CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Human Reproduction Ncert Exemplar 2 Mark Questions 2021
By QB365 on 24 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated NCERT Examplar Questions for Class 12 Biology, and also provide the detail solution for each and every ncert examplar questions , QB365 will give all kind of study materials will help to get more marks
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Human Reproduction Ncert Exemplar 2 Mark Questions 2021
12th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Biology
-
Given below are the stages in human reproduction.Write them in the correct sequential order:
Insemination, Gametogenesis, Fertilisation, Parturition, Gestation, Implantation.(a)Gametogenesis \(\rightarrow \) Insemination \(\rightarrow \) Fertilisation \(\rightarrow \) Implantation \(\rightarrow \) Gestation \(\rightarrow \) Parturition .
-
Why are menstrual cycles absent during pregnancy?
(a)During pregnancy,the corpus luteum secretes large quantity of progesterone,which inhibits maturation of any other follicle or ovulation;hence menstrual cycles are absent.
-
What is capacitation?
(a) -
Name two organisms which lack sexual reproduction and are immortal. What is an asexual reproductive unit called?
(a) -
Differentiate between spermatogenesis and spermiogenesis.
(a) -
Write the effect of the high concentration of LH on a mature Graafian follicle.
(a) -
The diagram shows the side view of the female reproductive system (i) Label the parts A to D.
(ii) In which region are sperms released during intercourse?
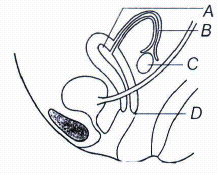 (a)
(a) -
Placenta acts as an endocrine gland. Explain.
(a) -
How is the milk production regulated by hormones in human female? Explain.
(a) -
How does zona pellucida of ovum help in preventing polyspermy?
(a)
2 Marks
*****************************************
CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Human Reproduction Ncert Exemplar 2 Mark Questions 2021 Answer Keys
-
Gametogenesis \(\rightarrow \) Insemination \(\rightarrow \) Fertilisation \(\rightarrow \) Implantation \(\rightarrow \) Gestation \(\rightarrow \) Parturition .
Gametogenesis \(\rightarrow \) Insemination \(\rightarrow \) Fertilisation \(\rightarrow \) Implantation \(\rightarrow \) Gestation \(\rightarrow \) Parturition .
-
During pregnancy,the corpus luteum secretes large quantity of progesterone,which inhibits maturation of any other follicle or ovulation;hence menstrual cycles are absent.
During pregnancy,the corpus luteum secretes large quantity of progesterone,which inhibits maturation of any other follicle or ovulation;hence menstrual cycles are absent.
-
Activation of sperms within the female tract of mammals is called capacitation, without which fertilization is impossible.
-
Amoeba, Euglena; blastos.
-
Differences between spermatogenesis and spermiogenesis are
Spermatogenesis Spermiogenesis It is a process of formation of sperms from immature germ cells. It is a process of transformation of a non-motile spermatid to a motile spermatozoa. Number of cells increased as each spermatogonium produces four spermatids. No change in number of cells as only one spermatid develops into a spermatozoa. -
The high concentrations of LH induce rupture of mature Graafian follicle and causes the release of secondary oocyte thereby causing ovulation in females.
-
(i) A - Utreus B - Fallopian tube C - Ovary D - Vagina
(ii) The penis reaches into the vaginal area thus, the sperms are released in vagina. -
The placenta secretes hormones like human gonadotropins, human placental lactogen, oestrogen and progesterone that are necessary to maintain pregnancy. Due to the secretion of these hormones, it is called an endocrine gland.
-
Prolactin hormone controls the synthesis of milk proteins in the mammary glands, Progesterone controls the development of alveoli of mammary glands and the release of milk during lactation is stimulated by the rise in the level of oxytocin.
-
Polyspermy means an egg has been fertilized by more than one sperms. The zona pellucida is modified by proteases. The proteases destroy the protein link between the cell membrane and the vitelline membrane, remove any receptors that other sperm have bound to, and help to form the fertilization membrane that prevents polyspermy.
2 Marks






































