CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject HOT Questions 3 Mark Questions With Solution 2021
By QB365 on 29 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the HOT Question Papers for Class 10 Science, and also provide the detail solution for each and every HOT Questions. HOT Questions will help to get more idea about question pattern in every exams and also will help to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject HOT Questions 3 Mark Questions With Solution 2021
10th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Science
-
State one advantage and one disadvantage of corrosion
(a) -
Ahmad took a magnesium ribbon (cleaned) and burned it on a flame. The white powder formed was taken in a test tube and water was added to it. He then tested the solution formed with red and blue litmus paper. What change was seen and why?
(a) -
Arnav took magnesium and reacted it with dil. HCI to record the observation. Then Deepak took the same piece of magnesium and reacted it with conc. HNO3 and dil. H2SO4 but did not see a reaction. Explain this behavior.
(a) -
Four beakers with chemicals are shown below. Name the beakers which will show exothermic reaction and those which will be endothermic in nature.
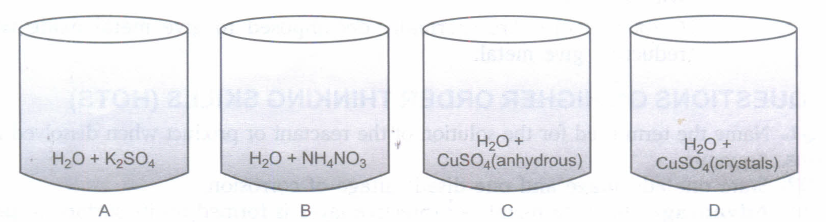 (a)
(a) -
Blue crystals of copper sulphate on heating in a dry test tube become colourless. Give reasons.
(a) -
FeSO4.7H2O, green colour crystals on heating, changes colour. Why?
(a) -
Study the given diagram and answer the questions.
Creation of diversity over succeeding generations. The original organism at the top will give rise to, say, two individuals, similar in body design, but with subtle differences. Each of them, in turn, will give rise to two individuals in the next generation. Each of the four individuals in the bottom row will be different from each other. While some of these differences will be unique, others will be inherited
from their respective parents, who were different from each other.
(i) Why do we find all bottom row individuals different from each other?
(ii) What is similar in all the individuals(a) -
Male individual has 23 pairs of chromosomes, female individual has 23 pairs of chromosomes Then why don't an offspring have 46 pairs of chromosomes which is obtained by the fusion of these two eggs.
(a) -
The magnification produced by a plane mirror is +1. What does it mean?
(a) -
Define the following.
(a) What is ray? (b) What is beam?
(c) What is reflection of light? (d) What is reflector?
(e) What is focal length? (f) What is principal focus?
(g) What is refraction? (h) What is optically rare medium?
(i) What is optically denser medium? (j) What is power?
(k) What is 1 dioptre?(a)(a) It is the path of light.
(b) Group of parallel light rays emitted by the source of light.
(Il) Bouncing back of light after striking any surface.
(d) The surface which reflects the light.
(e) The distance between the pole and the principal focus of the spherical mirror.
(f) A point of the principal axis where the rays of light parallel to principal axis meet.
(g) Bending of light ray when it travels from one medium to another.
(h) When the speed of light is more as compared to other medium.
(i) When the speed of light is less as compared to another medium.
(j) The degree of convergence or divergence of light rays achieved by a lens is expressed in terms of its power
(k) It is the power of lens whose focal length is 1 m.
*****************************************
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject HOT Questions 3 Mark Questions With Solution 2021 Answer Keys
-
Advantage: In some metals a protective layer is formed on its surface to prevent it from further corrosion.
E.g., aluminium (Al) forms a layer of Aluminium oxide (Al2O3) by corrosion. The layer prevents further corrosion.
Disadvantage: Loss of the metal. -
Red litmus turned blue.
Blue litmus remained blue.
This is because the magnesium ribbon on burning in air, forms the white magnesium oxide. When this is dissolved in water, it forms magnesium hydroxide, which is basic in nature. -
Arnav had already reacted Mg with dil. HCI to form MgCl2 and gas. The piece of metal that Deepak used was not magnesium but magnesium chloride (MgCl2), hence it did not react with the given acids.
-
Exothermic reaction: Beaker A, Beaker B.
Endothermic reaction: Beaker C, Beaker D. -
The blue colour of copper sulphate is due to its crystalline nature which holds 5 water molecules (water of crystallization). On heating, the water molecules disappear and anhydrous copper sulphate (white in colour) is left back.
-
The green colour of ferrous sulphate crystals is due to the presence of 7 water molecules (water of crystallization). :It loses the water of crystallization on heating, thus leading to change in colour.
-
(i) The differences can be due to inheritance of acquired traits. When respective parents are different from each other the variation occurs due to inheritance.
(ii) Body design. -
Male individual has 23 pairs of chromosomes but the gamete that is formed by the meiotic cell division contain only half the number of chromosomes i.e., 23 chromosomes in male sperm and 23 chromosomes in female egg. It is the fusion of this sperm and egg which leads to an offspring with 23 pairs of chromosomes.
-
If magnification is 1, the image size is same as that of object size.
Since, magnification is positive, the image is erect and virtual. -
(a) It is the path of light.
(b) Group of parallel light rays emitted by the source of light.
(c) Bouncing back of light after striking any surface.
(d) The surface which reflects the light.
(e) The distance between the pole and the principal focus of the spherical mirror.
(f) A point of the principal axis where the rays of light parallel to principal axis meet.
(g) Bending of light ray when it travels from one medium to another.
(h) When the speed of light is more as compared to other medium.
(i) When the speed of light is less as compared to another medium.
(j) The degree of convergence or divergence of light rays achieved by a lens is expressed in terms of its power
(k) It is the power of lens whose focal length is 1 m.(a) It is the path of light.
(b) Group of parallel light rays emitted by the source of light.
(c) Bouncing back of light after striking any surface.
(d) The surface which reflects the light.
(e) The distance between the pole and the principal focus of the spherical mirror.
(f) A point of the principal axis where the rays of light parallel to principal axis meet.
(g) Bending of light ray when it travels from one medium to another.
(h) When the speed of light is more as compared to other medium.
(i) When the speed of light is less as compared to another medium.
(j) The degree of convergence or divergence of light rays achieved by a lens is expressed in terms of its power
(k) It is the power of lens whose focal length is 1 m.

























