CBSE 11th Business Studies - Nature and Purpose of Business Model Question Paper
By QB365 on 20 Nov, 2019
Nature and Purpose of Business
Nature and Purpose of Business Model Question Paper
11th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Business Studies
-
Which of the broad categories of industries covers, oil refinery and sugar mills?
(a)Primary
(b)Secondary
(c)Tertiary
(d)None of them
-
Which of the following cannot be classified as an objective of business?
(a)Investment
(b)Productivity
(c)Innovation
(d)Profit earning
-
Which of the following is not a business activity?
(a)Production of goods
(b)Trading of goods
(c)Storage of goods
(d)Working in a hospital for wages
-
Which of the following is a cause of business risk?
(a)Natural causes
(b)Political causes
(c)Economic causes
(d)All of the above
-
Which of the following is an example of genetic industry?
(a)Mining
(b)Lumbering
(c)Animal husbandry
(d)Hunting
-
What are various types of industries?
(a) -
Explain any two business activities which are auxiliaries to trade.
(a) -
What are the functions of commerce?
(a) -
Explain political and legal causes of business risks.
(a) -
What are the hindrances in the commerce? Which agencies are used to remove these hindrances?
(a) -
Describe the activities relating to commerce.
(a) -
Why does business need multiple objectives? Explain any five such objectives.
(a) -
What factors are important to be considered while starting a business? Explain.
(a) -
Define commerce. Discuss its importance in the business world.
(a) -
"Economic and non-economic activities don't substitute, but complementary to each other." Do you agree? Explain.
(a) -
If one starts a business, which objective will be of utmost importance to you and why?
(a)
*****************************************
Nature and Purpose of Business Model Question Paper Answer Keys
-
(a)
Primary
-
(a)
Investment
-
(d)
Working in a hospital for wages
-
(d)
All of the above
-
(c)
Animal husbandry
-
Different types of industries are as follows:
1. Primary Industry: The primary industry includes those activities through which the natural resources are used to provide raw materials to other industries. Primary industries are of two types.
(i) Extractive: It refers to those industries under which something is extracted out of the earth, water or air e.g., coal, iron, gas etc.
(ii) Genetic: It refers to those industries under which the breed of animals and vegetables are improved and made more useful e.g., poultry farms, tree planting etc.
2. Secondary Industry: Under this industry, new products are manufactured by using the previously produced things e.g., producing cotton is a primary industry and manufacturing cloth out of cotton is a secondary industry. It is of two types.
(i) Manufacturing: These industries convert raw materials or semi finished products into finished products e.g., paper from bamboo, sugar from sugar cane.vIt is further being divided into four parts.
(ii) Analytical: Different things are manufactured out of one thing e.g., petrol, diesel, gasoline out of crude oil.
(iii) Processing: Those industries wherein useful things are manufactured by making the raw material to pass through different production process e.g., steel from iron ores.
(iv) Synthetic: Many raw materials are mixed to produce more useful product e.g., paints, cosmetics etc.
(v) Assembling: The parts manufactured by different industries are assembled to produce new and useful product e.g., computers, watches etc.
(vi) Construction Industry: Such types of industries constructions of roads, bridges, buildings etc. are covered.
3. Tertiary or Service Industry: It includes those services which help business to move smoothly e.g. transport, bank, insurance, storage and advertising. -
Two business activities which are auxiliary to trade are explained below:
(a) Transportation and Communication: The production of goods takes place at one place whereas these are demanded in different parts of the country. The obstacle of place is removed by the transport. Along with transport, communication is also an important service. It helps in exchange of information between producers, consumers and traders. The common communication services are postal service, telephone, fax, internet etc.
(b) Banking and Finance: Business needs funds for acquiring assets, purchasing raw materials and meeting other expenses. Necessary funds can be obtained from a bank. Finance is the life blood of any business. We cannot think of any business which does not need finance and providing finance to other businesses become another business. Finance is also required for consumption purposes. -
The functions of commerce are as follows:
1. Removing the hindrance of person and that means lack of information to producer about consumer and to consumer about the producer. It is removed by advertising.
2. Transportation removes hindrance of place.
3. Storage and warehousing activities remove the hindrance of time.
4. Banking removes the hindrance of finance.
5. Insurance removes the hindrance of risk.
6. Advertising removes the hindrance of information -
The causes of business risk include:
(a) Changes in government policies regarding foreign trade
(b) Entry of multinational companies
(c) Changes in laws affecting the business like licensing, taxation etc.
(d) Changes in consumer laws and labour laws.
For example, an increase in tax rates may reduce profit margin of the business or an increase in minimum wages may increase labour cost for the business. -
Following are the hindrances in commerce:
a) Lack of Personal Contact: This hindrance is removed by traders and middlemen.
b) Distance or Place: This hindrance is removed by transportation.
c) Finance: This hindrance is removed by banking.
d) Time or Storage: This hindrance is removed by warehousing.
e) Risk: This hindrance is removed by insurance companies.
f) Information: This hindrance is removed by advertisement or communication. -
Commerce refers to all those activities which are concerned with the transfer of goods and services from the producers to the consumers. It embraces all those activities which are necessary for maintaining a free flow of goods and services. It includes trade and auxiliary to trade.
Commerce = Trade + Auxiliary to Trade
1. Trade: Trade refers to buying and selling of goods and services with the objective of earning profit. It is classified into two categories.
(i) Internal Trade: It takes place within a country. Internal trade is classified into two categories-retail trade and wholesale trade.
(ii) Retail Trade: It refers to buying of goods and services in relatively small quantities and selling them to the ultimate consumers.
(a) External Trade: It is done between two or more countries. External trade can be classified into three categories.
(b) Import Trade: If goods are purchased from another country, it is called import trade.
(c) Export Trade: If goods are sold to other countries, it is called export trade.
(d) Entrecote Trade: Where goods are imported for export to other countries e.g., Indian firm may import some goods from America and export the same goods to Nepal.
2. Auxiliaries to Trade: All those activities which help in removing various hindrances which arise in connection with the production and distribution of goods are called auxiliaries to trade. An overview of these activities is given below.
1. Transportation and Communication: The production of goods takes place at one place whereas these are demanded in different parts of the country. The obstacle of place is removed by the transport. Along with transport, communication is also an important service. It helps in exchange of information between producers consumers and traders. The common communication services are postal service, telephone, fax, internet etc.
2. Banking and Finance: Business needs funds for acquiring assets, purchasing raw materials and meeting other expenses. Necessary funds can be obtained from a bank.
3. Insurance: It provides a cover against the loss of goods, in the process of transit, storage, theft., fire and other natural calamities.
4. Warehousing: There is generally a time lag between the production and consumption of goods. This problem can be solved by storing the goods in warehouses.
5. Advertising: Advertising brings goods and services to the knowledge of prospective buyers. It is through advertising that the customers come to know about the new products and their utility.
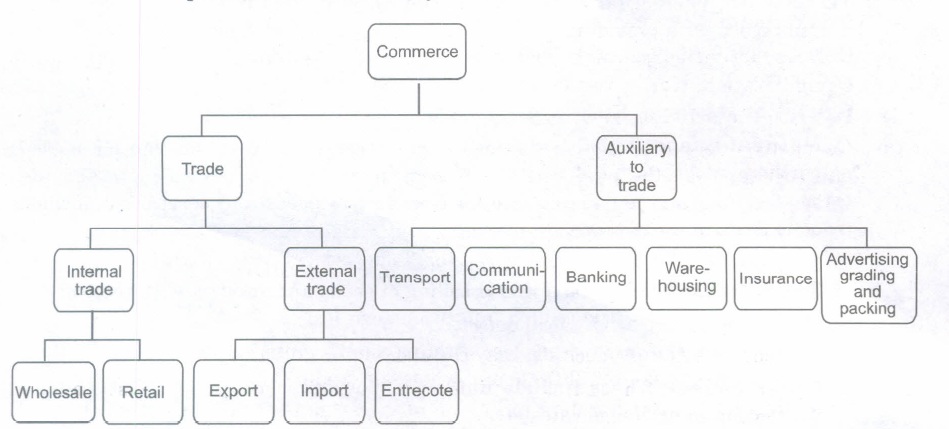
-
Since a business has to balance a number of needs and goals, it requires multiple objectives.
Business is dependent on many people's satisfaction whose objectives for being involved in it are different and many times conflicting. Owners want profits, employees want good working conditions and remuneration, investors want good return and consumers want good quality product. Therefore, a business needs to have multiple objectives. Some of these objectives are given below:
(a) Market standing: Business can survive for a longer period only if it is able to capture a big share in the market and has market standing.
(b) Innovation: It means developing new products and their multiple uses. Old customers can be maintained and new can be attracted by innovation only.
(c) Improving productivity: Every business enterprise must aim at greater productivity by making optimum use of available resources.
(d) Earning profit: One of the objectives of business is to earn profits on the capital invested. Every business must earn a reasonable profit to survive and grow.
(e)Optimum use of physical and financial resources: Every business requires physical (plant, machine, office etc) and financial resources (money or funds) to produce goodsand services; the business enterprise must aim to use them efficiently.
(f) Workers performance and attitude: Ev.ery business enterprise must aim at improving its workers' performance and creating positive attitudes towards workers. It will boost the morale of the employees.
(g) Social Responsibility: A business is a part of society and so it must meet the expectations of the society. It can set goals in the areas of the environmental protection, supply of desired quality of products, employment generation etc. -
Following factors are considered while starting a new business:
1. Selecting the line of business: The first thing to be decided by the entrepreneur is the line and type of business to be undertaken.
2. Scale or size of business: After deciding the line of business the businessman must decide whether he/she wants to set up largescale or small scale business.
3. Choice of form of business organization: The next decision must be taken is to finalise the form of business i.e., to set up sale, proprietorship, partnership or joint stock company.
4. Location of business enterprise: The entrepreneur has to decide the place where the business will be located. Before taking this decision he/she must find out availability of raw materials, power, labour, banking, transportation etc.
5. Financial requirement: The businessman must analyse the amount of capital he/ she might require to buy for fixed assets and for working assets). Proper financial planning must be done to determine the amount of funds needed.
6.Physical facilities: It includes machinery, equipment building etc. This decision depends upon the size, scale and type of business activities he/she wants to carry on.
7. Plant layout: Showing the physical arrangement of machines and equipment needed to manufacture a product.
8. Competent and committed workforce: The entrepreneur must find out the requirement of skilled and unskilled workers and managerial staff to perform various activities.
9. Tax planning: The entrepreneur must try to analyse the types of taxes, because there are a number of tax laws in the country which affect the functioning of business.
10. Setting up the enterprise: After analysing the above mentioned points carefully the entrepreneur can start the business which would mean mobilising various resources and completing legal formalities. -
Commerce is related to the exchange and distribution of goods and services. It involves bade and activities which facilitate trade like transportation, banking, warehousing, and finance, etc. Commerce can be defined as the sum total of all such activities which are related to transfer of goods and services from manufacturer to consumer, i.e., from the place of production to the place of consumption.
Commerce is of great importance in the business world:
1. Removal of Obstacles or Hindrance of Trade:
(a) Removing the hindrance of person: It means lack of information to producer about consumer and to consumer about the producer. It is removed by advertising.
(b) Transportation removes the hindrance of place.
(c) Storage and warehousing activities remove the hindrance of time.
(d) Banking removes the hindrance of finance.
(e) Insurance removes the hindrance of risk.
(f) Advertising removes the hindrance of information.
These functions are divided into:
1. Service Functions
Those activities which help in removing hindrance of place, i.e. distance, knowledge, information and risk are included in service functions. These activities make use of the following means:
(i) Transportation
(ii) Communication
(iii) Insurance
(iv) Advertisement
(v) Entertainment services.
2. Financial Functions
It includes those activities which help in removing hindrance to finance. It includes:
(i) Commercial banks
(ii) Financial institutions like LIC, UTI, etc.
(iii) Stock exchanges
(iv) Private financiers
(v) Lease, hire purchase and installment supply agencies.
3. Marketing Functions
Those activities which help in the removal of the hindrances of exchange and person are included in this category. It includes:
(i) Channels of distribution
(ii) Storing and warehousing facilities
(iii) Packaging, grading and trade marks. -
Yes, we agree. Economic activities are undertaken with an economic motive, i.e., to earn money, but non-economic activities are undertaken without any economic purpose. For example, when our parents go to office or workplace, it is an economic activity, but when a mother cooks food for their children, we do some donations, we get pocket money, we take a bath, and these are non economic activities. But these activities cannot take place unless and until we have money to support them.
No one can work without getting a sound sleep, while sleeping is a non-economic activity. Similarly, bathing is a non-economic activity, but it is compulsory to be healthy. Without being healthy getting involved in economic activity is not possible. Therefore, economic and non-economic activities don't substitute, but complementary to each other. -
If one starts their own business, our social objectives will be of utmost importance to me because:
(a) It will create employment opportunities in the economy. He/she will make use of such methods which are desirable from society point of view.
(b) It will help us to provide good quality product at reasonable prices to customers.
(c) It will keep environment pollution free.
(d) When we will concentrate on these objectives, it will satisfy one consumers and employees. Consumer satisfaction will lead to improvement in these goodwill and market standing. Employee satisfaction will lead to increase in productivity. These two factors will increase profits in the long run automatically.



































