CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Light Reflection and Refraction Chapter Case Study Questions With Solution 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Questions With Solution 2021
10th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Science
-
The curved surface of a spoon can be considered as a spherical mirror. A highly smooth polished surface is called mirror. The mirror whose reflecting surface is curved inwards or outwards is called a spherical mirror. Inner part works as a concave mirror and the outer bulging part acts as a convex mirror. The center of the reflecting surface of a mirror is called pole and the radius of the sphere of which the mirror is formed is called radius of curvature.
(i) When a concave mirror is held towards the sun and its sharp image is formed on a piece of carbon paper for some time, a hole is burnt in the carbon paper. What is the name given to the distance between the mirror and carbon paper?(a) Radius of curvature (b) Focal length (c) Principal focus (d) Principal axis (ii) The distance between pole and focal point of a spherical mirror is equal to the distance between
(a) pole and center of curvature (b) focus point and center of curvature (c) pole and object (d) object and image (iii) The focal length of a mirror is 15 cm. The radius of curvature is
(a) 15 cm (b) 30 cm (c) 45 cm (d) 60 cm (iv) The normal at any point on the mirror passes through
(a) focus (b) pole (c) center of curvature (d) any point (v) In a convex spherical mirror, reflection of light takes place at
(a) a flat surface (b) a bent-in surface (c) a bulging-out surface (d) an uneven surface (a) -
The spherical mirror forms different types of images when the object is placed at different locations.
When the image is formed on screen, the image is real and when the image does not form on screen, the image is virtual. When the two reflected rays meet actually, the image is real and when they appear to meet, the image is virtual.
A concave mirror always forms a real and inverted image for different positions of the object. But if the object is placed between the focus and pole, the image formed is virtual and erect.
A convex mirror always forms a virtual, erect and diminished image. A concave mirror is used as doctor's head mirror to focus light on body parts like eyes, ears, nose etc., to be examined because it can form erect and magnified image of the object. The convex mirror is used as a rear view mirrors in automobiles because it can form an small and erect image of an object.
(i) When an object is placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror, the image formed is(a) larger than the object (b) smaller than the object (c) same size as that of the object (d) highly enlarged. (ii) No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be
(a) plane (b) concave (c) convex (d) either plane or convex. (iii) A child is standing in front of a magic mirror. She finds the image of her head bigger, the middle portion of her body of the same size and that of the legs smaller. The following is the order of combinations for the magic mirror from the top.
(a) Plane, convex and concave (b) Convex, concave and plane (c) Concave, plane and convex (d) Convex, plane and concave (iv) To get an image larger than the object, one can use
(a) convex mirror but not a concave mirror
(b) a concave mirror but not a convex mirror
(c) either a convex mirror or a concave mirror
(d) a plane mirror.
(v) A convex mirror has wider field of view because
(a) the image formed is much smaller than the object and large number of images can be seen
(b) the image formed is much closer to the mirror
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these.(a) -
The relation between distance of an object from the mirror (u), distance of image from the mirror (v) and the focal length (F) is called mirror formula. This formula is valid in all situations for all spherical mirrors for all positions of the object. The size of image formed by a spherical mirror depends on the position of the object from the mirror. The image formed by a spherical mirror can be bigger than the object, equal to the object or smaller than the object. The size of the image relative to the object is given by the linear magnification (m). Thus, the magnification is given by the ratio of height of image to the height of object. If magnification is negative, image is real and if it is positive, image is virtual.
(i) What is the position of an image when an object is placed at a distance of 20 em from a concave mirror of
focal length 20 cm?(a) 5 cm (b) 20 cm (c) 10 cm (d) infinity (ii) Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on a concave mirror as shown in figure?
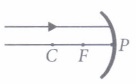
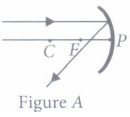
(a) Figure A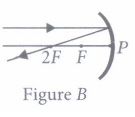
(b) Figure B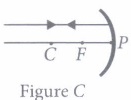
(C) Figure C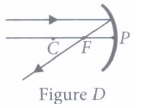
(d) Figure D(iii) If the magnification of an image is -2, the characteristic of image will be
(a) real and inverted (b) virtual and enlarged (c) virtual and inverted (d) real and small (iv) The mirror formula holds for
(a) concave mirror (b) convex mirror (c) plane mirror (d) all of these (v) A parallel beam of light is made to fall on a concave mirror. An image is formed at a distance of7.5 from the mirror. The focal length of the mirror is
(a) 15 cm (b) 7.5 cm (c) 3.75 cm (d) 10 cm (a) -
When the rays of light travels from one transparent medium to another, the path of light is deviated. This phenomena is called refraction of light. The bending of light depends on the optical density of medium through which the light pass.
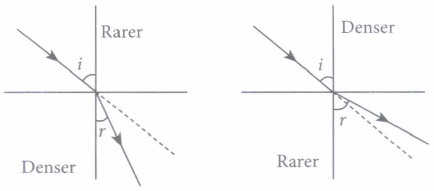
The speed of light varies from medium to medium. A medium in which the speed of light is more is optically rarer medium whereas in which the speed of light is less is optically denser medium. Whenever light goes from one medium to another, the frequency of light does not change however, speed and wavelength change. It concluded that change in speed of light is the basic cause of refraction.
(i) When light travels from air to glass, the ray of light bends(a) towards the normal (b) away from normal (c) anywhere (d) none of these (ii) A ray of light passes from a medium A to another medium B. No bending of light occurs if the ray of light hits the boundary of medium B at an angle of
(a) 0° (b) 45° (c) 90° (d) 120° (iii) When light passes from one medium to another, the frequency of light
(a) increases (b) decreases (c) remains same (d) none of these (iv) When light passes from glass to water, the speed of light
(a) increases (b) decreases (c) remains same (d) first increases then decrease (v) The bottom of pool filled with water appears to be ______ due to refraction of light
(a) shallower (b) deeper (c) at same depth (d) empty (a)
*****************************************
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Questions With Solution 2021 Answer Keys
-
(i) (b): The focal length of a concave mirror is the distance between its pole and principal focus.
(ii) (b)
(iii) (b): Given that, f = 15 cm
Radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is given as
R= 2F
R = 2 x 15 = 30 cm.
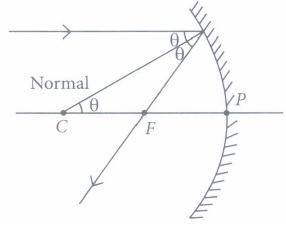
(iv) (c): In a spherical mirror, normal drawn at any point passes through the centre of curvature
(v) (c) -
(i) (c):
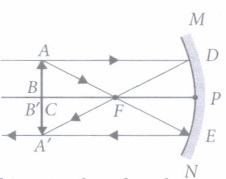
When the object is placed at the centre of curvature of concave mirror, the image formed is real, inverted and of the same size as that of the object.
(ii) (d): The image is erect in a plane mirror and also in a convex mirror, for all positions of the object.
(iii) (c) : As the image of head is bigger, the upper portion of magic mirror is concave. The middle portion of the image is of same size, so, middle portion of magic mirror is plane. Now, the image of legs looks smaller, therefore, the lower portion of magic mirror is convex.
(iv) (b)
(v) (c) -
(i) (d): When an object is placed at the focus of a concave mirror, the image is formed at infinity.
(ii) (d): When a light ray parallel to the principal axis is incident on a concave mirror, it passes through the principal focus after reflection. Therefore, figure D is correct.
(iii) (a) : If m is negative, the image will be real and inverted.
(iv) (d)
(v) (b): The distance of object from mirror = \(\infty\)
Using, \(\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{f}\)
\(\frac{1}{\infty}-\left(-\frac{1}{7.5}\right)=\frac{1}{f}\)
f = 7.5 cm -
(i) (a): When, a ray of light travels from air to glass, it bends towards the normal.
(ii) (c): No bending of light occurs when light is incident normally or perpendicularly on a boundary of two media since angle of incidence and angle of refraction both are zero.
(iii) (c): When light goes from one medium to other medium, its frequency does not change
(iv) (a): The speed to light increases when light passes from glass to water as water is optically rarer medium.
(v) (a): The bottom of a pool of water appears to be less deep than it actually is due to refraction.

























