CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Life Processes Chapter Case Study Questions With Solution 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Life Processes Case Study Questions With Solution 2021
10th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Science
-
In fermentation, the incomplete oxidation of glucose achieved under anaerobic conditions by sets of reactions where pyruvic acid is converted to CO2 and ethanol. The enzymes, pyruvic acid decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase catalyse these reactions.
(i) The given experimental set-up demonstrates
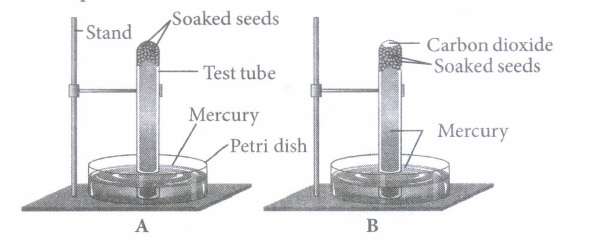
(a) photosynthesis (b) aerobic respiration (c) anaerobic respiration (d) ascent of sap (ii) Fermentation is represented by the equation
\(\text { (a) } \mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{12} \mathrm{O}_{6}+6 \mathrm{O}_{2} \rightarrow 6 \mathrm{CO}_{2}+6 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+686 \mathrm{kcal}\)
\(\text { (b) } \mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{12} \mathrm{O}_{6} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{C}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{5} \mathrm{OH}+2 \mathrm{CO}_{2}+59 \mathrm{kcal}\)
\(\text { (c) } 6 \mathrm{CO}_{2}+12 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \frac{\text { Light }}{\text { Chlorophyll }}>\mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{12} \mathrm{O}_{6}+6 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+6 \mathrm{O}_{2}\)
\(\text { (d) } 6 \mathrm{CO}_{2}+6 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{12} \mathrm{O}_{6}+6 \mathrm{O}_{2} \text { . }\)
(iii) A test tube containing molasses solution and yeast is kept in a warm place overnight. The gas collected from this mixture(a) extinguishes the flame (b) bursts into flame when ignited (c) turns lime water milky (d) both (a) and (c) (iv) Ethyl alcohol fermentation occurs in
(a) Lactobacillus (b) muscles of humans (c) Yeast (d) all of these (v) Though vertebrates are aerobes, but their (i) show anaerobic respiration during (ii) During this (iii) of skeletal muscle fibres is broken down-to release lactic acid and energy. Lactic acid, if accumulates causes muscle fatigue.
Fill up the blanks in the above paragraph and select the correct option(i) (ii) (iii) (a) skeletal muscles heavy exercise glucose (d) skeletal muscles mild exercise glycogen (c) skeletal muscles heavy exercise glycogen (d) cardiac muscles heavy exercise glycogen (a) -
Double circulation is a type of circulating system in which the blood passes through the heart twice before completing a full circuit of the body. Blood is pumped from the heart to the lungs and returns to the heart before being distributed to other organs and tissues of the body.
(i) The figure shows blood circulation in humans with labels A to D. Select the option which gives correct identification of label and functions of the part.
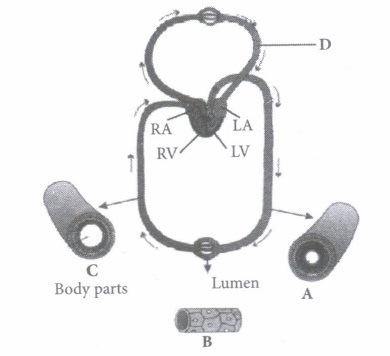
(a) B - Capillary- Thin without muscle layer and wall two cell layers thick
(b) C - Vein-Thin walled and blood flows in jerks/spurts
(c) D - Pulmonary vein-Takes oxygenated blood to heart, PO2 = 95 mm Hg
(d) A - Artery-Thick walled and blood flows evenly
(ii) Incomplete double circulation is seen in(a) mammals (b) pisces (c) aves (d) amphibians. (iii) Which of the following animals shows double circulatory pathway?
(a) Snake (b) Frog (c) Eel (d) Whale (iv) The given figure is of circulatory system. Identify the labelled parts (A-D) from the list (I-VII).
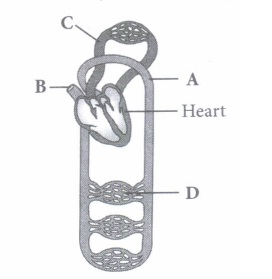
(I) Pulmonary circulation (II) Systemic circulation (III) Superior vena cava (IV) Inferior vena cava
(V) Aorta (VI) Veins and venules (VII)Arterioles and capillaries(a) A-(V), B-(lII), C-(I), D-(VII) (b) A-(VII), B-(IV), C-(I), D-(VI) (c) A-(V), B-(III), C-(lI), D-(VII) (d) A-(VII), B-(V), C- (I), D-(VI) (v) Select the option which properly represents pulmonary circulation in humans.
\(\text { (a) Left auricle } \frac{\text { Deoxygenated }}{\text { blood }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Lungs } \frac{\text { Oxygenated }}{\text { blood }} \text { Right ventricle }\)
\(\text { (b) Left auricle } \frac{\text { Oxygenated }}{\text { blood }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Lungs } \frac{\text { Deoxygenated }}{\text { blood }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Right ventricle }\)
\(\text { (c) Right ventricle } \frac{\text { Deoxygenated }}{\text { blood }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Lungs } \frac{\text { Oxygenated }}{\text { blood }} \rightarrow \text { Left auricle }\)
\(\text { (d) Right ventricle } \frac{\text { Oxygenated }}{\text { blood }}>\text { Lungs } \frac{\text { Deoxygenated }}{\text { blood }} \gg \text { Left auricle }\)(a) -
Transpiration is the evaporative loss of water by plants. It occurs mainly through the stoma in the leaves. Besides the loss of water vapour in transpiration, exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the leaf also occurs through pores called stomata. Normally stomata remain open in the day time and close during the night
(i) Which of the following will not directly affect transpiration?(a) Temperature (b) Light (c) Wind speed (d) Chlorophyll content of leaves (ii) Water vapour comes out from the plant leaf through the stomatal opening. Through the same stomatal opening, carbon dioxide diffuses into the plant during photosynthesis. Reason out the above statements . using one of following options.
(a) The above processes happen only during night time.
(b) One process occurs during day time and the other at night.
(c) Both processes cannot happen Simultaneously.
(d) Both processes can happen together at day time.
(iii) Which of the following statements is not true for stomatal apparatus?
(a) Guard cells invariably possess chloroplasts and mitochondria.
(b) Guard cells are always surrounded by subsidiary cells.
(c) Stomata are involved in gaseous exchange.
(d) Inner wall of guard cells are thick.
(iv) Which of the following is not a purpose of transpiration?
(a) Helps in absorption and transport in plants
(b) Prevents loss of water
(c) Maintains shape and structure of plants by keeping the cells turgid
(d) Supplies water for photosynthesis
(v) Refer to the given graphs regarding factors affecting transpiration rate and select the correct option.
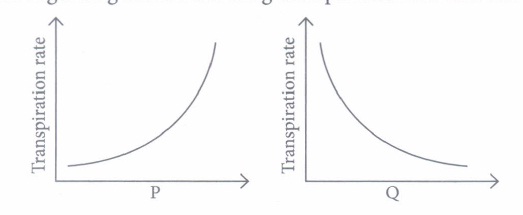
(a) P-Atmospheric temperature; Q-Atmospheric pressure
(b) P-Relative humidity; Q-Atmospheric temperature
(c) P-Air movement; Q-Light
(d) P-Atmospheric pressure; Q-Relative humidity(a) -
We need energy to perform various activities. This energy is derived from the catabolism of various components of food, e.g., proteins, carbohydrates, fats, etc. Oxygen is required for catabolic processes and carbon dioxide is released in the process. So, the body requires a continuous exchange of gases, oxygen from the atmosphere is taken inside and carbon dioxide produced is given out. In human beings, respiratory pigment called haemoglobin present in RBCs has very high affinity for oxygen. In tissues, exchange of gases occurs between oxygenated blood and tissue cells.
(i) People living at sea level have around 5 million RBCs per cubic millimetre of their blood whereas those living at an altitude of 5400 metres have around 8 million. This is because at high altitude
(a) people eat more nutritive food, therefore more RBCs are formed
(b) people get pollution-free air to breathe and more oxygen is available
(c) atmospheric 02 levelisless and hence more RBCs are needed to absorb the required amount of 02 to survive
(d) there is more UV radiation which enhances RBC production.
(ii) The given graph illustrates the changes in lung volume during the process of breathing .
The change from II to III indicates the(a) movement of diaphragm away from the lungs (b) expansion of the thoracic cavity (c) movement of air out of the lungs (d) expansion of ribs. (iii) Which one of the following is a possibility for most of us in regard to breathing, by making a conscious effort?
(a) One can breathe out air totally without oxygen.
(b) One can breathe out air through Eustachian tube by closing both nose and mouth.
(c) One can consciously breathe in and breathe out by moving the diaphragm alone, without moving the ribs at all.
(d) The lungs can be made fully empty by forcefully breathing out all air from them.
(iv) Refer to the given figure and answer the following question .
Which of these parts
(I) are the actual sites of respiratory gas exchange?
(II) is the common passage for air and food?
(III) is provided with incomplete cartilaginous rings?
(IV) relaxes and gets back to its original shape during expiration?
(v) moves upwards and outwards during inspiration?(a) (I) - s, (II) - p, (III) - q, (IV) - r, (V) - t
(c) (I) - t, (II) - q, (III) - r, (IV) - s, (V) - P (b) (I) - r, (II) - p, (III) - q, (IV) - s, (V) - t (d) (I) - p, (II) - q, (III) - r, (IV) - s, (V) - t (v) Which of the following sequences is correct to initiate inspiration?
(I) The contraction of intercostal muscles raises the ribs and sternum
(II) Volume of thorax increases
(III) Intrathoracic pressure of the lungs decreases
(IV) Diaphragm contraction
(v) Air rushes into lungs(a) (I), (II), (IV), (V), (III) (b) (I), (II), (III), (IV), (V) (c) (I), (IV), (II), (III), (V) (d) (V), (I), (II), (III), (IV) (a) -
The green plants make their food, through photosynthesis and are therefore called autotrophs. All other organisms depend upon green plants for food and are referred to as heterotrophs. Green plants carry out photosynthesis by using light energy of sun. The first phase of reactions are directly light driven therefore called light reactions. The second phase of reactions are not directly light driven but are dependent on the products of light reactions and are called dark reactions.
(i) Which of the following is produced during the light phase of photosynthesis?(a) ATP (b) NADPH (c) Carbohydrate (d) Both (a) and (b) (ii) In the overall process of photosynthesis, the number of sugar molecules produced is
(a) 12 (b) 6 (c) 4 (d) l (iii) A plant is provided with ideal conditions for photosynthesis and supplied with isotope 14CO2. When the products of the process are analysed carefully, what would be the nature of products?
(a) Both glucose and oxygen are normal.
(b) Both glucose and oxygen are labelled.
(c) Only glucose is labelled and oxygen is normal.
(d) Only oxygen is labelled and glucose is normal.
(iv) Refer to the given diagrammatic representation of an electron micrograph of a section of chloroplast and answer the question .
Select the option which correctly depicts the functions of parts X, Y and Z.X Y Z (a) Dark reaction Light reaction Carbohydrate synthesis (b) Light reaction Carbohydrate synthesis Carbohydrate storage (c) Light reaction Carbohydrate storage Carbohydrate synthesis (d) Carbohydrate synthesis Carbohydrate storage Cytoplasmic inheritance (v) Following table summarises the differences between light and dark reactions.
Light reactions Dark reactions (I) These are also called biosynthetic phase These are also called photochemical phase. (II) These reactions occur over thylakoids. These reactions occur in stroma of chloroplasts (III) These produce assimilatory power i.e NADPH and ATP These consume NADPH and ATP (IV) These are directly dependent upon light They depend upon the products synthesised during light reactions Which of the following is correct group of differences?
(a) (I), (II) and (III) (b) (II), (III) and (IV) (c) (II) and (III) (d) (I) and (IV) (a)
*****************************************
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Life Processes Case Study Questions With Solution 2021 Answer Keys
-
(i) (c): In the test tube full of mercury (figure A) there is no air and, therefore, the introduced soaked seeds do not get air for aerobic respiration. But they are capable of respiration in the absence of oxygen as is indicated by the evolution of carbon dioxide (figure B). Therefore, anaerobic respiration takes place in the seeds in the absence of free oxygen. The experiment also shows that CO2 is evolved in anaerobic respiration of seeds.
(ii) (b)
(iii) (d): The given process is an example of alcoholic fermentation, thus the gas produced is CO2 .
(iv) (c): Ethyl alcohol fermentation occurs in fungi such as Rhizopus, yeast and bacteria.
(v) (a): Muscle fatigue is the reduction in force of contraction of a muscle after prolonged stimulation. In the absence of oxygen, skeletal muscle of human beings can contract for a short time, but it gets fatigued soon. This is due to the fact that in the absence of oxygen, products of glycolysis mainly lactic acid is not disposed off and accumulates in the muscles. This leads to muscle fatigue and pain in the muscles. A muscle gets fatigued sooner after a strenuous exercise than after a mild exercise. Faster breathing for sometime after a strenuous exercise supplies extra oxygen, disposes off excess lactic acid and muscle fatigue disappears. -
(i) (c): A- Artery: Carries blood from heart to different body parts. It is thick-walled and elastic. It acts as a "pressure reservoir" for maintaining the blood flow. B - Capillary : Nutrients, hormones, gases, etc. can diffuse into tissue cells through capillaries and vice versa. It is thin-walled, and only one cell layer thick resting on basement membrane. C - Vein: Brings blood from different body parts to the heart. It is thin-walled and act as low-resistance conduct for blood flow. D - Pulmonary vein: Two pulmonary veins from each lung transport the oxygenated blood to the left atrium.
(ii) (d): In amphibians, the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the gills/lungs/skin and the right atrium gets the deoxygenated blood from other body parts. However, they get mixed up in the single ventricle which pumps out mixed blood i.e., incomplete double circulation
(iii) (d): Whale is a mammal and in mammals, two separate circulatory pathways are found - systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation. Oxygenated and deoxygenated bloods received by the left and right atria respectively pass on to the left and right ventricles. Thus, oxygenated and deoxygenated bloods are not mixed. This is referred to as double circulation.
(iv) (a)
(v) (c): Pulmonary circulation is the movement of blood between heart and lungs. During this pathway deoxygenated blood entering the right atrium, moves into the right ventricle. From here it moves through the pulmonary arch into the lungs for oxygenation. Then from lungs the oxygenated blood moves into the left atrium through pulmonary veins. -
(i) (d)
(ii) (d)
(iii) (b): The epidermal surface of the leaf exhibits a large number of minute openings called stomata. The stomata are bordered by two specialized epidermal cells - the guard cells which in some cases are accompanied by subsidiary cells. The walls of guard cells are unevenly thickened. Each guard cell has thick, inelastic inner wall and thin, elastic outer wall. Stomatal aperture is present in between the guard cells. Guard cells are not always surrounded by accessory cells or subsidiary cells.
(iv) (b)
(v) (a) -
(i) (c) :Number of RBCs per cubic millimetre of blood is likely to be higher in people living at high altitudes. This is in response to the air being less dense at high altitude and thus more RBCs (and hence more Hb) are needed to absorb the required amount of O2 from the air having low pO2 (partial pressure of O2).
(ii) (c): The change from II to III indicates decrease in the volume of lungs and thus, increase in the pressure of air inside the lungs. This results in movement of air out of the lungs.
(iii) (c)
(iv) (b): p-pharynx, q-trachea, r-alveoli, s-diaphragm, t-ribs
(v) (c) -
(i) (d):In light reaction of photosynthesis assimilatory power is produced, i.e., energy rich ATP molecules and reduced coenzyme NADPH.
(ii) (d): The equation of photosynthesis may be represented as \(6 \mathrm{CO}_{2}+12 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{12} \mathrm{O}_{6}+6 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+6 \mathrm{O}_{2}\)
No. of C6H12O6 (sugar) molecules produced =1
(iii) (c)
(iv) (b): Light reactions (or photochemical phase) of photosynthesis mainly occur on the grana thylakoids. Dark reactions (or biosynthetic phase) which involve synthesis of carbohydrates by CO2 fixation, occur inthe stroma (or matrix) of chloroplasts. The chloroplast matrix of higher plants stores starch temporarily in the form of starch granules.
(v) (b): Light reactions are also called photochemical phase whereas dark reactions are also called biochemical phase.

























