CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Organisms and Populations Case Study Questions With Solutions 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 12 Biology, and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Organisms and Populations Case Study Questions With Solutions 2021
12th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Biology
-
The graph given below depicts the organismic response to changing external environmental conditions. According to their response, the organisms are grouped into two types.
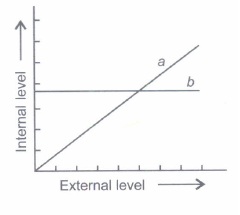
Answer the following questions.
(a) Name the group of organisms, which will show pattern A. Give an example.
(b) ame the group of organisms, which will show pattern B. Give an example.
(c) Define homeostasis.(a) -
'The population of a metro city experiences fluctuations in its population density over a period of time'.
(a) When does the population in a metro city tend to increase?
(b) When does the population in a metro city tend to decline?
(c) If 'N' is the population density at the time 't', write the population density at the time 't + l'.(Delhi 2020).(a) -
If in a population of size 'N', the birth rate is represented as 'b' and the death rate as 'd', the increase or decrease in 'N' during a unit time period 't' will be
dN/dt = (b - d) x N
The equation given above can also be represented as
dN/dt = r x N, where r = (b - d).
(a) What does 'r' represent in the above?
(b) Write anyone significance of calculating 'r' for any population.
(c) In a pond there are 100 frogs. 20 more were born in a year. Calculate the birth rate of this population.(a) -
There is no natural habitat on earth, which is occupied by a single species. In nature, plants, animals and microbes do not and cannot live in isolation. Interspecific interactions arise from the interaction of populations of two different species.
(a) Even a plant species, which makes its own food cannot live alone. Give two examples, where plants depend on other species for survival.
(b) Name the type of interspecific interaction seen in each of the following examples.
(i) Disappearance of smaller barnacles when Balanus dominated intertidal area of the sea coasts of Scotland.
(ii) Clown fish living among the stinging tentacles of sea anemone.
(iii) The Wasp species pollinating a fig inflorescence.
(iv) Cuscuta growing on hedge plants.(a) -
It is generally believed that competition occurs only when closely related species compete for the same resources that are limiting.
Give two examples to show that the above statement is not always true.(a)
Case Study Questions
*****************************************
CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Organisms and Populations Case Study Questions With Solutions 2021 Answer Keys
-
(a) Pattern A - Conformers
e.g. Amphibians
(b) Pattern B - Regulaters
e.g. Mammals
(c) Homeostasis is the process of maintaining a constant internal environment despite the varying external environmental conditions. -
(a) When the sum total of immigration (I) and natality (B) is more than the sum total of emigration (E) and mortality (D), the population increases.
(b) When the sum total of emigration (E) and mortality (D) is more than the sum total of immigration (I) and natality (B), the population declines.

-
(a) 'r ' represents the 'intrinsic rate of natural increase'.
(b) It is an important parameter for assessing the impacts of any biotic and abiotic factor on population growth.
(c) The birth rate is 20/100 or 0.5/frog/year. -
(a) Plants depend on
(i) the soil microbes to break down the organic matter in soil to return the inorganic nutrients for their absorption.
(ii) animals for pollination, without which fruits and seeds cannot be formed.
(b) (i) Competition
(ii) Commensalism
(iii) Mutualism
(iv) Parasitism -
(i) Competition can occur between two unrelated species, when they compete for the same resource, e.g. the visiting flamingoes compete with the resident fishes for zooplanktons in some shallow lakes in South America.
(ii) Resources need not be limiting; in interference competition, the feeding efficiency of one species might be reduced due to the interfering and inhibitory presence of the other species, e.g the abingdon tortoise became extinct within a decade after goats were introduced into Galapagos Islands.
Case Study Questions






































