CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Human Reproduction Ncert Exemplar 5 Mark Questions With Solution 2021
By QB365 on 24 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated NCERT Examplar Questions for Class 12 Biology, and also provide the detail solution for each and every ncert examplar questions , QB365 will give all kind of study materials will help to get more marks
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Human Reproduction Ncert Exemplar 5 Mark Questions With Solution 2021
12th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Biology
-
What roles does pituitary gonadotrophins play during follicular and ovulatory phases of menstrual cycle? Explain the shifts in steroidal secretions.
(a) -
The zygote passes through several development stages till implantation.Describe each stage briefly with suitable diagrams.
(a) -
Describe the specific action of FSH, LH, oestrogen and progesterone in the menstrual cycle.
(a) -
Study the graph given below and answer the questions that follow.
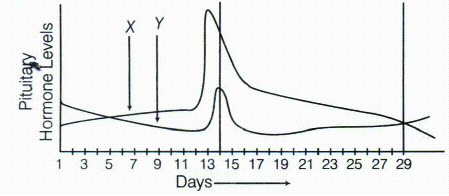
(i) Name the hormones 'X' and 'Y'.
(ii) Identify the ovarian phases during menstrual cycle.
(a) 5th-12th day of the cycle.
(b) 14th day of the cycle.
(c) 16th-25th day of the cycle.
(iii) Explain the ovarian events (a), (b) and (c) under the influence of hormones 'X' and 'Y'(a) -
With reference for events starting from menstrued cycle till the events of parturition give the name of the hormones involved at each stage and explain their role.
(a)
5 Marks
*****************************************
CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Human Reproduction Ncert Exemplar 5 Mark Questions With Solution 2021 Answer Keys
-
Hormonal Control of Menstrual Cycle.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) also called Gonadotropin-releasing Factor (GnRF), is secreted by the hypothalamus of the brain, which stimulates the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH).FSH stimulates the ovarian follicles to produce oestrogens during proliferative phase.LH stimulates the corpus luteum of the ovary to secrete progesterone.
1.Menstrual phase is caused by the reduction of progesterone and oestrogens.
2.Proliferative phase is caused by the increased production of oestrogens.
3.LH causes ovulation.
LH also causes transformation of empty Graafian follicle into corpus luteum by luteinisation inside the ovary. LH also stimulates corpus luteum to secrete progesterone hormone to help in implantation, placentation and maintenance of pregnancy.
4.Secretary phase is caused by increased production of progesterone. -
Cleavage is holoblastic type but there is tendency to show size differences of the blastomeres from the very start. Cleavage occurs during its passage through fallopian tube to uterus.
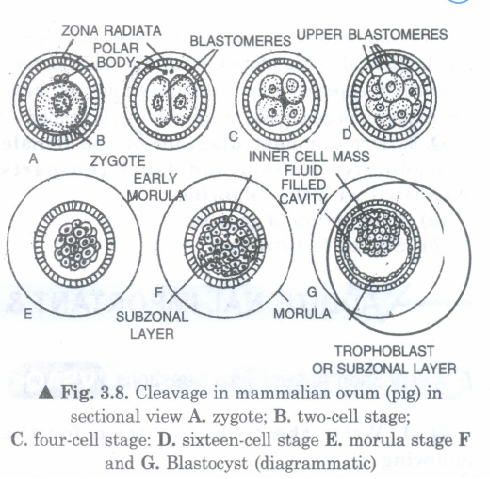
The first cleavage takes place in the cytoplasm of ovum on an imaginary axis (Animal pole to vegetal pole). The first division results into two blastomeres. One blastomere is slightly larger than the other. The larger cell divides first and thus forms the three blastomeres. Then the smaller blastomere divides and thus four blastomeres are formed. It is 4 celled stage.
2nd cleavage is at right angle to the 1st cleavage. One member of the large blastomeres of 4-cell stage divides forming 5-cell condition followed 6-7 stage ultimately 8 celled stage. Successive cleavage divisions result in the formation of solid mass of cells. Thus solid ball-like stage is called morula stage.
Conversion of morula into blastula is initiated by dynamic rearrangement of small blastomeres. A central fluid filled cavity called blastocoel (segmentation cavity) appears. Externally placed blastomeres lose their rounded form and become flat. This trophoblast along with lining of uterus forms extra-embryonic membranes. This provides protection and nourishment to the developing embryo.
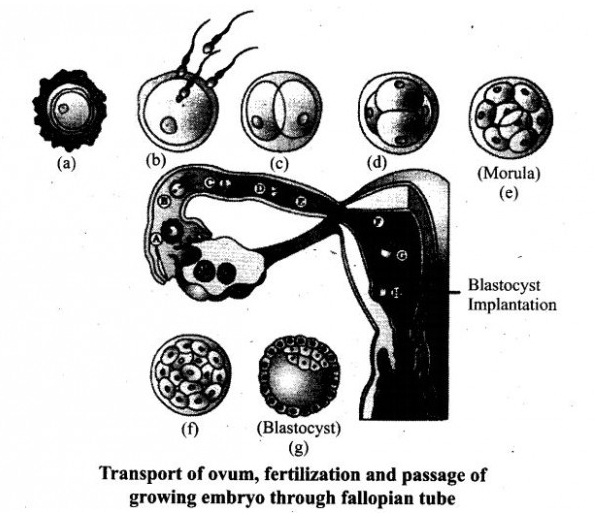
Simultaneouslyzonapellucidadisappears and embryo gets implanted to the uterus. Below the blastodermic vehicle there appears formative tissue i.e. inner cellmass. From this inner cell mass, proper embryo is formed. -
The menstrual cycle is controlled by rhythmic synthesis and release of ovarian hormones under feedback control from the hormones of anterior pituitary. These are discussed below:
(i) Pituitary hormones The gonadotroph cells, of anterior pituitary secrete FSH and LH in females. Their role in menstrual cycle are:
(a) Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) It is secreted during the follicular phase of the cycle and is responsible for follicular development on induction of LH receptors on granulosa cells of the ovary.
(b) Luteinising Hormone (LH) Its primary function is to stimulate the formation of corpus luteum and secretion of estradiol and progesterone from ovary.
(ii) Ovarian hormones Ovary secretes the following hormones under the effect of FSH and LH.
(a) Oestrogen It influences proliferation of the uterine endometrium to prepare for implantation of the fertilised oocyte.
(b) Progesterone secreted from corpus luteum under LH influence, maintains endometrium for implantation It rising level inhibits LH. -
(i) Horne 'X' is Luteinising Hormone (LH) and 'Y' is Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH).
(ii) (a) Follicular phase (proliferative phase).
(b) Ovulatory phase (release of ovum) followed by luteal phase.
(c) Luteal phase.
(iii) (a) FSH is secreted by the anterior pituitary, which stimulates the ovarian follicle to secrete oestrogen, which in turn stimulates the proliferation of the endometrium of the uterine wall.
(b) Both LH and FSH attain a peak level in the middle of cycle (about 14th day). Rapid secretion of LH leading to its maximum level during the mid-cycle is called LH surge. It induces rupture of Graafian follicle and thereby the release of ovum (ovulation). Due to these events, this phase is termed as evulatory phase of menstruate cycle.
(c) The remaining cells of ovarian follicles are stimulated by the LH to develop corpos luteum. The corpus luteum secretes large amount of progesterone, which is essential for the maintenance of endometrium. This is known as luteral phase. -
(i) Rapid release of Luteinising Hormone (LH) ruptures Graafian follicle and release ovum (ovulation).
(ii) Corpus luteum secretes large amount of progesterone hormone that is essential for the maintenance of the endometrium required for implantation of blastocyst leading to pregnancy.
(iii) Placenta produces several hormones like human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG), human Placental Lactogen (hPL). Relaxin is also produced during later phase of pregnancy. Levels of other hormones like oestrogen, progestogen, cortisol, prolactin and thyroxine also increase, which is essential for supporting foetal growth, metabolic changes in mother and maintenance of pregnancy.
(iv) Parturition signals originate from the fully developed foetus and the placenta that induce mild uterine contractions which triggers the release of oxytocin from pituitary. Oxytocin acts on the uterine muscle causing stronger uterine contractions.
5 Marks






































