CBSE 11th Standard Chemistry Subject State of Matter Ncert Exemplar 3 Mark Questions 2021
By QB365 on 26 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated NCERT Exemplar Questions for Class
11, and also provide the detail solution for each and every NCERT
Exemplar questions. NCERT Exemplar questions are latest updated
question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 11th Standard Chemistry Subject State of Matter Ncert Exemplar 3 Mark Questions 2021
11th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Chemistry
-
Calculate the total pressure in a mixture of 8 g of dioxygen and 4 g of dihydrogen confined in a vessel of 1 dm3 at 27\(^{o}\)C. (R = 0.083 bar dm3 K-1 mol-1)
(a) -
Explain the term 'Laminar flow'. Is the velocity of molecules same in all the layers in laminar flow? Explain your answer.
(a) -
The variation of the vapour pressure of different liquids with temperature is shown in the figure below.
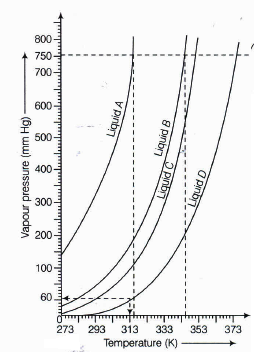
If we take liquid C in a closed vessel and heat it continuously, at what temperature will it boil?(a) -
A vessel of 120 mL capacity contains a certain amount of gas at 35°C and 1.2 bar pressure. The gas is transferred to another vessel of volume 180 mL at 35°C. What would be its pressure?
(a) -
The values of the van der Waal's constants for a gas are a = 4.10 dm6 bar mol-2 and b = 0.035 dm3 mol-1. Calculate the values of the critical temperature and critical pressure for the gas.
(a)
*****************************************
CBSE 11th Standard Chemistry Subject State of Matter Ncert Exemplar 3 Mark Questions 2021 Answer Keys
-
Moles of O2, nO2 = \(\cfrac{mass}{mol.wt.}=\cfrac{8}{32}=0.25mol\)
[mol.wt. of O2 = 16\(\times\)2 = 32]
Moles of H2, nH2 = \(\cfrac{4}{2}=2.0mol\)
[mol.wt. of H2 = 1 \(\times\)2 = 2 ]
Total number of moles = 0.25 + 2.0 = 2.25mol
Pressure, p = \(\cfrac{nRT}{V}\)
\(\cfrac { 2.25mol\times 0.083bar \ dm^{ 3 }K^{ -1 }mol^{ -1 }\times 300K) }{ (1 \ dm^{ 3 }) } \)
p = 56.025 bar -
When a liquid flows over a fixed surface, the layer of molecules in the immediate contact of surface is stationary. The velocity of the upper layers increases as the distance of layers from the fixed layer increases. This type of flow in which there is a regular gradation of velocity in passing from one layer to the next is called laminar flow.
In laminar flow, the velocity of molecules is not same in all the layers because every layers offers some resistance or friction to the layer immediately below it.

Graduation of velocity in the laminar flow. -
In a closed vessel, liquid C will not boil because pressure inside keep on increasing.
-
Given,
Initial pressure, p1 = 1.2 bar
Initial volume, V1 = 120 mL
Final volume, V2 = 180 mL
Since the temperature remains constant, the final pressure (p2) can be calculated using Boyle’s law.
According to Boyle’s law,
\( p_{1} V_{1}=p_{2} V_{2} \)
\(p_{2}=\frac{p_{1} V_{1}}{V_{2}} \)
\(=\frac{1.2 \times 120}{180} \mathrm{bar} \)
\(=0.8 \mathrm{bar} \)
Therefore, the pressure would be 0.8 bar. -
(i) Calculation of critical temperature (Tc)
a = 4.10 dm6 bar mol-1
b = 0.035 dm3 mol-1
R = 0.0821 dm3 bar mol-1 K-1.
Now, critical temperature, Tc = \(\frac{8a}{27Rb}\)
Substituting the values, Tc = \(\frac{8\times4.10}{27\times0.0821\times0.035}\)
(ii) Calculation of critical pressure (Pc)
Pc\(\frac{a}{27b^2}\) = \(\frac{4.10}{27\times0.0821\times0.035}\) = 123.96 bar



































