CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Biotechnology: Principles and Processes Case Study Questions With Solution 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 12 Biology, and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Biotechnology: Principles and Processes Case Study Questions With Solution 2021
12th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Biology
-
A schematic representation of the steps in Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is shown below. Answer the questions that follow:
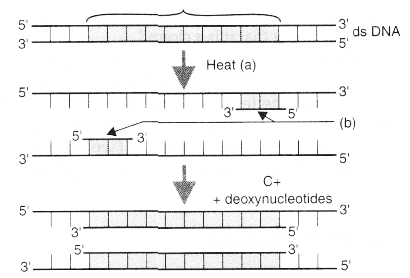
(a) Name the steps A and D in the PCR.
(b) Identify B. What are they chemically?
(c) What is C? Name its source organism.(a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Gene manipulation is a fast emerging science. It started with development of recombinant DNA molecule. It is named variously as DNA manipulation biotechnology, recombinant DNA technology and genetic engineering. This technology, that mostly involves cutting and pasting of desired DNA fragments, is based on two important discoveries in bacteria, i.e., presence of plasmid in bacteria and restriction endonucleases. Paul Berg was able to introduce a gene of SV-40 into a bacterium. The science of recombinant DNA technology took birth when Cohen and Boyer (1973) were able to introduce a piece of gene containing foreign DNA into plasmid of E.coli.
(i) Biotechnology is also known as(a) DNA manipulation biotechnology (b) recombinant DNA technology (c) genetic engineering (d) all of these. (ii) A bacterial plasmid is a/an
(a) extra chromosomal material that do not replicate (b) extra chromosomal material that undergo replication with or without chromosomal DNA (c) tubular structures that help in conjugation (d) bristle like solid structure that help in adhesion. (iii) Father of genetic engineering is
(a) Paul Berg (b) Arber (c) Nathan (d) Smith. (iv) Which of the following is used by Paul Berg to introduce a gene of SV-40 in a bacterium?
(a) E. coli (b) cos-plasmids (c) Lambda phage (d) None of these (v) Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Assertion : Biotechnology started with the development of recombinant DNA molecule.
Reason : Biotechnology mostly involves cutting and pasting of desired DNA fragments.(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion. (b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion. (c) Assertion is true but reason is false. (d) Both assertion and reason are false. (a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
The foundations of recombinant DNA (rDNA) were laid by the discovery of restriction enzymes. These enzymes are present in many bacterias where they function as a part of their defense mechanism called the Restriction Modification system (RM system). Molecular basis of this system was explained first by Werner Arber in 1962. The Restriction t-'l0dification system consists of two components:
1. A restriction enzyme (called restriction endonuclease) identifies the introduced foreign DNA and cuts it into pieces.
2.The second component is a modification enzyme (methylase) that adds a methyl group to DNA at specific site to protect it from the restriction enzyme cleavage.
(i) Restriction endonucleases are enzymes present in (i) where they function as a part of (ii) mechanism.(a) (i) bacteria (ii) digestive (b) (i) protists (ii) transcription (c) (i) plant cells (ii) replication (d) (i) prokaryotes (ii) defence (ii) Which of the following statements regarding modification enzyme is correct?
(a) It adds methyl group to one or two bases usually within the host DNA sequence to protect it from the restriction enzyme. (b) It adds ethyl group to one or two bases usually within the sequence recognised by the restriction enzymes. (c) It adds methyl group to only one of bases within the foreign DNA sequence that is recognised by the restriction enzymes. (d) None of these (iii) Which of the following is a type II restriction enzyme?
(a) Alu I (b) EcoR I (c) BamH I (d) All of these (iv) Which of the following is the first discovered restriction endonuclease?
(a) Sal I (b) EcoR I (c) Hind II (d) EcoR II (v) Components of Restriction Modification System include
(a) restriction enzyme (b) modification enzyme (c) lysing enzyme (d) both (a) and (b). (a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to(v) given below:
In recombinant DNA technology, the fragments of DNA generated after cutting the DNA by restriction enzymes are separated according to their size or length by gel electrophoresis. Gel electrophoresis is performed in a gel matrix so that molecules of similar electric charges can be separated on the basis of size. Most commonly used matrix in gel electrophoresis is agarose. The fragments are separated under the influence of electric field. The separated DNA fragments can be seen only after staining the DNA with compound known as ethidium bromide (EtBr) followed by exposure to UV radiation as bright orange band.
(i) Gel electrophoresis is used for the separation of(a) DNA only (b) DNA and RNA only (c) DNA and proteins only (d) DNA, RNA and proteins. (ii) Most commonly used matrix is (i) which is a (ii) extracted from (iii).
(a) (i) agarose (ii) polysaccharide (iii) sea weed (b) (i) agarose (ii) protein (iii) sea weed (c) (i) EtBr (ii) polysaccharide (iii) sea weed (d) (i) EtBr (ii) protein (iii) bacteria (iii) A DNA molecule was treated with a restriction endonuclease and three fragments of size (i) 426 kb, (ii) 129 kb and (iii) 46 kb were obtained. Identify the order in which these bands will arrange themselves in the gel plate after gel electrophoresis is completed. (Assuming that negative part of electrode is towards the well)
(a) (iii) ➝ (ii) ➝ (i) (b) (i) ➝ (ii) ➝(iii) (c) (i) ➝ (iii) ➝ (ii) (d) (iii) ➝ (i) ➝ (ii) (iv) Which of the following statements regarding gel electrophoresis is incorrect?
(a) Separated DNA fragments can be seen only after staining DNA with EtBr. (b) DNA fragments are separated according to their size. (c) Under the influence of electric field, positively charged molecules move towards the anode and negatively charged molecules move towards the cathode. (d) None of these (v) The factor that will not affect the rate of DNA migration in gel electrophoresis is
(a) size of DNA molecule (b) concentration of DNA (c) voltage supplied (d) concentration of the gel (a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
The DNA, which is transferred from one organism into another by joining it with the vehicle DNA is called passenger or foreign DNA. Generally three types of passenger DNAs are used. These are complementary DNA (cDNA), synthetic DNA (sDNA) and random DNA. Complementary DNA (cDNA) is synthesized on RNA template (usually mRNA) with the help of reverse transcriptase. Synthetic DNA (sDNA) is synthesized on DNA template or without a template. Random DNA are small fragments formed by breaking a chromosome of an organism in the p.resence of restriction endonucleases.
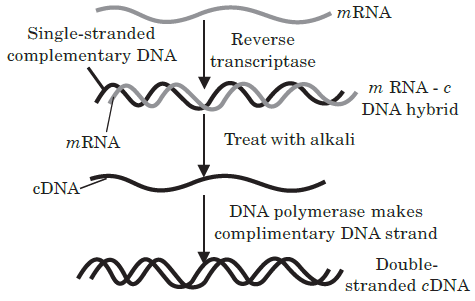
(i) Reverse transcriptase enzyme was discovered by(a) Temin and Baltimore (b) Cohen and Boyer (c) Arber and Nathan (d) Paul Berg. (ii) During cDNA formation, what would happen if DNA formed by reverse transcriptase is not treated with the alkali?
(a) cDNA will not be digested (b) mRNA will not be digested (c) Hydrogen bonds will not form between base pairs (d) mRNA will not be formed. (iii) Enzyme that helps in the formation of double stranded cDNA is
(a) DNA synthetase (b) ligase (c) DNA polymerase (d) helicase. (iv) DNA polymerase can be obtained form
(a) retrovirus (b) Agrobacterium (c) tobacco mosaic virus (d) Thermus aquaticus (v) DNA synthesised without a template is referred to as
(a) complementary DNA (b) random DNA (c) synthetic DNA (d) Z-DNA (a)
Case Study Questions
*****************************************
CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Biotechnology: Principles and Processes Case Study Questions With Solution 2021 Answer Keys
-
(a) A - Denaturation; D - Extension.
(b) B - Primers; they are oligonucleotides.
(c) C - Taq polymerase; its source organism is Thermus aquaticus. -
(i) (d)
(ii) (b) : Plasmid in a bacterial cell is an extra chromosomal material that undergo replication with or without chromosomal DNA.
(iii) (a)
(iv) (c) : In 1972, Paul Berg was able to introduce a gene of SV-40 virus into a bacterium with the help of lambda phage.
(v) (b) -
(i) (d)
(ii) (a)
(iii) (d) : Different examples of Type II restriction endonuclease are Alu I, EcoR I, BamH I, etc.
(iv) (c)
(v) (d) : The restriction modification system consists of two components
(i) A restriction enzyme called restriction endonucleases which identifies the introduced foreign DNA and cuts it into pieces and
(ii) A modification enzyme (methylase) that adds a methyl group to DNA at a specific site to protect the site from restriction endonuclease cleavage. -
(i) (d) : Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate fragments of molecules, i.e., DNA, RNA and protein.
(ii) (a)
(iii) (b)
(iv) (c) : Under the influence of electric field positively charged molecules move towards the cathode and negatively charged molecules move towards the anode.
(v) (b) : Concentration of DNA will not affect the migration of DNA molecule in a gel electrophoresis. As in gel electrophoresis, molecules separate according to their size therefore DNA size will affect migration. Increased voltage supply will increase rate of migration and the more concentrated gel will reduce rate of migration. -
(i) (a)
(ii) (b) : The cDNA formation involves the alkaline denaturation of the mRNA-cDNA hybrid. The double stranded DNA molecule formed after the activity of reverse transcriptase is treated with alkali to digest mRNA.
(iii) (c) : A cDNA strand is formed on the separated single stranded DNA template with the help of DNA polymerase enzyme.
(iv) (d)
(v) (c)
Case Study Questions






































