CBSE 11th Standard Chemistry Subject Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Ncert Exemplar 3 Mark Questions 2021
By QB365 on 27 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated NCERT Exemplar Questions for Class
11, and also provide the detail solution for each and every NCERT Exemplar questions. NCERT Exemplar questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 11th Standard Chemistry Subject Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Ncert Exemplar 3 Mark Questions 2021
11th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Chemistry
-
Explain the non-linear shape of H2S and non-planar shape of pcl3 using valence shell electron pair repulsion theory.
(a) -
Give reasons for the following. Covalent bonds are directional bond while ionic bonds are non-directional.
(a) -
Give reasons for the following. Ethyne molecule is linear.
(a) -
Which of these compounds has the highest dipole moment?
(a) -
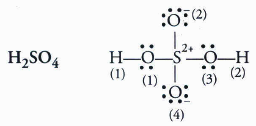
Write lewis structure of the following compounds and show formal charge each atom.
(a)
*****************************************
CBSE 11th Standard Chemistry Subject Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Ncert Exemplar 3 Mark Questions 2021 Answer Keys
-
H2S-In the central atom is sulphur. There are 6 electrons in its valence shell (16S = 2,8,6).Two electrons are shared with two H-atoms and the remaining four electrons are present as two one pair. Hence, total pairs of electrons are four(2 bond pairs and 2 lone pairs).
Due to the presence of 2 lone pairs the shape becomes distorted tetrahedral or angular or bent (non-linear).
PCl3-In the central atom is phosphorus. There are 5 electrons in its valence shell (16P = 2,8,5).Three electrons are shared with three Cl-atoms and the remaining two electrons are present as one long pair. Hence, total pairs of electrons are four(1 lone pairs and 3 bond pairs). Due to the presence of one lone pair, the shape becomes pyramidal (non-planar). -
A covalent bond is formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals. The direction of overlapping gives the direction of bond. In ionic bond, the electrostatic field of an ion is non-directional. Each positive ion is surrounded by a number of anions in any direction depending upon its size and vice-versa.
That's why covalent bonds are directional bonds while ionic bonds are non-directional. -
In ethyne molecule, both the carbon atoms are sp hybridised having two unhybridised orbitals, i.e. 2Px and 2Py. The two sp hybrid orbitals of both the carbon atoms are oriented in opposite direction forming an angle of 180o.
\(H-C\overset { \sigma }{ \underset { 2\pi -bond }{ \equiv } C } -H\)
That's why ethyne molecule is linear. -
Z has seven electrons in its valence shell. It is the most electronegative element. Therefore, HZ will have the highest dipole moment.
-

Formal charge on an atom in a Lewis structure
= [total number of valence electrons in free atom]
- [total number of non-bonding (lone pairs) electrons]
- \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)[total number of bonding or shared electron]
Formal charge on H = 1 - 0 x 2 = 0
Formal charge on N = 5 - 0 x 8 = 1
Formal charge on O (1) = 6 - 4 - x 4 = 0
Formal charge on O (2) = 6 - 4 - x 4 = 0
Formal charge on O (3) = 6 - 6 - x 2 = -1
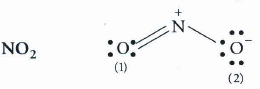
On solving we get, formal charges on O(1), N and O(2) as 0, +1 and -1 respectively.
Similarly, on solving we get formal charge on H(1), H(2), O(2), O(3), O(4) ans S, as 0, 0, 0, -1 , 0, -1 and +2 respectively.



































