CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Light Reflection and Refraction Chapter Case Study Questions 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Questions 2021
10th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Science
-
The refraction of light on going from one medium to another takes place according to two laws which are known as the laws of refraction of light. These laws are
1. The ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction is always constant for the pair of media in contact.
\(\frac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\mu=\text { constant }\)
This constant is called refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first medium.
Refractive index is also defined as the ratio of speed of light in vacuum to the speed of light in medium.
2. The incident ray, refracted ray and normal all lie in the same plane.
This law is called Snell's law of refraction.
(i) When light travels from air to glass,
(a) angle of incidence > angle of refraction
(b) angle of incidence < angle of refraction
(c) angle of incidence = angle of refraction
(d) can't say
(ii) When light travels from air to medium, the angle of incidence is 45° and angle of refraction is 30°. The refractive index of second medium with respect to the first medium is(a) 1.41 (b) 1.50 (c) 1.23 (d) 1 (iii) In which medium, the speed of light is minimum?
(a) Air (b) Glass (c) Water (d) Diamond (iv) If the refractive index of glass is 1.5 and speed of light in air is 3 x 108 m/s. The speed of light in glass is
(a) 2 x 108 mls (b) 2.9 x 108 mls (c) 4.5 x 108 mls (d) 3 x 108 mls (v) Refractive index of a with respect to b is 2. Find the refractive index of b with respect to a.
(a) 0.4 (b) 0.5 (c) 0.25 (d) 2. (a) -
A lens is a piece of any transparent material bounded by two curved surfaces. There are two types of lenses convex lens and concave lens.
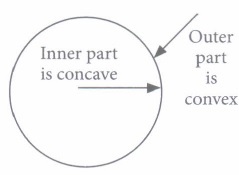
Convex lens is made up of a transparent medium bounded by two spherical surfaces such that thicker at the middle and thinner at the edges. Concave lens is also made up of a transparent medium such that thicker at the edge and thinner at the middle. The mid point of the lens is called optical centre.
A point on the principal axis, where the incident parallel rays meet or appears to come out after refraction is called focus.
A convex lens converges a parallel beam of light to other side whereas concave lens spreads out.
(i) Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in dictionary?
(a) A convex lens of focal length 50 cm
(b) A concave lens of focal length 50 cm
(c) A convex lens of focal length 5 cm
(d) A concave lens of focal length 5 cm
(ii) Which type of lenes are shown in given figure (i) and (ii).
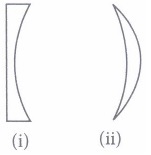
(a) Plano concave, concavo convex
(b) Plano convex, convexo concave
(c) Double concave, concave convex
(d) Convexo concave, double convex
(iii) A small bulb is placed at the focal point of a converging lens. When the bulb is switched on, the lens produces
(a) a convergent beam of light
(b) a divergent beam of light
(c) a parallel beam of light
(d) a patch of coloured light
(iv) The part oflens through which the refraction takes place is called(a) aperture (b) centre of curvature (c) principal axis (d) focus (v) A water drop acts as a
(a) convex lens (b) concave lens (c) double concave lens (d) none of these (a) -
The lenses forms different types of images when object placed at different locations. When a ray is incident parallel to the principal axis, then after refraction, it passes through the focus or appears to come from the focus. When a ray goes through the optical centre of the lens, it passes without any deviation.
If the object is placed between focus and optical center of the convex lens, erect and magnified image is formed. As the object is brought closer to the convex lens from infinity to focus, the image moves away from the convex lens from focus to infinity. Also the size of image goes on increasing and the image is always real and inverted. A concave lens always gives a virtual, erect and diminished image irrespective to the position of the object.
(i) The location of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at infinity is(a) at focus (b) at 2F (c) at optical center (d) between F and 2F (ii) When the object is placed at the focus of concave lens, the image formed is
(a) real and smaller (b) virtual and inverted (c) virtual and smaller (d) real and erect (iii) The size of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at the focus of convex lens is
(a) small (b) point in size (c) highly magnified (d) same as that of object (iv) When the object is placed at 2F in front of convex lens, the location of image is
(a) at F (b) at 2 F on the other side (c) at infinity (d) between F and optical center (a) -
The relationship between the distance of object from the lens (u), distance of image from the lens (v) and the focal length (j) of the lens is called lens formula. It can be written as\(\begin{equation} \frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u} \end{equation}\)
The size of image formed by a lens depends on the position of the object from the lens. A lens of short focal length has more power whereas a lens of long focal length has less power. When the lens is convex, the power is positive and for concave lens, the power is negative.
The magnification produced by a lens is the ratio of height of image to the height of object as the size of the image relative to the object is given by linear magnification (m).
When, m is negative, image formed is real and when m is positive, image formed is virtual. If m < 1, size of image is smaller than the object. If m > 1, size of image is larger than the object.
(i) An object 4 cm in height is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The position of image is(a) - 20 cm (b) 20 cm (c) -10 cm (d) 10 cm (ii) In the above question, the size of image is
(a) 16 cm (b) 8 cm (c) 4 cm (d) 2 cm (iii) An object is ,placed 50 cm from a concave lens and produces a virtual image at a distance of 10 cm in front of lens. The focal length of lens is
(a) - 25 cm (b) -12.5 cm (c) 12.5 cm (d) 10 cm (iv) A convex lens forms an image of magnification -2 of the height of image is 6 cm, the height of object is
(a) 6 cm (b) 4 cm (c) 3 cm (d) 2 cm (v) A concave lens of focal length 5 cm, the power of lens is
(a) 20D (b) -20D (c) 90D (d) -5 D (a)
*****************************************
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Questions 2021 Answer Keys
-
(i) (a): According to Snell's law of refraction,
\(\frac{\sin i}{\sin r}>1 \text { or } \sin i>\sin r\)
or i > r.
(ii) (a:) As, 1 \(\mu^{2}=\frac{\sin i}{\sin r}\)
\(\frac{\sin 45^{\circ}}{\sin 30^{\circ}}=\frac{1 / \sqrt{2}}{1 / 2}=1.41\)
(iii) (d): As diamond has maximum value of refractive index, therefore it has minimum speed of light in medium.
(iv) (a): As, \(\mu_{\text {glass }}=1.5, c=3 \times 10^{8} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\)
\(\begin{equation} \begin{array}{l} \mu=\frac{c}{v} \text { or } 1.5=\frac{3 \times 10^{8}}{v} \\ v=2 \times 10^{8} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s} \end{array} \end{equation}\)
(v) (b): Given, refractive index of a with respect to b is \(\begin{equation} { }^{b} \mu_{a}=2 \end{equation}\)
Refractive index of b with respect to a is
\(\begin{equation} \frac{1}{b_{\mu_{a}}}={ }^{a} \mu_{b}=\frac{1}{2}=0.5 \end{equation}\) -
(i) (c): Convex lens is used as magnifying glass.
For better performance its focal length should be small.
(ii) (a)
(iii) (c)
(iv) (a): A aperture is the area of the lens available for refraction.
(v) (a): Water droplets behave like a convex lens only as refraction takes place on outer surface. -
(i) (a): When an object is placed at infinity of convex lens, image will be formed at focus F.
(ii) (b): Virtual and inverted image is formed, when object is placed at focus of the concave lens.
(iii) (c) : When object is placed at focus of a convex lens, highly enlarged or magnified image is formed.
(iv) (b): When an object is placed at distance 2F in front of a convex lens, then the image formed is at a distance 2F on the other of the lens.
(v) (a): Image if formed between focus and optical centre when the object is placed anywhere between optical centre and infinity. -
(i) (a):Given, f= 20 cm, U = -10 cm
Using, \(\begin{equation} \frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u} \end{equation}\)
\(\begin{equation} \frac{1}{20}=\frac{1}{v}-\left(-\frac{1}{10}\right) \Rightarrow v=-20 \mathrm{~cm} \end{equation}\)
(ii) (b): As,\(\begin{equation} m=\frac{v}{u}=\left(\frac{-20}{-10}\right)=2 \end{equation}\)
\(\begin{equation} \begin{array}{l} m=\frac{h_{2}}{h_{1}} \\ 2=\frac{h_{2}}{4} \Rightarrow h_{2}=8 \mathrm{~cm} \end{array} \end{equation}\)
(iii) (b): Here u = -50 cm, v = 10 cm,f=?
Using, \(\begin{equation} \frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{10}-\frac{1}{50} \Rightarrow f=-12.5 \mathrm{~cm} \end{equation}\)
(iv) (c): Here, m = - 2
h2 = - 6 cm
h1 =?
As,\(\begin{equation} m=\frac{h_{2}}{h_{1}} \Rightarrow-2=\frac{-6}{h_{2}} \Rightarrow h_{1}=3 \mathrm{~cm} \end{equation}\)
(v) (b):As \(\begin{equation} P=\frac{1}{f}(\because f=5 \mathrm{~cm}) \end{equation}\)
\(\begin{equation} P=\frac{-1}{0.05 \mathrm{~m}}=-20 \mathrm{D} \end{equation}\)

























