CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Biotechnology and its Applications Case Study Questions With Solution 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 12 Biology, and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Biotechnology and its Applications Case Study Questions With Solution 2021
12th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Biology
-
After green revolution, now a stage has come when further increase in crop yield with the existing crop varieties is not possible. Use of agro-chemicals is two expensive for the farmers and are too harmful for animals and the environment. The answer to the questions whether there is a method to increase the yield and reduce the use of agro-chemicals, is the use of genetically modified (GM) crops.
Write six points on the advantages ofthe GM crops.(a) -
In mammals, insulin is synthcsised as a pro-hormone. Observe the diagram showing the maturation of pro-insulin into insulin given below and answer the questions that follow.
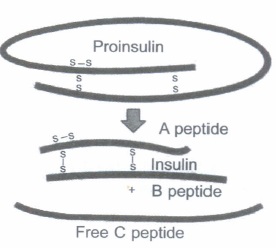
(a) Why is it called pro-insulin?
(b) Mention the chemical changes that the proinsulin undergoes to become the mature functional insulin.
(c) What is the challenge in the production ofinsulin using rDNA techniques?(a) -
A multinational company (XYZ) marketed a medicine extracted from medicinal herbs grown in the sprawling fields in a foreign country. This herb is found growing in our country only and no compensation was paid or permission taken from the relevant authority.
(a) What is the term used to refer to such an act committed by the multinational company?
(b) Justify the meaning of the term.
(c) What has the Indian Government done to prevent such deeds?(a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Transgenic cows have extra gene or genes inserted into their DNA. Firstly the genes for the desired product is identified and sequenced. Then a gene construct containing this desired gene is introduced into female cow cells. Transgenic bovine cells are selected and fused with bovine oocytes that have had all of their chromosomes removed. Once fused with the oocyte, the transgenic cells chromosomes are reprogrammed to direct development into an embryo which can be implanted into a recipient cow. The resulting transgenic cow only express the trans gene in her milk. This is because expression of the trans gene is controlled by a promoter specific to lactating mammary cells. The first transgenic cow was 'Rosie:
(i) The gene construct with desired gene is introduced into female cow cells by(a) transformation (b) transduction (c) transfection (d) transplantation. (ii) Production of transgenic cow fulfill the objective of
(a) increased milk production (b) increased meat production (c) molecularfarming (d) all of these (iii) The name of first transgenic cow is
(a) Tracy (b) Dolly (c) Rosie (d) AND!. (iv) Transgenic cow is produced through the implantation of _____containing transgene into recipient cow.
(a) ova (b) embryo (c) mammary cell (d) both (a) and (b) (v) Assertion : Transgenes only express in the mammary glands of transgenic cow.
Reason : Transgenes are present in chromosomes of every cell in transgenic cow(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion. (b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion (c) Asgertion is true but reason is false. (d) Both assertion and reason are false. (a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Insulin used to cure diabetes was earlier extracted from pancreas of slaughtered cattle and pigs. Insulin extracted from an animal source, though caused some patients to develop allergy or other types of reactions to the foreign protein. Human insulin consists of two short polypeptide chains: chain A and chain B, that are linked together by disulphide bridges. In mammals including humans, insulin is synthesised as a pro-hormone which contains an extra stretch called the C-peptide. This C peptide is not present in mature insulin and is removed during maturation into insulin.
(i) Identify A in the given figure.
(a) Polypeptide chain A (b) Polypeptide chain B (c) Polypeptide chain C (d) None of these (ii) The following is a list of some stages involved in producing human insulin from genetically engineered bacteria.
1. The bacteria are cultured in a fermenter for large scale production.
2. Recombinant insulin is extracted from the bacterial cells that expresses insulin gene.
3. The same restriction enzyme is used again to cut the bacterial plasmid for insertion of the human insulin gene.
4. Bacteria take up the plasmid carrying the insulin gene.
5. A restriction enzyme is used to cut human DNA to extract the insulin gene.
Select the correct order of these stages.(a) 1,5,3,4,2 (b) 2,4,3,5,1 (c) 4,5,3,2,1 (d) 5,3,4,1,2 (iii) To insert the insulin gene into bacterial DNA, both the bacterial plasmid and the human chromosome containing the insulin gene are treated with the same restriction enzyme. Using the same restriction enzyme ensures that
(a) DNA ligase is able to join the segments of human and bacterial DNA (b) the exact length of nucleotides matching the insulin gene is removed from the plasmid (c) both the bacterial and human DNA will contain sticky ends (d) Sticky ends in the cut plasmid and insulin gene are complementary. (iv) Why is the fermentor important for the production of human insulin by transgenic bacteria
(a) It provides optimal conditions for the transgenic to multiply rapidly. (b) It facilitates the extraction and purification of insulin from the transgenic bacteria. (c) It maximise the rate of fermentation of the transgenic bacteria. (d) It provides the low-oxygen conditions that are important for insulin production. (v) A bacteriologist carries out his first attempt at engineering E.coli with the gene for human insulin. During the process, he realises that his stock of DNA ligase has depleted but decides to continue anyway. What is a likely consequence of his decision?
(a) Bacteria with the rDNA will not be able to form colonies in a fermenter (b) The resulting plasm ids are not able to enter the E.coli bacteria even after applying heat shock. (c) The resulting E.coli bacteria do not contain the human insulin gene. (d) The bacterial plasm ids do not have sticky ends and are unable to accommodate the human gene. (a)
Case Study Questions
*****************************************
CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Biotechnology and its Applications Case Study Questions With Solution 2021 Answer Keys
-
Advantages:
(i) Genetic modification has made the crops more tolerant to abiotic stresses like cold, heat, drought, salinity, etc.
(ii) It has reduced the dependence of crops on chemical pesticides as they are made pest-resistant.
(iii) Post-harvest losses are much reduced.
(iv) As the plants have increased efficiency of mineral usage, the early exhaustion of fertility of soil is prevented.
(v) Food produced from GM (Genetically Modified) crops has enhanced nutritional value.
(vi) Genetic modification has been used to create tailormade plants to supply resources such as starch, fuels, pharmaceuticals, etc. to industries -
(a) It is called pro-insulin because it needs to be processed before it becomes a mature and fully functional hormone, insulin.
(b) (i) The C-peptide is removed.
(ii) The peptides A and B are joined by disulphide bridges.
(c) The major challenge was getting the two polypeptide chains assembled intoa mature form. -
(a) Biopiracy
(b) Biopiracy refers to the use of bioresources by multinational companies and other organisations without proper authorisation from the countries and people concerned without compensatory payment.
(c) (i) India has framed the Indian Patents Bill.
(ii) Recently, the parliament has cleared the second amendment of the Indian Patents Bill. -
(i) (c)
(ii) (d) : The two chief objectives of transgenic cow production are as follows: (i) increased milk and meat production and (ii) molecular farming.
(iii) (c)
(iv) (b) : Transgenic bovine cells are selected and fused with bovine oocytes that have had all its chromosomes removed. Once fused with oocyte, the transgenic cells chromosomes are reprogrammed to direct development into embryo which is implanted into recipient cow.
(v) (b) -
(i) (c) : A represents polypeptide chain C which is removed prior to insulin formation.
(ii) (d)
(iii) (d) : Each particular restriction enzyme produces unique sticky ends. Using the same enzyme for both the bacterial and human DNA will produce complementary sticky ends that can bind together by complementary base pairing. This would allow the human insulin gene to be inserted into the plasmid.
(iv) (a) : The optimal temperature, pH, oxygen and nutrient conditions in the fermenter allow the bacteria containing the insulin gene to reproduce quickly and produce large quantities of it.
(v) (c) : DNA ligase forms strong hydrogen bonds between the DNA bases on the human insulin gene and the bacterial plasmid, producing a continuous double stranded DNA loop. Without DNA ligase, the human insulin gene, despite being able to undergo complementary base pairing with the bacterial DNA at the sticky ends would not be securely inserted into the plasmid. Thus, the resulting E.coli bacteria would receive plasm ids that lack the human insulin gene.
Case Study Questions






































