CBSE 12th Standard Physics Subject Communication Systems HOT Questions 2 Mark Questions 2021
By QB365 on 27 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the HOT Question Papers for Class 12 Physics, and also provide the detail solution for each and every HOT Questions. HOT Questions will help to get more idea about question pattern in every exams and also will help to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 12th Standard Physics Subject Communication Systems HOT Questions 2 Mark Questions 2021
12th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Physics
-
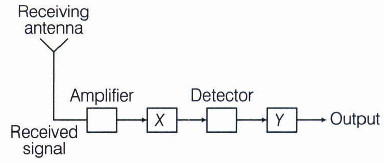
In the given block diagram of a receiver identify the boxes labelled as X and Y and write their functions.
 (a)
(a) -
(a) Describe briefly the three factors which justify the need for translating a low frequency signal into high frequencies before transmission.
(b) Figure shows a block diagram of a detector for AM signal.
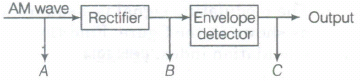
Draw the waveforms for the
(i) input AM wave at A,
(ii) output B at the rectifier, and (iii) output signal at C.(a) -
Differentiate between (i) PAM and (ii) PPM
(a) -
An AM wave is represented by the expression: v = 5 (1 + 0.6 cos 6280 t) sin 221 x 104 t volts
(i) What are the maximum and minimum amplitudes of the AM wave.
(ii) What frequency components are contained in the modulated wave(a) -
The antenna current of an AM transmitter is 8A when only carrier is sent but it increases to 8.93A when the carrier is sinusoidally modulated. Find the percent-age modulation index
(a)
*****************************************
CBSE 12th Standard Physics Subject Communication Systems HOT Questions 2 Mark Questions 2021 Answer Keys
-
X \(\rightarrow\) Intermediate Frequency (IF) stage
Y \(\rightarrow\) Power amplifier
The IF stage change the high-frequency carrier wave into lower frequency wave and amplifier enhances the strength of the signals. -
(a) There are three factors:
(i) Wider Bandwidth: High frequency provide wider bandwidth.
(ii) Distance: High-frequency wave used to carry baseband signals (low-frequency signal) over a distance of several thousand kilometres.
(iii) Cost: High frequency transmits with low cost.
-
(i) Pulse Amplitude Modulation : Amplitude of the pulse varies in accordance with the modulating signal.
.jpg)
(ii) (ii) Pulse Position Modulation. : Pulse position (ie) time of rise or fall of the pulse ) changes with the modulating signal.
-
The AM wave equation is given by ;
v = 5(1+0.6cos6280t) sin 221 X 104 t volts ………….(i)
(i) Maximum amplitude of AM wave
= EC + maEC =5 + 0.6 X 5 = 8V
Minimum amplitude of AM wave
= Ec - maEC =5 - 0.6 X 5 = 2V
(ii) The AM wave will contain three frequency vizfc-fs fc fc+fs 336-1 336 336+1 335KHz 336Khz 337KHz -
Ps = 1/2 ma2 Pc
1.246 = 1 + \(\frac { ma^{ 2 } }{ 2 } \)
ma2/2 = 0.246
ma = (2 x 0.246)1/2 = 0.701 = 70.1%






































