CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Life Processes Chapter Case Study Questions 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Life Processes Case Study Questions 2021
10th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Science
-
Digestion is a catabolic process in which complex and large components of food are broken down into their respective simpler and smaller forms with the help of various hydrolytic enzymes. In human, the process of intake of essential nutrients in the form of food takes place through an entire system known as digestive system. The digestive system in human includes alimentary canal and its associated digestive glands.
(i) Identify the cells whose secretion protects the lining of gastro-intestinal tract from various enzymes.(a) Duodenal cells (b) Chief cells (c) Goblet cells (d) Oxyntic cells (ii) Digestion of proteins is incomplete in the absence of enterokinase, because
(a) trypsinogen is not converted into trypsin
(b) pepsinogen is not converted into pepsin
(c) prorennin is not converted into rennin
(d) chymotrypsinogen is not converted into chymotrypsin
(iii) Match the column I with column II and column III. Choose the correct option.Column I Column II Column III (Substrate) (Enzyme) (Product) 1. Lactose A. Lipase I. Galactose 2. Fatty acid B. Trypsin II. Maltose 3. Starch C. Lactase III. Glycerol 4. Proteins D. Amylase IV. Dipeptides (a) 1- A-I; 2-C-II; 3-B-III; 4-D-IV (b) I-D-I; 2-A-II; 3-B-III; 4-C-IV (c) l-C-I; 2-A-III; 3-D-II; 4-B-IV (d) l-C-I; 2-A-II; 3-D-III; 4-B-IV (iv) A and B in the given graph are the action spectra of the two enzymes. The two enzymes are
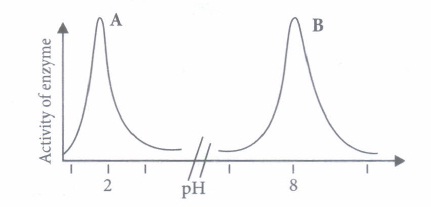
(a) A: amylase B: trypsin (b) A: pepsin B: trypsin (c) A: chymotrypsin B: rennin (d) A: lactate dehydrogenase B: amylase. (v) If the inner surface of the ileum in the human small intestine was smooth, rather than being folded and subdivided into villi, which of the following statements would be true?
(a) The rate of absorption of digested food molecules would be higher, because the digested food would pass more easily through the digestive tract.
(b) Digestion would not be as effective, because there would be fewer cells secreting trypsin (a proteindigesting enzyme).
(c) Humans would have needed to evolve a much longer small intestine to absorb sufficient nutrients from their food.
(d) Humans would not be able to survive, because the digestive tract would be more susceptible to damage.(a) -
Respiration is an energy releasing enzymatically controlled process which involves a stepwise oxidative breakdown of food substances inside living cells. The oxidative breakdown of respiratory substrates with the help of atmospheric oxygen is aerobic respiration. Glucose is completely broken down into CO2 and H2O by this process of oxidation and large amount of energy is produced.
(i) Site of Krebs' cycle is(a) peroxisome (b) cytoplasm (c) mitochondria (d) none of these. (ii) The pathway of respiration common in all living organisms is X ;it occurs in the Y and the products formed are two molecules of Z.
Identify X, Y and Z in the above paragraph and select the correct answer.X Y Z (a) glycolysis mitochondrion pyruvic acid (b) glycolysis cytoplasm pyruvic acid (c) Krebs' cycle cytoplasm acetyl CoA (d) Krebs' cycle mitochondrion acetyl CoA (iii) Number of oxygen molecules utilised in glycolysis is ____________.
(a) 0 (b) 2 (c) 4 (d) 6 (iv) How many ATP molecules could maximally be generated from one molecule of glucose, if the complete oxidation of one molecule of glucose to CO2 and H2O yields 686 kcal and the useful chemical energy available in the high energy phosphate bond of one molecule of ATP is 12 kcal?
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 30 (d) 57 (v) The end product of aerobic respiration is
(a) NADH (b) oxygen (c) ADP (d) CO2 + ATP + H2O (a) -
Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms obtain readymade organic food from outside sources. The organisms that depend upon outside sources for obtaining organic nutrients are called heterotrophs. Heterotrophic nutrition is of three types: saprophytic, parasitic and holozoic nutrition.
(i) In which of the following groups of organisms food material is broken outside the body and absorbed?(a) Mushroom, green plants, Amoeba (b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould (c) Paramecium, Amoeba, Cuscuta (d) Cuscuta, lice, tapeworm (ii) Which of the following is a parasite?
(a) Yeast (b) Taenia (c) Amoeba (d) Earthworm (iii) Which of the following is an example of saprotroph?
(a) Grass (b) Mushroom (c) Amoeba (d) Paramecium (iv) Heterotrophic nutrition involves
(a) production of simple sugar from inorganic compounds
(b) utilisation of chemical energy to prepare food
(c) utilisation of energy obtained by plants
(d) all of these.(v) In Paramecium, food enters the body through
(a) mouth (b) pseudopodia (c) cilia (d) cytostome (a) -
The small intestine is a tubular structure within the abdominal cavity that carries the food in continuation with the stomach up to the colon from where the large intestine carries it to the rectum and out of the body. The main function of this organ is to aid in digestion. All nutrients are usually absorbed into blood across the mucosa of the small intestine. In addition, the small intestine absorbs water and electrolytes, thus playing critical role in maintenance of body water and acid-base balance.
(i) Which of the following is incorrect regarding intestinal villi?
(a) They possess microvilli.
(b) They increase the surface area.
(c) They are supplied with capillaries and the lacteal vessels.
(d) They only participate in digestion of fats
(ii) Which enzymes are likely to act on the baked potatoes eaten by a man, starting from the mouth as they move down the alimentary canal?
(a) Pancreatic amylase \(\rightarrow\) Salivary amylase \(\rightarrow\) Lipases
(b) Disaccharidase like maltase \(\rightarrow\) Lipases \(\rightarrow\) Nucleases
(c) Salivary amylase \(\rightarrow\) Pancreatic amylase \(\rightarrow\) Disaccharidases
(d) Salivary maltase \(\rightarrow\) Carboxypeptidase \(\rightarrow\) Trypsinogen
(iii) After surgical removal of an infected gall bladder, a person must be especially careful to restrict dietary intake of
(a) starch (b) protein (c) sugar (d) fat.
(iv) The given flow chart shows the fate of carbohydrates during digestion in the human alimentary canal. Identify the enzymes acting at stages indicated as A, B, C and D and select the correct option.
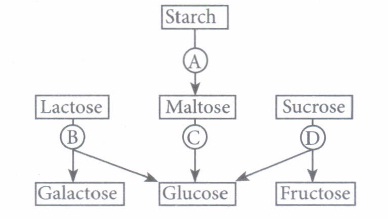
(a) A - Amylase, B - Maltase, C - Lactase, D - Invertase
(b) A - Amylase, B - Maltase, C - Invertase, D - Lactase
(c) A - Amylase, B - Invertase, C - Maltase, D - Lactase
(d) A - Amylase, B - Lactase, C - Maltase, D - Invertase
(v) The given diagram represents a section of small intestinal mucosa. Identify A, Band C.(a) A-Villi, B-Lacteal, C-Capillaries (b) A-Lacteal, B-Villi, C-Capillaries (c) A-Villi, B-Lacteal, C-Crypts (d) A-Crypts, B-Lacteal, C-Capillaries (a) -
The food which is prepared by the process of photosynthesis in the leaves of a plant has to be transported to other parts like stem, roots, branches, etc. Therefore this food is transported to other parts of the plant through phloem.
(i) A few drops of sap were collected by cutting across a plant stem by a suitable method. The sap was tested chemically. Which one of the following test results indicates that it is phloem sap?(a) Acidic (b) Alkaline (c) Low refractive index (d) Absence of sugar (ii) What is the direction of movement of sugars in phloem?
(a) Bi-directional (b) Non-directional (c) Upward (d) Downward (iii) The given diagram shows a potato plant forming new tubers. Which route would be taken by most of the food at this time?
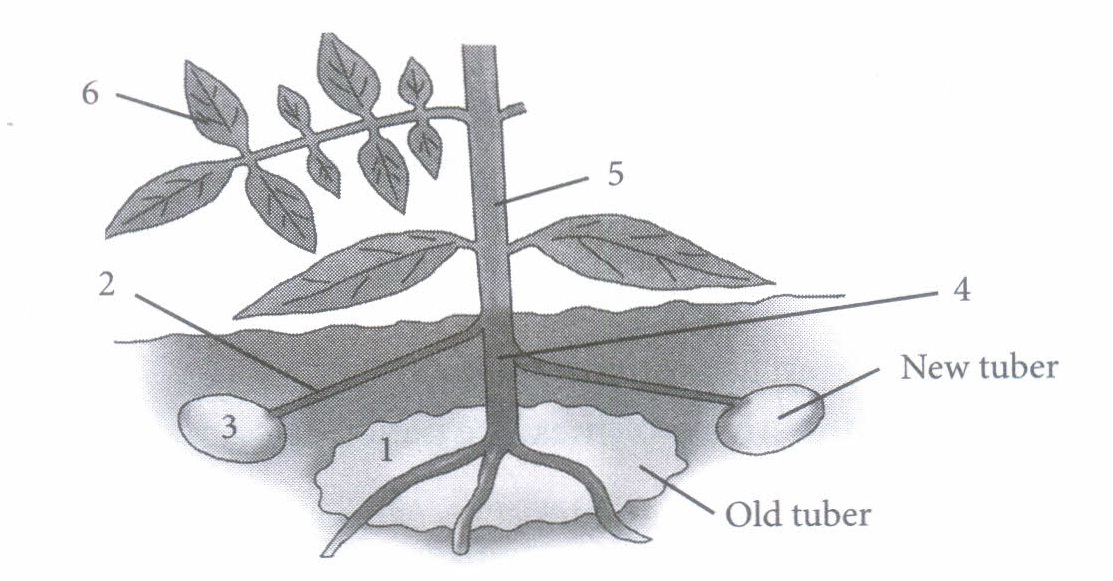
\(\text { (a) } 1 \rightarrow 4 \rightarrow 2 \rightarrow 3\) \(\text { (b) } 6 \rightarrow 5 \rightarrow 2 \rightarrow 3\) \(\text { (c) } 1 \rightarrow 4 \rightarrow 5 \rightarrow 6\) \(\text { (d) } 6 \rightarrow 5 \rightarrow 4 \rightarrow 1\) (iv) A girdled plant (upto bast) may survive for some time but it will eventually die, because
(a) water will not move downwards
(b) water will not move upwards
(c) sugars and other organic materials will not move downwards
(d) sugars and other organic materials will not move upwards
(v) Phloem sap is mainly made of(a) water and sucrose (b) water and minerals (c) oligosaccharides and hormones (d) sucrose only (a)
*****************************************
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Life Processes Case Study Questions 2021 Answer Keys
-
(i) (c): Goblet cells or mucous cells are present throughout the epithelium of gastric glands and secrete mucus, which protects gastro-intestinallining from enzymatic action.
(ii) (a)
(iii) (c)
(iv) (b): Pepsin and trypsin both are protein digesting enzymes, but they work at different locations and different pH in alimentary canal. Pepsin, which is most active at pH of 1.5 to 2.5, is an important peptic enzyme in stomach. Trypsin, which is a pancreatic protease, acts mostly in upper small intestine (duodenum and jejunum), works at an optimum pH of 7.5 - 8.5.
(v) (c): The absorptive surface of small intestinal mucosa have many folds, which increase its surface area. Also located on epithelial surface of small intestine are millions of small villi. Intestinal epithelial cell on each villus is characterised by a brush- border which further increases the surface area. Thus, to compensate for this and to have effective absorption of nutrients, intestine would need to be much longer in length. -
(i) Krebs' cycle takes place in mitochondrial matrix.
(ii) (b)
(iii) (a) : Glycolysis does not utilise any oxygen as it is an anaerobic process.
(iv) (d)
(v) (d): In aerobic respiration, glucose is completely broken down to CO2 and H2O with the production of a large amount of energy (ATP). -
(i) (b): Yeast, mushroom and bread mould have a saprophytic mode of nutrition which is chemoheterotrophic in nature. They breakdown complex organic substances by secreting digestive enzyme outside their body and absorb simple molecules as nutrients.
(ii) (b)
(iii) (b): Yeast, mushroom and bread mould have a saprophytic mode of nutrition which is chemoheterotrophic in nature. They breakdown complex organic substances by secreting digestive enzyme outside their body and absorb simple molecules as nutrients.
(iv) (c): Heterotrophic nutrition is mode of nutrition in which an organism depends on other living organisms for food.
(v) (a) -
(i) (d)
(ii) (c): Baked potatoes consist of starch which is a polysaccharide. In oral cavity, the food is mixed with saliva that contains an enzyme salivary amylase which converts starch into maltose, isomaltose and small dextrins.
The pancreatic juice (present in small intestine) contains pancreatic amylase which converts starch into maltose, isomaltose and \(\alpha\)-dextrins.
\(\text { Starch } \frac{\text { Pancreatic }}{\alpha \text { -amylase }}>\text { Maltose }+\text { Isomaltose }+\alpha \text { -Dextrins }\)
Further, disaccharidases such as maltase (present in intestinal juice in small intestine) break down disaccharides such as maltose into monosaccharides or simpler sugars.
(iii) (d): After removal of gall bladder, bile could no longer to be stored and hence fat metabolism would be affected. Therefore, fat intake should be restricted.
(iv) (d)
(v) (c) -
(i) (b)
(ii) (a): Food is transported by vascular tissue phloem from source to sink. Source is a part that synthesise food and sink is a part that stores or needs the food. Since source and sink can be reversed depending on plant's need, therefore direction of movement of sugar in phloem can be bidirectional, i.e., both upwards or downwards.
(iii) (b)
(iv) (c)

























