CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Heredity and Evolution Chapter Case Study Questions With Solution 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Heredity and Evolution Case Study Questions With Solution 2021
10th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Science
-
Sex determination is the method by which distinction between males and females is established in a species. The sex of an individual is determined by specific chromosomes. These chromosomes are called sex chromosomes or allosomes. X and Y chromosomes are called sex chromosomes. The normal chromosomes other than the sex chromosomes of an individual are known as autosomes.
(i) In XX-XO type of sex determination
(a) females produce two different types of gametes
(b) males produce two different types of gametes
(c) females produce gametes with Y chromosome
(d) males produce gametes with Y chromosome.
(ii) A couple has six daughters. What is the possibility of their having a girl next time?(a) 10% (b) 50% (c) 90% (d) 100% (iii) Number of autosomes present in liver cells of a human female is
(a) 22 autosomes (b) 22 pairs (c) 23 autosomes (d) 23 pairs. (iv) XX-XO type of sex determination and XX-XY type of sex determination are the examples of
(a) male heterogamety (b) female heterogamety (c) male homogamety (d) both (b) and (c). (v) Select the incorrect statement.
(a) In male grasshoppers, 50% of sperms have no sex chromosome
(b) Female fruitfly is heterogametic
(c) Human male produces two types of sperms 50% having X chromosome and 50% having Y chromosomes
(d) In turtle, sex determination is regulated by environmental factors.(a) -
Gregor Mendel conducted hybridisation experiments on garden peas for seven years and proposed the laws of inheritance in living organisms. He investigated characters in the garden pea plant that were manifested as two opposing traits, e.g., tall or dwarf plants, yellow and green seeds, etc.
(i) Among the seven pairs of contrasting traits in pea plant as studied by Mendel, the number of traits related
to flower, pod and seed respectively were(a) 2,2,2 (b) 2,2,1 (c) 1,2,2 (d) 1,1,2. (ii) The colour based contrasting traits in seven contrasting pairs, studied by Mendel in pea plant were
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4. (iii) Refer to the given table of contrasting traits in pea plants studied by Mendel.
Character Dominant trait Recessive trait (i) Seed colour 

(ii) Flower colour 

(iii) Pod shape 

(iv) Flower position 
Which of the given traits is correctly placed?
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii) only
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv) only
(c) (ii) and (iii) only
(d) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(iv) Some of the dominant traits studied by Mendel were
(a) round seed shape, green seed colour and axial flower position
(b) terminal flower position, green pod colour and inflated pod shape
(c) violet flower colour, green pod colour and round seed shape
(d) wrinkled seed shape, yellow pod colour and axial flower position.
(v) Which of the following characters was not chosen by Mendel?(a) Pod shape (b) Pod colour (c) Position of flower (d) Position of pod (a) -
Mendel crossed tall and dwarf pea plants to study the inheritance of one gene. He collected the seeds produced as a result of this cross and grew them to generate plants of the first hybrid generation which is called the first filial progeny or F1: Mendel then self pollinated the tall F1 plants and he obtained F2 generation.
(i) In garden pea, round shape of seeds is dominant over wrinkled shape. A pea plant heterozygous for round shape of seed is selfed and 1600 seeds produced during the cross are subsequently germinated. How many seedlings would have non-parental phenotype?(a) 1600 (b) 1200 (c) 400 (d) 800 (ii) If 'A' represents the dominant gene and 'a' represents its recessive allele, which of the following would be the most likely result in the first generation offspring when Aa is crossed with aa ?
(a) All will exhibit dominant phenotype.
(b) All will exhibit recessive phenotype.
(c) Dominant and recessive phenotypes will be 50% each.
(d) Dominant phenotype will be 75%.
(iii) Which of the following crosses will give tall and dwarf pea plants in same proportions?A) 
B) 
c) 
D) 
(iv) What result Mendel would have got, if he self pollinated a homozygous tall F2 plant?
(a) TT and Tt
(b) All Tt
(c) All TT
(d) All tt
(v) In plant, tall phenotype is dominant over dwarf phenotype, and the alleles are designated as T and t, respectively. Upon crossing one tall and one dwarf plant, total 250 plants were obtained, out of which 124 displayed tall phenotype and rest were dwarf. Thus, the genotype of the parent plants were
(a) TT x TT
(b) TT x tt
(c) Tt x Tt
d) Tt x tt.(a) -
The cross that include the inheritance of two pairs of contrasting characters simultaneously is referred as dihybrid cross. Mendel chose pure breeding plants for yellow and green seeds and round and wrinkled shape of seeds. He cross pollinated the plant having yellow round seeds with plant having green wrinkled seeds. All the plants produced in F1 generation were having, yellow round seeds. The plants raised from these seeds were self pollinated, that resulted in production of plants having four phenotypically different types of seeds.
(i) When a cross is made between a yellow round seeded plant (YyRr) and a yellow wrinkled seeded plant (Yyrr), what is true regarding the proportions of phenotypes of the offsprings in F1 generation?Proportion of yellow wrinkled seeds Proportion of green wrinkled seeds (a) 3/8 1/8 (b) 2/8 1/8 (c) 1/8 3/8 (d) 2/8 2/8 (ii) How many types of gametes can be produced by YYrr?
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4 (iii) In Mendelian dihybrid cross, when heterozygous tall plant with green seeds are self crossed the progenies are
(a) TtYy, TtYY, TTYy (b) Ttyy, TTyy, ttyy (c) ttYy, ttyy (d) Ttyy, TTyy (iv) When round yellow seeded heterozygous pea plants are self fertilised, the frequency of occurrence of RrYY genotype among the offsprings is
(a) 9/16 (b) 3/16 (c) 2/16 (d) 1/16. (v) The percentage of yr gamete produced by YyRr parent will be
(a) 25% (b) 50% (c) 75% (d) 12.5%. (a) -
In human, the allele for brown eyes (B) is dominant over that for blue eyes (b). A brown eyed woman marries a blue eyed man, and they have six children. Four of the children are brown eyed and two of them are blue eyed.
(i) What is the genotype of blue eyed offspring?(a) BB (b) Bb (c) bb (d) Cannot be determined (ii) What is the woman's genotype?
(a) BB (b) Bb (c) bb (d) Cannot be determined (iii) The ovum, produced by the mother carries the gene regarding eye colour is
(a) BB (b) Bb (c) B or b (d) B only. (iv) The ratio of brown eyed children to blue eyed children in this family is 2 : 1, which deviates from typical phenotypic ratios for monohybrid inheritance. What might be the reason?
(a) Gametes carrying the brown eyed allele are more viable then those with the blue eyed allele.
(b) A different pattern of inheritance other than monohybrid inheritance is involved.
(c) Not all of their babies survived childbirth, thus causing a distortion in the actual ratio.
(d) The actual ratio differs from the expected ratio because the sample size is too small.
(v) What is the gene carried by of the man's sperm regarding the eye colour?(a) BB (b) Bb (c) b only (d) b or B. (a)
*****************************************
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Heredity and Evolution Case Study Questions With Solution 2021 Answer Keys
-
(i) (b) : In XX-XO type and XX-XY type of sex determining mechanisms, males produce two different types of gametes, either with or without X-chromosome (XO type), or some gametes with X-chromosome and some with Y-chromosome (XY type). Such type of sex determination mechanism is designated to be the example of male heterogamety. In both, females are homogametic and produce X type of gametes in both the cases and have XX genotype.
(ii) (b): The possibility of having a girl or boy child is equal i.e., 50%, as 50% male gametes are Y type and 50% are X type. Fusion of egg with X type sperm will produce a girl child.
(iii) (b): In humans, number of autosomes are 2n = 44 or 22 pairs regardless of the sex.
(iv) (a): In XX-XO type and XX-XY type of sex determining mechanisms, males produce two different types of gametes, either with or without X-chromosome (XO type), or some gametes with X-chromosome and some with Y-chromosome (XY type). Such type of sex determination mechanism is designated to be the example of male heterogamety. In both, females are homogametic and produce X type of gametes in both the cases and have XX genotype.
(v) (b): Male fruitfly is heterogametic whereas female fruitfly is homogametic. -
(i) (a): Characters studied by Mendel are as follows:
Trait studied Dominant Recessive 1 Plant height Tall (T) Dwarf (t) 2 Flower position Axial (A) Terminal (a) 3 Flower colour Violet (V) or (W) White (v) or (w) 4 Pod shape Full or Inflated (I) or (C) Constricted (i) or (c) 5 Pod colour Green (G) or (Y) Yellow (g) or (y)
6 Seed shape Round (R) or (W) Wrinkled (r) or (w) 7 Seed colour Yellow (Y) or (G) Green (y) or (g) (ii) (c)
Trait studied Dominant Recessive 1 Plant height Tall (T) Dwarf (t) 2 Flower position Axial (A) Terminal (a) 3 Flower colour Violet (V) or (W) White (v) or (w) 4 Pod shape Full or Inflated (I) or (C) Constricted (i) or (c) 5 Pod colour Green (G) or (Y) Yellow (g) or (y)
6 Seed shape Round (R) or (W) Wrinkled (r) or (w) 7 Seed colour Yellow (Y) or (G) Green (y) or (g) (iii) (d)
Trait studied Dominant Recessive 1 Plant height Tall (T) Dwarf (t) 2 Flower position Axial (A) Terminal (a) 3 Flower colour Violet (V) or (W) White (v) or (w) 4 Pod shape Full or Inflated (I) or (C) Constricted (i) or (c) 5 Pod colour Green (G) or (Y) Yellow (g) or (y)
6 Seed shape Round (R) or (W) Wrinkled (r) or (w) 7 Seed colour Yellow (Y) or (G) Green (y) or (g) (iv) (c)
Trait studied Dominant Recessive 1 Plant height Tall (T) Dwarf (t) 2 Flower position Axial (A) Terminal (a) 3 Flower colour Violet (V) or (W) White (v) or (w) 4 Pod shape Full or Inflated (I) or (C) Constricted (i) or (c) 5 Pod colour Green (G) or (Y) Yellow (g) or (y)
6 Seed shape Round (R) or (W) Wrinkled (r) or (w) 7 Seed colour Yellow (Y) or (G) Green (y) or (g) (v) (d)
Trait studied Dominant Recessive 1 Plant height Tall (T) Dwarf (t) 2 Flower position Axial (A) Terminal (a) 3 Flower colour Violet (V) or (W) White (v) or (w) 4 Pod shape Full or Inflated (I) or (C) Constricted (i) or (c) 5 Pod colour Green (G) or (Y) Yellow (g) or (y)
6 Seed shape Round (R) or (W) Wrinkled (r) or (w) 7 Seed colour Yellow (Y) or (G) Green (y) or (g) -
(i) (c): Since this pea plant is heterozygous for round shape, its genotype would be Rr.
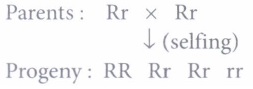
Phenotypically, the ratio will be 3 : 1, i.e., only rr seedlings will show wrinkled seed phenotype, rest will show round seed shape.
1200 \(\Rightarrow\) Round shape (RR, Rr)
400 \(\Rightarrow\) Wrinkled (rr)
(ii) (c): 'A'. represents the dominant gene and 'a' represents its recessive allele. The most likely result in the first generation offspring when Aa is crossed with aa is:

Hence, Aa: aa
1 : 1
(iii) (b): This is an example of a test cross in which a cross is made between heterozygous tall and homozygous dwarf individuals and tall and dwarf plants are obtained in same proportion.
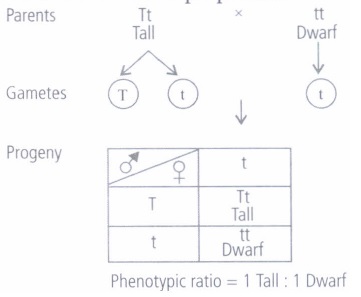
(iv) (c): Self pollination of homozygous tall F2 plant (TT) will give rise to all individuals of genotype TT.
(v) (d) -
(i) (a): A cross between yellow round seeds (YyRr) and yellow wrinkled seeds (Yyrr) will be:
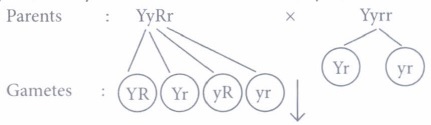
Progenies :
Yr yr YR YYRr
Yellow roundYyRr
Yellow roundYr YYrr
Yellow wrinkledYy rr
Yellow wrinkledyR YyRr
Yellow roundyy Rr
Green roundyr Yy rr
Yellow wrinkledyyrr
Green wrinkledPhenotypic ratio is:
Yellow round seeds : Yellow wrinkled seeds: Green round seeds : Green wrinkled seeds: 3: 3: 1: 1 3/8, 3/8, 1/8, 1/8 (ii) (a)
(iii) (b)
(iv) (c): Round yellow heterozygous pea plant may be represented by genotype RrYy. On selfing such plants following results will be obtained.
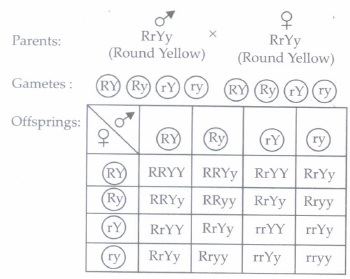
Hence, total 16 genotypes will be obtained in the next generation out of which the frequency of occurrence of RrYY genotype is 2, as illustrated by the given Punnett square chart.
(v) (a): Gametes produced by YyRr parent would be 25% YR, 25% yR, 25% Yr and 25% yr. -
(i) (c)
(ii) (b): According to the given passage some children show recessive trait, i.e., homozygous. So, the woman must be heterozygous.
(iii) (c): Human ova are haploid, hence they only contain one copy of each gene. Since the woman has a Bb genotype her ova would contain either B or b allele.
(iv) (d): According to the given passage, within a single family, the sample size of offspring in each generation is very small. Hence, the actual phenotypic and genotypic ratios often deviate from expected ratios. It is only when sample sizes of offspring is large that actual ratios approach theoretical or expected ratios more closely.
(v) (c): Human sperm is haploid, hence they only contain one copy of each gene. Since the man has a bb genotype, his sperm would contain allele b only.

























