and green coloured seeds (Q) 108 Plants with wrinkled and yellow coloured seeds (R) 101 Plants with wrinkled and green coloured seeds (S) 32 (i) Which of the following would be the phenotype of F1 generation regarding given data of F2 generation?
(a) Plants with round and yellow coloured seeds
(b) Plants with round and green coloured seeds
(c) Plants with wrinkled and yellow coloured seeds
(d) Plants with wrinkled and green coloured seeds.
(ii) Which of the following would be the genotype of parental generation regarding given result of F2 generation?(a) YYRR and yyrr (b) YYRR and YYRR (c) YYRR and YyRr (d) YyRr and YyRr (iii) If plant with wrinkled and green coloured seeds (S) is crossed with plant having wrinkled and yellow coloured seeds (R), what will be the probable phenotype of offsprings?
(a) All plants with wrinkled and yellow coloured seeds
(b) 50% plants with wrinkled and yellow coloured seeds and 50% plants with wrinkled and green coloured seeds
(c) All plants with wrinkled and green coloured seeds
(d) Both (a) and (b).
(iv) Which of the following will result when plant YyRr is self-pollinated?
(a) 9: 3 : 3 : 1 ratio of phenotypes only
(b) 9: 3 : 3 : 1 ratio of genotypes only
(c) 1-: 1 : 1 : 1 ratio of phenotypes only
(d) 1: 1 : 1 : 1 ratio of phenotypes and genotypes
(v) The percentage of yR gamete produced by YyRR parent will be(a) 25% (b) 50% (c) 75% (d) 12.5% (a) -
Pea plants can have smooth seeds or wrinkled seeds. One of the phenotypes is completely dominant over the other. A farmer decides to pollinate one flower of a plant with smooth seeds using pollen from plant with wrinkled seeds. The resulting pea pod has all smooth seeds.
(i) Which of the following conclusions can be drawn?
1. The allele for smooth seeds is dominated over that of wrinkled seeds.
2. The plant with smooth seeds is heterozygous.
3. The plant with wrinkled seeds is homozygous.(a) 1 only (b) 1 and 2 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 (ii) Which of the following crosses will give smooth and wrinkled seeds in same proportion?
(a) RR x rr (b) Rr x rr (c) RR x Rr (d) rr x rr (iii) Which of the following cross can be used to determine the genotype of a plant with dominant phenotype?
(a) RR x RR (b) Rr x Rr (c) Rr x RR (d) RR x rr (iv) On crossing of two heterozygous smooth seeded plants (Rr), a total of 1000 plants were obtained in F1 generation. What will be the respective number of smooth and wrinkled seeds obtained in F1 generation?
(a) 750,250 (b) 500,500 (c) 800,200 (d) 950,50 (v) The characters which appear in the first filial generation are called
(a) recessive characters (b) dominant characters (c) lethal characters (d) non-mendelian characters (a)
*****************************************
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Heredity and Evolution Case Study Questions 2021 Answer Keys
-
(i) (d)
(ii) (b)
(iii) (b): Factors representing the alternate or same form of a character are called alleles. In heterozygous individuals or hybrids, a character is represented by two contrasting alleles. Out of the two contrasting alleles, only one is able to express its effect in the individual. It is called dominant allele. The other allele which does not show its effect in the heterozygous individual is called recessive allele, e.g., in case of hybrid tall pea plants (Tt). 'T' is dominant allele whereas 't' is recessive allele.
(iv) (d): Factors representing the alternate or same form of a character are called alleles. In heterozygous individuals or hybrids, a character is represented by two contrasting alleles. Out of the two contrasting alleles, only one is able to express its effect in the individual. It is called dominant allele. The other allele which does not show its effect in the heterozygous individual is called recessive allele, e.g., in case of hybrid tall pea plants (Tt). 'T' is dominant allele whereas 't' is recessive allele.
(v) (c): In given case, genotypic ratio of F2 progeny will be 1: 2 : 1 where, one is homozygous dominant, two are heterozygous dominant and one is homozygous recessive. -
(i) (d)
(ii) (a)
(iii) (a): 25% of the total number of eggs will not hatch (genotype cc). 50% of the offspring will be curlywinged (Cc) and 25% of the offspring are straightwinged (CC).
(iv) (c)
(v) (b) -
(i) (c): X and Y parents must have 'a' allele (recessive) that is respective for albinism, the genotype of both X and Y individuals would be Aa and Aa as they are normal and 3rd generation, normal and albino male and female is formed in 3 : 1 ratio.
(ii) (b): Albinism is caused by the recessive allele. The children of generation -1, male and female all are normal (Aa). So, in generation-L, the genotype of female must be AA as she is normal and genotype of male is aa as he is albino male.
(iii) (d): Albinism is caused by the recessive allele and father of X is albino male so, the genotype of X is Aa and genotype of albino female is aa. So, the probability that their children would be albino is 50%.
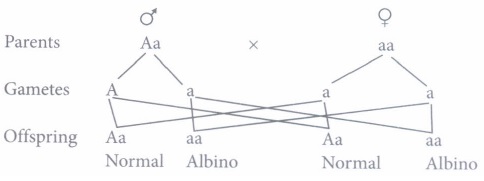
(iv) (a)
(v) (a) -
(i) (a)
(ii) (a)
(iii) (d): Plant with wrinkled and green coloured seeds (S) (genotype rryy) is crossed with plant with wrinkled and yellow coloured seeds (R) (genotype rrYY or rrYr). If plant with wrinkled and green coloured seeds (rryy) is crossed with plant having wrinkled and yellow coloured seeds of genotype rrYY then all plants produced with wrinkled and yellow coloured seeds whereas if plant with wrinkled and green coloured seeds (rryy) is crossed with plant having wrinkled and yellow coloured seeds that has genotype rrYy then 50% plants with wrinkled and yellow coloured seeds and 50% plants with wrinkled and green coloured seeds are produced.
(iv) (a): When plant YyRr is self pollinated, 9: 3 :3 : 1 ratio of phenotypes will be observed. This can be explained as follows:
Parents: \(\begin{array}{ll} \text { YyRr } & \times \quad \text { YyRr } \end{array}\)
Progenies:
YR Yr yR yr YR YYRR
Yellow roundYYRr
Yellow roundYyRR
Yellow roundYyRr
Yellow roundYr YYRr
Yellow roundYYrr
Yellow WrinkledYyRr
Yellow roundYyrr
Yellow WrinkledyR YyRR
Yellow roundYyRr
Yellow roundyyRR
Green roundyyRr
Green roundyr YyRr
Yellow roundYyrr
Yellow WrinkledyyRr
Green roundyyrr
Green WrinkledPhenotypic ratio = 9 yellow and round: 3 yellow and wrinkled: 3 green and round: 1 green and wrinkled.
(v) (b): Gametes produced by YyRR parent would be 50% YR and 50% yR. -
(i) (c)
(ii) (b)
(iii) (d)
(iv) (a): The crossing between two heterozygous smooth seeded (Rr) plants would give phenotypic ratio of 3 smooth seeded plant : 1 wrinkled seeded plant. If plants obtained were 1000, then the number of smooth and wrinkled plants will be closed to 750 and 250 respectively.
(v) (b)

























