CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Biotechnology: Principles and Processes Case Study Questions 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 12 Biology, and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Biotechnology: Principles and Processes Case Study Questions 2021
12th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Biology
-
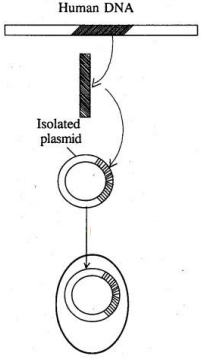
(a) Name the particular technique in Biotechnology, whose steps are shown in the figure.
(b) Name the steps 1 to 4 marked in the figure.
(c) Give an example where a human gene product is. obtained from transgenic bacteria.(a) -
(a) Name and write the significance of enzyme X.
(b) Name and write the role of enzyme Y.
(c) Name the processes A and B.(a) -
Restriction enzymes typically recognize a symmetrical sequence of DNA.
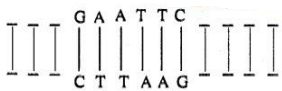
Notice that the top strand is the same as the bottom strand, but reads backward. When the enzyme cuts the strand between G and A, it leaves overhanging chains:

(a) What is this symmetrical sequence of DNA known as?
(b) What is the significance of these overhanging chains?
(c) Name the restriction enzyme that cuts the strand between G and A.(a) -
The following diagram illustrates the linking of DNA fragements. Answer the questions that follow the illustration.
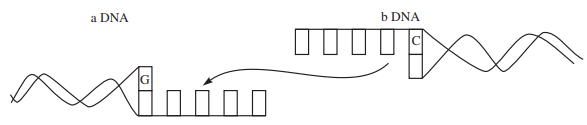
(a) Name 'a' and 'b'.
(b) Complete the palindrome, which is recognised by EcoRI.
(c) Name the enzyme that can link the two DNA fragments.(a) -
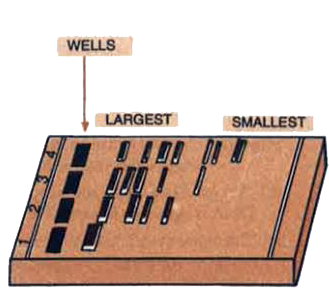
(a) What does the diagram given above, depict?
(b) What is meant by 'largest' and 'smallest' in the diagram'?
(c) Name the compound used to visualise them.
(d) Define elution.(a)
Case Study Questions
*****************************************
CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Biotechnology: Principles and Processes Case Study Questions 2021 Answer Keys
-
(a) Recombinant DN Atechnology/Genetic engineering.
(b) 1. Isolation of the desired segment of DNA.
2. Ligation of the isolated DNA to a plasmid vector.
3. Introduction of rDNA into the bacterial cell.
4. The bacterium produces the gene product.
(c) Human insulin is produced by transgenic Escherichia coli cells. -
(a) Restriction endonuclease - the same restriction enzyme cuts the foreign DNA and vector/plasmid DNA.
(b) DNA ligase joins the foreign DNA segment to the plasmid.
(c) A is transformation.
B is cell division or clone formation. -
(a) It is called a palindromic sequence.
(b) The overhanging chains, called 'sticky ends' facilitate the action of DNA ligase.
(c) EcoRI. -
(i) a–Vector DNA
b–Foreign DNA
(ii) 5' — GAATTC — 3'
3' — CTTAAG — 5'
(iii) DNA ligase -
(a) It depicts agarose gel electrophoresis used for separation of DNA fragments.
(b) The 'largest' and 'smallest' mean the DNA fragments oflarge size and small size, respectively.
(c) Ethidium bromide.
(d) Elution is the process in which the separated bands of DNA are cut out from the gel and extracted.
Case Study Questions






































