CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Light Reflection and Refraction Ncert Exemplar 5 Mark Questions With Solution 2021
By QB365 on 26 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated NCERT Exemplar Questions for Class
10, and also provide the detail solution for each and every NCERT Exemplar questions. NCERT Exemplar questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Light Reflection and Refraction Ncert Exemplar 5 Mark Questions With Solution 2021
10th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Science
-
(i) " A convex lens can form a magnified erect as well as magnified inverted image of an object placed in front of it. " Draw ray diagram to justify this statement stating the position of the object with respect to the lens in each case.
(ii) As object of height 4 cm is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a concave lens of focal length 10 cm. Use lens formula to determine the position of the image formed.(a) -
(a) State the laws of refraction of light. Explain the term absolute refractive index of a medium and write an expression to relate it with the speed of light in vaccum.
(b) The absolute refractive indices of two media 'A' and 'B' are 2.0 and 1.5 respectively. If the speed of light in medium 'B' is \({ 2\times 10 }^{ 8 }\) m/s. calculate the speed of light in : (i) Vacuum, (ii) medium 'A'(a) -
(a) Draw ray diagram to show the refraction of light through a glass slab and mark angle of refraction and the lateral shift suffered by the ray of the light while passing through the slab.
(b) If the refractive index of glass for light going from air to glass is 3/2, find the refractive index of air for light going from glass to air.(a) -
List the sign conventions for reflection of light by spherical mirrors. Draw a diagram and apply these conventions in the determination of focal length of a spherical mirror which forms a three times magnified real image of an object placed 16 cm in front of it.
(a) -
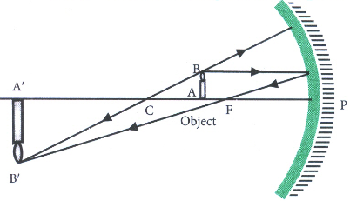
To construct a ray diagram we use two light rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from mirror. List these two rays and state the path of these rays after reflection. Use these rays to locate the image of an object placed between centre of curvature and focus of a concave mirror.
(a)
*****************************************
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Light Reflection and Refraction Ncert Exemplar 5 Mark Questions With Solution 2021 Answer Keys
-
(i) A convex lens can form a magnified erect image when the object is placed between the optical centre and principal focus of the convex lens (i.e. between O and F).
-S.png)
(ii) A convex lens can form a magnified erect image when the object is placed between focus and the centre of curvature (i.e. between F' and 2F).
-S.png)
Object height, h = 4 cm;
Object distance, u = -20 cm
Nature of the lens = concave lens;
Focal length = f = +10 cm
Image distance, v = ?
According to the lens formula,
\(\frac { 1 }{ f } =\frac { 1 }{ v } -\frac { 1 }{ u } \)
\(\Rightarrow \frac { 1 }{ v } =\frac { 1 }{ f } +\frac { 1 }{ u } \)
\(\frac { 1 }{ v } =\frac { 1 }{ +10 } +\frac { 1 }{ -20 } =\frac { 1 }{ 10 } -\frac { 1 }{ 20 } =\frac { 2-1 }{ 20 } =\frac { 1 }{ 20 } \)
∴ v=20cm
The image is formed at a distance of 20 cm from the lens on the opposite side. -
(a)Laws of refraction of light states that the incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
(ii)The second law of refraction of light is the Snell's Law of Refraction. It state that the ratio of sine of angle of refraction is a constant for given pair of medium.
\({sin\ i\over sin\ r}\)=Constant (n)
This constant (n) is called refractive index of the medium.
(i)When the light is going from vacuum to another medium, then the value of refractive index is called the absolute refractive index.
(ii)The ratio of speed of light in vacuum to the speed of light in a medium is called the absolute refractive index of the medium, i.e.,
Absolute refractive index (of medium)=\(Speed\ of\ light\ in\ vacuum(C)\over Speed\ of\ light\ in\ medium(V)\)
(b)nA=2.0;
nB=1.5;
vB=2 x 108m/s
(i)Speed of light in vacuum, c=?
\(n_B=1.5={c\over v_B}\)
c=nB
vB=1.5 x 2 x 108 m/s
=3 x 108 m/s
(ii)For medium 'A': nA=\(c\over v_A\)
\(\therefore\ v_A={c\over n_B}={3\times10^8m/s\over2}\)
=1.5 x 108 m/s -
-S.png)
(b) Refractive index of glass from air
\(_{ a }{ { n }_{ g } }=\frac { 3 }{ 2 } \)
Refractive index of air from glass:
\(_{ g }{ { n }_{ a } }=\frac { 1 }{ _{ a }{ { n }_{ g } } } \)
\(\Rightarrow \frac { 1 }{ 3/2 } =\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \) -
(a) Sign conventions
1. The object is always placed to the left of the mirror.
2. All the distances parallel to the principal axis are always measured from the pole of the spherical mirror.
3. All the distances measured along the direction of incident light (along +ve x-axis), are considered to be positive.
4. Those distances measured opposite to the direction of incidence light (i.e. along -ve x-axis), are taken as negative.
5. The distances measured in upward direction, i.e. perpendicular to and above the principal axis (along +ve y-axis), are taken as positive.
6. The distances measured in the downward direction, (along -ve y-axis), i.e. perpendicular to and below the principal axis are taken as negative.
(b) u=-16cm, m=-3 for real But \(m=-\frac { v }{ u } =-3\)
v = 3u = 3 (-16) = -48 cm.
Using mirror formula
\(\frac { 1 }{ f } =\frac { 1 }{ v } +\frac { 1 }{ u } \)
We get, \(\frac { 1 }{ f } =\frac { 1 }{ -48 } +\frac { 1 }{ -16 } \)
\(=\frac { 1 }{ -48 } -\frac { 1 }{ 16 } =\frac { -1-3 }{ 48 } =\frac { -4 }{ 48 } =\frac { -1 }{ 12 } \)
f=-12cm
(c) Negative sign of focal length indicated that mirror is concave in nature.
-S.png)
-
(i) A ray parallel to the principal axis and
(ii) A ray passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror or appear to pass through the centre of curvature of convex mirror.
Path of these rays after reflection is :
(i) After reflection, the first ray will pass through the principal focus of a concave mirror or appear to diverge In case of a convex mirror.
(ii) After reflection, the second ray is reflected back along the same path