CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject How do Organisms Reproduce Chapter Case Study Questions With Solution 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject How do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Questions With Solution 2021
10th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Science
-
There are two organisms X and Y that produce new offspring from single parent only.Organisms X when reaches its maximum growth, divides its body into two new organisms.
The parent organism does not exist any more and two new daughter organisms grow fully and divide again. Organism Y form a small outgrowth on its body called bud which detaches and develops into new organism .
Read the above paragraph and answer the questions that follow.
(I) Select the option that correctly identifies organisms X and Y.X Y (a) Amoeba Yeast (b) Paramecium Hydra (c) Leishmania Sycon (d) All of these (ii) Select the correct statement.
(a) Organism X reproduces asexually whereas organism Y reproduces sexually
(b) Organism X must be multicellular whereas organism Y should be unicellular
(c) Both organisms X and Y reproduce asexually
(d) Both organisms X and Yare always multicellular organisms
(iii) Identify the mode of reproduction in organisms X and Y.(a) X - Multiple fission
Y - Binary fission(b) X - Binary fission
Y - Budding(c) X - Regeneration
Y - Fragmentation(d) X - Fragmentation
Y - Multiple fission(iv) Which of the following is incorrect?
(a) Plasmodium reproduces by the same method as is adopted by organism X.
(b) Organism X could be any multicellular plant like Riccia, Sphagnum, etc.
(c) If organism Y is Hydra, then it may also reproduce through regeneration.
(d) Both (a) and (b)
(v) Which organism reproduces by the method shown in the given figure?
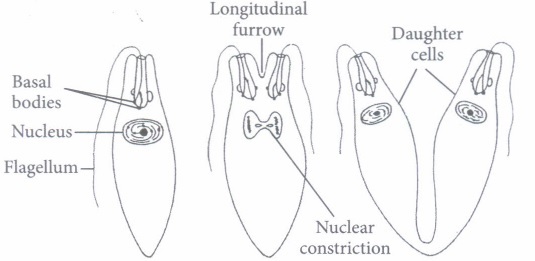
(a) Planaria (b) Amoeba (c) Euglena (d) Paramecium (a) -
Spore formation, method of asexual reproduction is used by unicellular as well as multicellular organisms.Spores are microscopic units which could be air borne or are present in soil, etc.
(i) A slice of bread kept in open for sometime shows growing white cottony mass which later turns black. This happens because
(a) bacterial spores present in air germinate on the surface of bread slice
(b) fungal spores present in air germinate on the surface of bread slice
(c) protozoan microbes start feeding on bread slice
(d) none ef these.
(ii) Spore formation can be seen in(a) Mucor (b) sweat potato (c) Spirogyra (d) all of these (iii) Bulb like structure at top of erect hyphae where spores are produced is
(a) sporangiophore (b) apophysis (c) columella (d) sporangia. (iv) Select the incorrect statement.
(a) Spores can be produced endogenously or exogenously in an organism.
(b) Spores can be air borne or soil borne.
(c) Bacteria produce only exospores.
(d) Rhizopus bears spores in special structures called sporangium.
(v) Observe the given figure showing spores formation in Rhizopus and select the option which is correctly labelled.
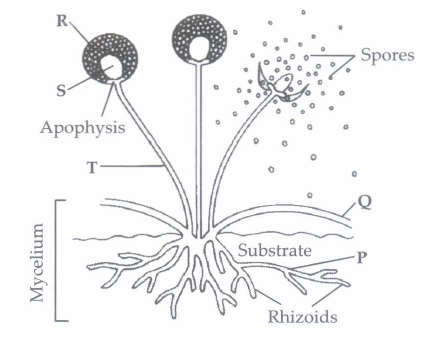
(a) P-Stolon, S-Columella, T-Sporangiophore
(b) Q-Stolon, P-Hypha, S-Sporangium
(c) R-Sporangium, S-Apophysis, T-Sporangiophore
(d) Q-Stolon, R-Sporangium, S-Colume!la(a) -
Radhika collected some pond water which was dark green in colour in a test tube. She took out green coloured mass from it and separated its filaments by using needles. She broke some filaments into small fragments and put them in a Petri dish containing clean water. She observed that after few days the small fragments gave rise to complete filaments.
(i) What do you think the mass of green filament was?
(a) It was a mass of Spirogyra filament
(b) It was a colony of Volvox algae
(c) It was kelp, i.e., large brown algae
(d) It was a mass of fungal filaments or hyphae.
(ii) The small fragment gave rise to new filament. What does it indicate?
(a) Spirogyra reproduces asexually through fragmentation
(b) Spirogyra reproduces asexually through vegetative propagation
(c) Spirogyra reproduces asexually through budding
(d) Spirogyra reproduces asexually through fission
(iii) Organism which reproduces in similar way as Spirogyra is(a) yeast (b) sea anemone (c) Entamoeba (d) all of these. (iv) Select the correct statement.
(a) Only multicellular organisms can undergo fragmentation
(b) Both unicellular and multicellular organisms can undergo fragmentation
(c) Fragmentation is sexual mode of reproduction
(d) Fragmentation is found only in algae.
(v) Which among the given organisms do not reproduce by fragmentation?(a) Riccia (b) Selaginella (c) Aurelia (d) Marchantia (a) -
Preeti is very fond of gardening. She has different flowering plants in her garden. One day few naughty children entered her garden and plucked many leaves of Bryophyllum plant and threw them here and there in the garden. After few days, Preeti observed that new Bryophyllum plants were coming out from the leaves which fell on the ground.
(i) What does the incidence cited in the paragraph indicate?
(a) Bryophyllum leaves have special buds that germinate to give rise to new plant
(b) Bryophyllum can propagate vegetatively through leaves
(c) Bryophyllum is a flowering plant that reproduces only asexually
(d) Both (a) and (b)
(ii) Which of the following plants can propagate vegetatively through leaves like Bryophyllum?(a) Guava (b) Begonia (c) Ginger (d) Mint (iii) Do you think any other vegetative part of Bryophyllum can help in propagation? If yes, then which part?
(a) Roots (b) Stems (c) Flowers (d) Fruits (iv) Which of the following plants is artificially propagated (vegetatively) by stem cuttings in horticultural practices?
(a) Potato (b) Snake plant (c) Rose (d) Water hyacinth (v) In which of the following pairs both the plants can be vegetatively propagated by leaf pieces?
(a) Adiantum and Kalanchoe (b) Chrysanthemum and Agave (c) Agave and Dioscorea (d) Bryophyllum and Asparagus (a) -
Horticultural methods of vegetative propagation multiply desired varieties of plants quickly from parts of their somatic body. A horticulturist used stem cutting of plant X to propagate it in a short span of time. For plant Y, he pulled a branch of towards ground and covered it with soil leaving the tip of branch exposed. He later on cut the branch from parent plant. The former developed into new plant. He propagated plant Z through underground stems called tubers. Identify the propagation methods used by horticulturist and answer the following questions.
(i) What could be plants X, Y and Z?X Y Z (a) Bougainvillea Jasmine Potato (b) Sugarcane Ginger Rose (c) Begonia Banana Chrysanthemum (d) Guava Onion Cactus (ii) Select the propagation methods in plants X, Y and Z.
(a) X - root tubers, Y - stem cutting, Z - stem tubers
(b) X - stem cutting, Y - layering, Z - underground stem
(c) X -Iayering, Y - underground stem, Z - underground roots
(d) X - grafting, Y - layering, Z - root tubers
(iii) Select the correct statement for plant Z if it is potato.
(a) Each tuber has many buds called ears
(b) It is necessary to plant the whole potato tuber in the soil to produce new potato plants
(c) Vegetative propagation of potato plants by tubers is much faster than production of potatoes by seeds
(d) All of these.
(iv) Select the plant which propagates by the same method adopted by gardener for plant Y, but naturally it propagates by stolons(a) Strawberry (b) Adiantum (c) Tulsi (d) Both (a) and (b) (v) Identify the given vegetative propagule.
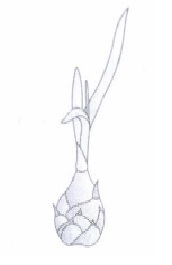
(a) Bulb (b) Runner (c) Rhizome (d) Bulbil (a)
*****************************************
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject How do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Questions With Solution 2021 Answer Keys
-
(i) (d): According to the given passage, organisms X and Y reproduce by binary fission and budding respectively. Amoeba, Paramecium and Leishmania reproduce by binary fission whereas Hydra, Sycon and yeast reproduce by budding.
(ii) (c): Both organisms X and Y are reproducing asexually i.e., by binary fission and budding respectively.Unicellular organisms can undergo binary fission whereas both unicellular (yeast) and multicellular (Hydra) organisms reproduce by budding.
(iii) (b)
(iv) (d): Plasmodium reproduces by multiple fission. Multicellular plants do not reproduce through binary fission.
(v) (c): Euglena reproduces by longitudinal binary fission. -
(i) (b): The tiny spores of bread mould (Rhizopus) are always present in air. On coming in contact with moist surface of bread slice they settle on it and germinate to form new fungal hyphae which first look like white cottony mass and later turns black.
(ii) (a): Mucor (fungus) reproduces asexually through spore formation.
(iii) (d)
(iv) (c): Bacteria produce endospore which is a dormant and tough structure that enables bacteria to remain dormant for extended periods under unfavorable conditions.
(v) (d) -
(i) (a): Spirogyra is a green filamentous alga that is found in huge numbers in ponds and lakes.
(ii) (a): When mature Spirogyra breaks into two or more pieces, then each fragment develops into an individual.
(iii) (b)
(iv) (a): Only multicellular organisms having simple body organisation can undergo fragmentation. It is asexual mode of reproduction.
(v) (c) -
(i) (d): Bryophyllum propagates vegetatively though buds present on the margins of its leaves.
(ii) (b): Begonia propagates vegetatively through its leaves.
(iii) (b): If a broken piece of stem of Bryophyllum is planted in soil, it develops into a new Bryophyllum plant.
(iv) (c): Rose plants are artificially propagated by stem cuttings. A piece of stem having bud is cut and buried in soil. After few days it develops roots and later on grows into new rose plant.
(v) (a) -
(i) (a)
(ii) (b)
(iii) (c)
(iv) (a): Many plants like strawberry and raspberry are propagated by the natural layering methods because these plants have runners (soft horizontal stem running above the ground). Whereas the ends of such runners touch the ground new plants are formed.
(v) (d)

























