CBSE 12th Standard Chemistry Subject Biomolecules Chapter Case Study Questions 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 12 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 12th Standard Chemistry Subject Biomolecules Case Study Questions 2021
12th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Chemistry
-
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
When a protein in its native form, is subjected to physical changes like change in temperature or chemical changes like change in pH, the hydrogenbonds are disturbed. Due to this, globules unfold and helix get uncoiled and protein loses its biological activity. This is called denaturation of protein.
The denaturation causes change in secondary and tertiary structures but primary structures remains intact. Examples of denaturation of protein are coagulation of egg white on boiling, curdling of milk, formation of cheese when an acid is added to milk.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
(i) Mark the wrong statement about denaturation of proteins(a) The primary structure of the protein does not change (b) Globular proteins are converted into fibrous proteins. (c) Fibrous proteins are converted into globular proteins. (d) The biological activity of the protein is destroyed. (ii) Which structure(s) of proteins remains(s) intact during denaturation process?
(a) Both secondary and tertiary structures (b) Primary structure only (c) Secondary structure only (d) Tertiary structure only (iii) Cheese is a
(a) globular protein (b) conjugated protein (c) denatured protein (d) derived protein (iv) Secondary structure of protein refers to
(a) mainly denatured proteins and structure of prosthetic groups (b) three-dimensional structure, especially the bond between amino acid residues that are distant from each other in the polypeptide chain (c) linear sequence of amino acid residues in the polypeptide chain (d) regular folding patterns of continuous portions of the polypeptide chain (a) -
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The sequence of bases along the DNA and RNA chain establishes its primary structure which controls the specific properties of the nucleic acid. An RNA molecule is usually a single chain of ribose-containing nucleotide. On the basis of X-ray analysis of DNA, J.D., Watson and F.H.C. crick (shared noble prize in 1962) proposed a three dimensional secondary structure for DNA. DNA molecule is a long and highly complex, spirally twisted, double helix, ladder like structure. The two polynucleotide chains or strands are linked up by hydrogen bonding between the nitrogeneous base molecules of their nucleotide monomers. Adenine (purine) always links with thymine (pyrimidine) with the help of two hydrogen bonds and guanine (purine) with cytosine (pyrimidine) with the help of three hydrogen bonds. Hence, the two strands extend in opposite directions, i.e., are antiparallel and complimentary.
In these questions (i-iv), a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
(i) Assertion: DNA molecules and RNA molecules are found in the nucleus of a cell.
Reason: There are two types of nitrogenous bases, purines and pyrimidines. Adenine (A) and guanine (G) are substituted purines; cytosine (C), thymine (T) and uracil (U) are substituted pyrimidines
(ii) Assertion: In both DNA and RNA, heterocyclic base and phosphate ester linkages are at C-1' and C-5' respectively of the sugar molecule.
Reason: Nucleotides and nucleosides mainly differ from each other in presence of phosphate units.
(iii) Assertion: The backbone ofRNA molecule is a linear chain consisting of an alternating units of a heterocylic base, D-ribose and a phosphate.
Reason: The segment of DNA which acts as the instruction manual for the synthesis of protein is ribose.
(iv) Assertion: The double helical structure of DNA was proposed by Emil Fischer.
Reason: A nucleoside is an N-glycoside of heterocyclic base.(a) -
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Proteins are high molecular mass complex biomolecules of amino acids. The important proteins required for our body are enzymes, hormones, antibodies, transport proteins, structural proteins, contractile proteins etc. Except for glycine, all a-amino acids have chiral carbon atom and most of them have L-configuration. The amino acids exists as dipolar ion called zwitter ion, in which a proton goes from the carboxyl group to the amino group. A large number of a-amino acids are joined by peptide bonds forming polypeptides. The pep tides having very large molecular mass (more than 10,000) are called proteins. The structure of proteins is described as primary structure giving sequence of linking of amino acids; secondary structure giving manner in which polypeptide chains are arranged and folded; tertiary structure giving folding, coiling or bonding polypeptide chains producing three dimensional structures and quaternary structure giving arrangement of sub-units in an aggregate protein molecule.
In these questions (i-iv), a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
(i) Assertion: All amino acids are optically active.
Reason: Amino acids contain asymmetric carbon atoms.
(ii) Assertion: In \(\alpha \) -helix structure, intramolecular H-bonding takes place whereas in \(\beta \) -pleated structure, intermolecular H-bonding takes place.
Reason: An egg contains a soluble globular protein called albumin which is present in the white part.
(iii) Assertion: Secondary structure of protein refers to regular folding patterns of continuos portions of the polypeptide chain.
Reason: Out of 20 amino acids, only 12 amino acids can be synthesised by human body.
(iv) Assertion: The helical structure of protein is stabilised by intramolecular hydrogen bond between -NH and carbonyl oxygen.
Reason: Sanger's reagent is used for the identification of N-terminal amino acid of peptide chain.(a) -
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Glucose is known as dextrose because it occurs in nature as the optically active dextrorotatory isomer. It is essential constituent of human blood. The blood normally contains 65 to 110 mg of glucose per 100 mL (hence named Blood sugar). The level may be much higher in diabetic persons. The urine of diabetic persons also contain considerable amount of glucose. In combined form, it occurs in cane sugar and polysaccharides such as starch and cellulose.
Glucose has an aldehyde group (-CHO), one primary alcoholic group (-CH2OH) and four secondary alcoholic groups (-CHOH) in their structure. Due to the presence five hydroxyl groups (-OH), glucose acetylation. Glucose also undergoes oxidation with mild oxidising agents like bromine water as well as with strong oxidising agents like nitric acid. Since glucose is readily oxidised, it acts as a strong reducing agent and reduces Tollen's reagent and Fehling solution. Glucose exists in two crystalline forms: \(\alpha \) -D-glucose and \(\beta \) -Dglucose undergoes If either of the two forms is dissolved in water and allowed to stand, the specific rotation of the solution changes gradually, until a constant value is obtained. This change is called mutarotation.
In these questions (i-iv), a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
(i) Assertion: A diabetic person carries a packet of glucose with him always.
Reason: Glucose increases the blood sugar level almost instantaneously.
(ii) Assertion: On oxidation with nitric acid, glucose as well as gluconic acid both yield saccharic acid.
Reason: The pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine indicating the absence of free -CHO group.
(iii) Assertion: Glucose reacts with acetyl chloride to form pentaacetyl glucose.
Reason: The formation of pentaacetyl derivative confirms the presence of five -OH groups in glucose.
(iv) Assertion: A certain compound gives negative test with ninhydrin and positive test with Benedict's solution, the compound is an amino acid.
Reason: Glucose is a monosaccharide.(a)
*****************************************
CBSE 12th Standard Chemistry Subject Biomolecules Case Study Questions 2021 Answer Keys
-
(i) (c)
(ii) (b)
(c) : Cheese is a denatured protein
(iv) (d) -
(i) (d): DNA occurs in nucleus of the cell while RNA is found mainly in cytoplasm of the cell.
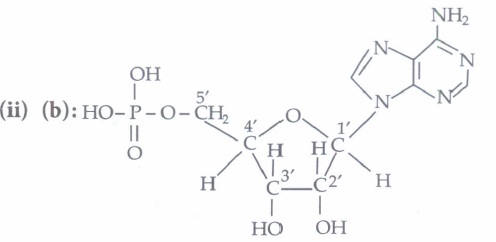
Nucleosides contain only sugar and a base whereas nucleotides contain sugar, base and a phosphate group as well.
(iii) (c): The segment of DNA which acts as the instruction mannual for the synthesis of protein is gene.
(iv) (d): The double helical structure of DNA was proposed by Watson and Crick. -
(i) (d) : All amino acids except glycine are optically active because they contain, asymmetric carbon atom. They exist in both D and L- forms. Most naturally occurring amino acids have L-configuration.
(ii) (b): In a-helix structure, the formation of hydrogen bonds takes place between -co- and -NH groups, whereas in ~-pleated structure, hydrogen bonds are formed between amide groups of two different chains.
(iii) (c) : Out of 20 amino acids, only 10 amino acids can be synthesised by human body.
(iv) (b) -
(i) (a)
(ii) (b):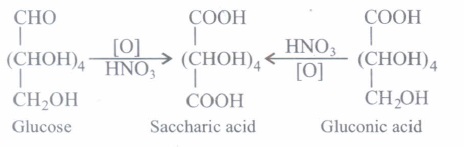
Strong oxidising agents like nitric acid oxidises both the terminal -CHO and -CH2OH groups of glucose to give the dibasic acid, saccharic acid.
(iii) (b)
(iv) (d): If a certain compound gives negative test with ninhydrin and positive test with Benedict's solution then the compound should be a monosaccharide.






































