CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Our Environment Chapter Case Study Questions 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Our Environment Case Study Questions 2021
10th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Science
-
Various steps of a food chain can be represented sequence wise with producers at base, herbivores above them, followed by primary carnivores and finally the top carnivore at the top. This graphic representation of ecological parameters like number, biomass, energy at different trophic levels is called ecological pyramid. Different types of pyramids are pyramid of energy, pyramid of biomass and pyramid of number.
(i) Refer to the given figure where various trophic levels are represented as P, Q, Rand S. At which level is maximum and minimum energy available respectively?
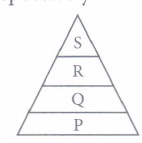
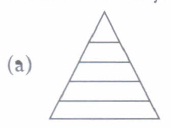
(a) P, S (b) S, P (c) P, R (d) Q, S (ii) On the basis of your knowledge, select the pyramid of biomass operating in a grassland ecosystem
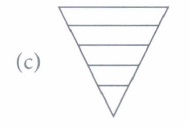
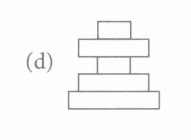
(iii) Which of the following food chains is most likely represented by the given pyramid of number?
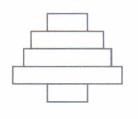
(a) Tree \(\rightarrow\) Aphid \(\rightarrow\) Lady bug - Bird \(\rightarrow\) Hawk
(b) Cyanobacteria \(\rightarrow\) Shrim\(\rightarrow\) Small fish \(\rightarrow\) Fish eating bird - Snake
(c) Plant\(\rightarrow\)Rat \(\rightarrow\)Snake \(\rightarrow\) Meerkat\(\rightarrow\)Lion
(d) Phytoplankton \(\rightarrow\) Zooplankton \(\rightarrow\)Shellfish\(\rightarrow\)Fish \(\rightarrow\)Shark
(iv) Which of the following pyramids is always upright?(a) Pyramid of number (b) Pyramid of biomass (c) Pyramid of energy (d) Both (a) and (c) (v) Refer to the given table
Trophic level Number of organisms Energy in trophic level (arbitrary units) W 100 10,000 X 1 100 Y 1000 100,000 Z 10 1000 Which of the following food chains is correct regarding the given data?
(a) W \(\rightarrow\) X\(\rightarrow\) Y \(\rightarrow\) Z (b) Y\(\rightarrow\) W \(\rightarrow\) Z\(\rightarrow\) X (c) W \(\rightarrow\)Z \(\rightarrow\)X\(\rightarrow\) Y (d) Y\(\rightarrow\)X\(\rightarrow\) Z\(\rightarrow\)W
(a) -
Various components of an ecosystem maintain a balance in nature. Disturbance in any component of the environment cause an imbalance. One of the main environmental problem caused by human activities is global warming. Global warming is a phenomenon caused by the increasing concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere resulting due to enhanced greenhouse effect.
(i) Refer to the given pie chart showing the contribution of different gases to global warming.
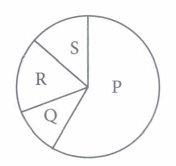
Identify gases P, Q, Rand S and select the incorrect statement regarding them.
(a) P could be a gas that increases in atmosphere due to excessive use of fossil fuel.
(b) Q could be a gas produced by complete combustion of biomass.
(c) R could be synthetic gaseous compounds used as refrigerants in air conditioners and refrigerators.
(d) S could be a gas produced by combustion of nitrogen rich fuel.
(ii) What could not be a source of gas Q given in the above pie chart?(a) Flooded paddy field (b) Cattle (c) Jet fuel (d) Marshes (iii) If there is no CO2 in the atmosphere, then what will be the most likely consequence of this on the temperature of earth?
(a) The temperature remain unchanged as it depends upon the oxygen content of the atmosphere.
(b) The temperature would increase as less greenhouse gases will be absorbed by CO2
(c) The temperature would decrease as CO2 is the principal greenhouse gas.
(d) None of these
(iv) Study carefully the following figure representing greenhouse effect.
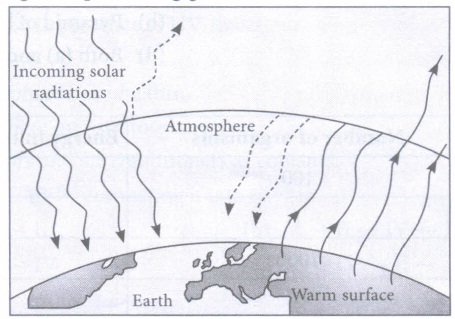
Select the correct statement regarding this.
(a) Much of the long wavelength infrared radiations re-radiated by the earth's surface are absorbed by the atmospheric greenhouse gases.
(b) CO2 , CH4 , CFCs and N2O are the gases which are responsible for greenhouse effect.
(c) The atmosphere is transparent to the incoming short-wavelength radiations and is translucent to the long-wavelength infra-red radiations.
(d) All of these(v) Greenhouse effect is due to
(a) accumulation of O3 and depletion of CO2 (b) accumulation of both O3 and CO2 (c) accumulation of CO2 and depletion of O3 (d) presence of green plants on the earth (a) -
Disposal of waste should be done scientifically. Solid wastes, i.e., paper, plastics, metals, etc., can be recycled by sending them to respective recycling units. For instance, paper is sent for recycling into special paper mills; broken plastics, plastic bags, buckets, bowls, dishes, mugs, disks, etc.) are sent to plastic processing factories where these are melted and then remoulded; waste metals are sent to specific metal industries for recycling. Industrial wastes are treated in special plants where valuable wastes are recycled. Certain wastes are mixed to generate useful materials. For instance, molten plastic is mixed with asphalt and the material is used for making roads. Household waste, chemical waste and hospital waste are generally disposed off by an incineration process
(i) What does A represent in the given figure showing an incinerator?
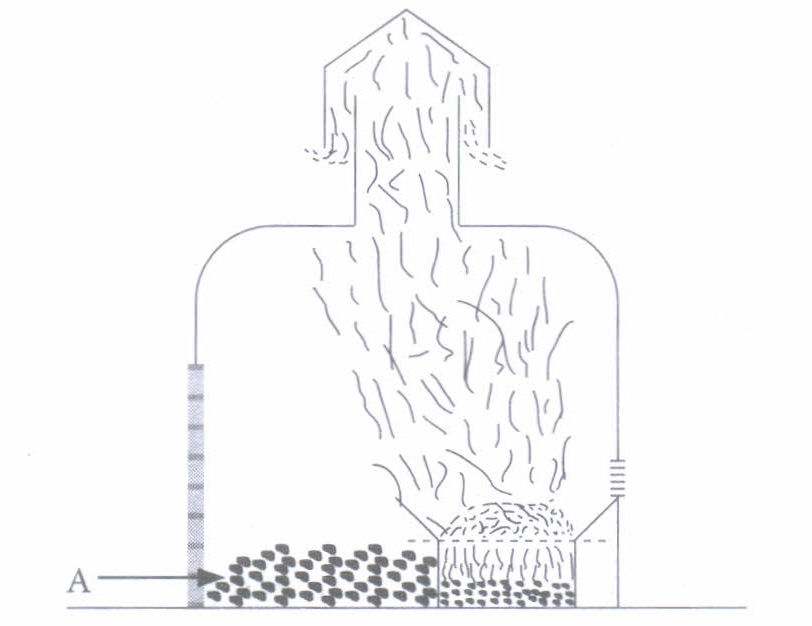
(a) Solid waste (b) Fire (c) Ash (d) None of these (ii) Which of the following statements regarding incineration is incorrect?
(a) It is the process of waste disposable by keeping waste at low temperature to stop enzymatic activity.
(b) Household waste, chemical waste and hospital waste are generally disposed by this method.
(c) Disposing waste by using this method generates carbon dioxide and water vapour.
(d) It involves aerobic burning of the combustible waste at high temperature
(iii) In the following groups of material which group contains only recyclable materials?
I. Wood, paper, fruit pulp
II. Plastic bottle, used aluminium foil, glass jug
III. Paper, metal key, plastic mug(a) I and II only (c) III only (b) II and III only (d) I, II and III (iv) Incineration and pyrolysis are two methods of waste disposal done at high temperature. The two differs from each other as in later
(a) aerobic burning occurs
(b) chemical energy and chemical constituents are the end products
(c) ashes are the end products
(d) medical wastes are burnt with clinkers as the end product.
(v) The committee members of Robin's society placed two bins-green coloured and blue coloured in their premises for collection of garbage.
Given is the list of few solid wastes generated in his societyPaper cup, credit card, fruit and vegetables peels, cardboard, metal rod, aluminium foil, plastic key chain, pencil, glass sheet Segregate the wastes in their respective bins and select the correct option.
Green bin Blue bin (a) Paper cup, credit card, pencil Fruit and vegetable peels, cardboard, metal rod, aluminium foil, plastic key chain, glass sheet (b) Paper cup, fruits and vegetables peels, cardboard, pencil Credit card, metal rod, aluminium foil, plastic key chain, glass sheet (c) Fruit and vegetables peels, cardboard, glass sheet,paper cup Credit card, metal rod, aluminium foil, plastic key chain, pencil (d) Credit card, metal rod, aluminium foil, glass sheet Paper cup, fruits and vegetables peels, cardboard, plastic key chain, pencil (a) -
A group of ecologists studied and monitored the change in population of three animal species X, Y and Z over a period of ten years. During their research, they found that a new animal species W appeared in the area and its population was also monitored.
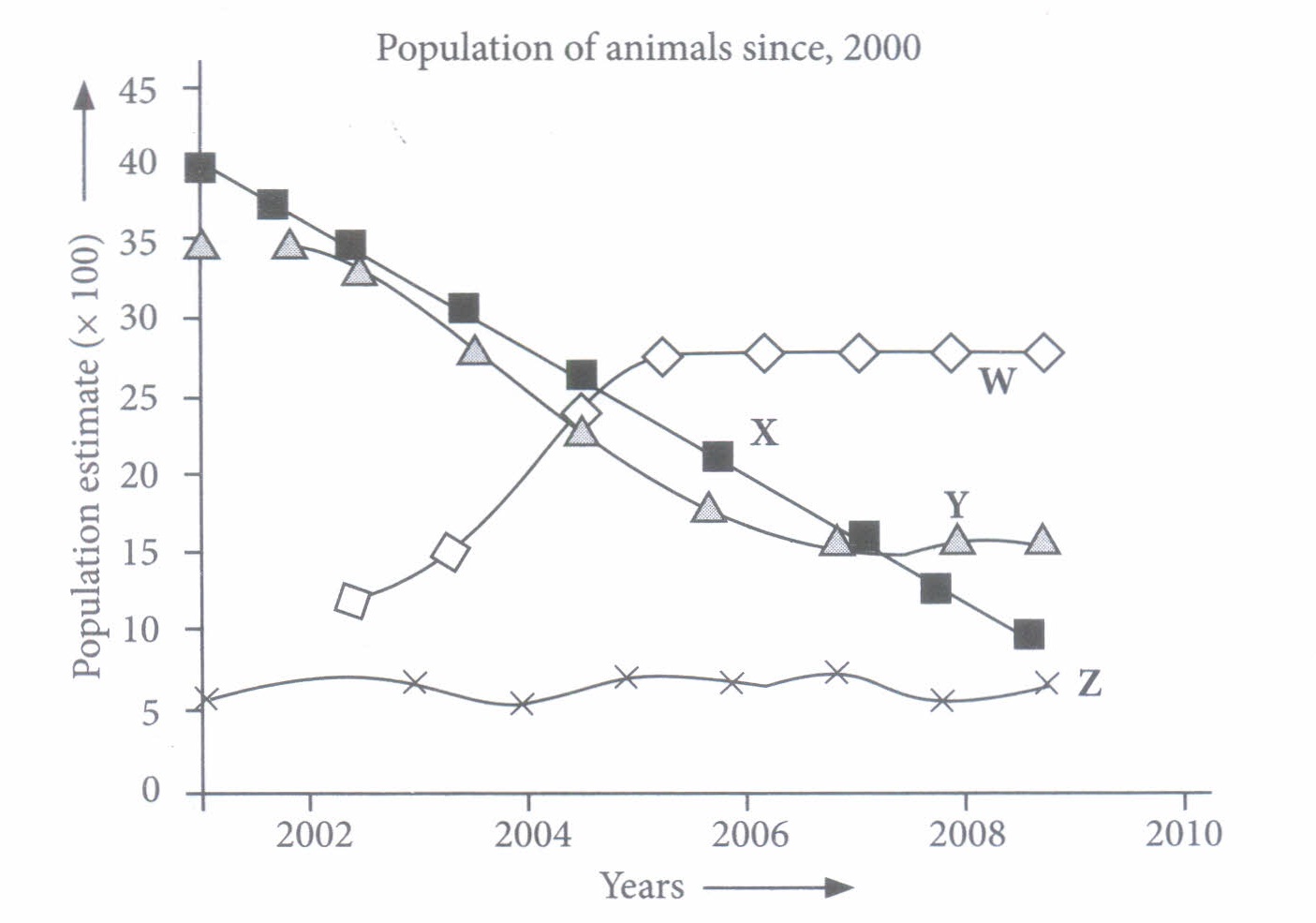
(I) Which animal species will unlikely to be alive in 10 years without some intervention?a) W (b) X (c) Y (d) Z (ii) Which of the following species is most likely be the food source of W?
(a) X (b) Y (c) Z (d) Both X and Z (iii) What will be the likely consequence if population of X completely declines?
(a) Populations of W, Y and Z also declines (b) Population of Y declines only. (c) Population of Z remains unchanged. (d) Population of Z increases. (iv) What would be the most probable reason for the constant population of Z?
(a) There is plenty of food available for Z.
(b) There is no predator of Z in the community.
(c) Ratio of death rate and birth rate is nearly equal in the population of Z.
(d) There is more number of preys for Z in the community.
(v) What could be the reason for declining of X?
(a) There could be more than one predator of X prevailing in the community.
(b) There is food scarcity for X.
(c) More number of prey species are present in the community for X.
(d) Both (a) and (b)(a) -
Food web is a network of food chains which become interconnected at various trophic levels so as to form a number of feeding connections amongst different organisms of a biotic community. Different food webs operate in different ecosystems. One such food web operating in an ecosystem is given ahead. Study it carefully and answer the following.
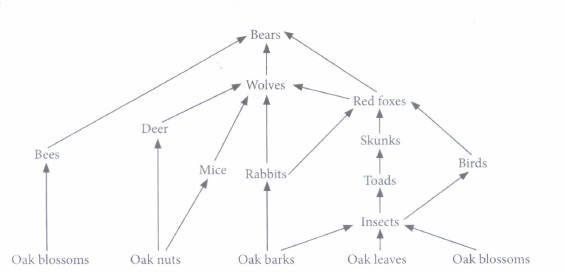
(i) What is the primary energy input in this food web?(a) Oak tree (b) Oak blossoms (c) Sunlight (d) Oak leaves (ii) How many food chains are operating in the given food web?
(a) 10 (b) 12 (c) 16 (d) 14 (iii) When a new species 'X' was introduced into the community, the population of toads rose and population of skunks fell over the subsequent two weeks. Species 'X' is most likely to be
(a) another herbivore like toad (b) a predator of insects only (b) a predator of insects only (d) a predator of skunks and prey of the toad (iv) Which of the following organisms in the food web passes most of its energy to the subsequent trophic levels?
(a) Bear (b) Wolf (c) Bee (d) Oak tree (v) Which organisms would be most affected if the oak tree fails to flower?
(a) Mice and insects (b) Birds and bees (c) Deer and mice (d) Insects and wolves (a)
*****************************************
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Our Environment Case Study Questions 2021 Answer Keys
-
(i) (a) : Producers contain maximum energy and as energy passes onto higher trophic level along with food, its amount decreases. Hence P has maximum energy while S has least.
(ii) (a): Pyramid of biomass in a grassland ecosystem is upright.
(iii) (a) : Pyramid of number in a tree ecosystem is spindle shaped.
(iv) (c)
(v) (b): The available energy is highest at the producer level and there is gradual decrease in available energy at successive trophic level.
-
(i) (b) :In the given pie chart, gases P, Q, Rand S respectively are CO2 , CH4 , CFCs and N2O. Methane is produced by incomplete combustion of biomass.
(ii) (c): Methane (gas Q) is produced by incomplete biomass combustion and incomplete decomposition mostly by anaerobic methanogens. Flooded paddy fields, marshes and cattles are the major source of this gas.
(iii) (c) : CO2 is the principal greenhouse gas that helps to keep the earth warm.
(iv) (d)
(v) (c) -
(i) (c)
(ii) (a) : Incineration is the process of burning substances at high temperature usually at about 1000°C.
(iii) (b)
(iv) (b) : Pyrolysis involves anaerobic destructive distillation of the combustible constituents of the solid wastes at high temperature so as to recover the chemical constituents and chemical energy of organic wastes.
(v) (b) -
(i) (b) : As population of X is declining constantly, it is most unlikely to be alive in next 10 years.
(ii) (b) : When population W appears in the area, there is decline in population of X and Y but as X is continuously decreasing and W becomes somewhat constant, this implies that W is not feeding on X. On the other hand as population of Y is becoming constant, population W also shows constant numbers. This shows that species W is likely to feed on species Y.
(iii) (c)
(iv) (c): As the population of Z is nearly constant, this may due to the nearly equal ratio of death and birth rate.
(v) (d) -
(i) (c) : The sun is the primary source of energy for almost all ecosystems. Sunlight is converted to chemical energy during photosynthesis by the oak tree.
(ii) (d): A total of 14 food chains are operating in the given food web.
(iii) (c) : A new predator of skunks would result in the fall of its population and thus corresponding rise in the population of toad since less would be preyed upon. A predator of skunk is unlikely to be the prey of toad.
(iv) (d) : The oak tree is the producer, thus the most energy passes through the oak compared to other organisms. By the time energy reaches the higher trophic levels, significant energy would have been lost between trophic levels.
(v) (c)

























