CBSE 12th Standard Physics Subject Electrostatic Potential And Capacitance Ncert Exemplar 2 Mark Questions With Solution 2021
By QB365 on 22 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated NCERT Exemplar Questions for Class 12, and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions. NCERT Exemplar questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
CBSE 12th Standard Physics Subject Electrostatic Potential And Capacitance Ncert Exemplar 2 Mark Questions With Solution 2021
12th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Physics
-
Faraday entered a big metallic cage supported on insulating pillars and then charged the cage by a powerful electric machine. He remains quite safe inside the cage. Do you believe on this happening?
(a) -
A charge q is placed at the center of the line joining two equal charges(Q). show that the system of three charges will be in equilibrium, if q \(=-\frac { Q }{ 4 } \)
(a) -
A 2m insulating slab with a large aluminum sheet of area 1m2 on its top is fixed by a man outside his house one evening. Will he get an electric shock, if he touches the metal sheet next morning?
(a) -
Guess a possible reason, why water has a much greater dielectric constant (= 80) than mica (= 6)?
(a) -
Automobile ignition failure occurs in damp weather. Explain, why?
(a)
*****************************************
CBSE 12th Standard Physics Subject Electrostatic Potential And Capacitance Ncert Exemplar 2 Mark Questions With Solution 2021 Answer Keys
-
Charges reside only on the surface of a conductor. Inside the conductor, charge is zero. So even, if the metallic cage was charge up with the help of powerful electric machine the charges resided on the surface. Therefore, we believe that Faraday was quite safe inside the cage.
-
Suppose the three charges be placed as shown in the figure.
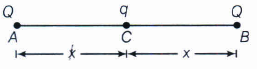
As,the net force on q is zero, so it is already in equilibrium.For equilibrium of other two changes, the net force on charge Q at B is
\(\frac { 1 }{ 4\pi \varepsilon _{ 0 } } .\frac { Q_{ q } }{ x^{ 2 } } +\frac { 1 }{ 4\pi \varepsilon _{ 0 } } .\frac { Q.Q }{ (2x)^{ 2 } } =0\)
or
\(\frac { 1 }{ 4\pi \varepsilon _{ 0 } } .\frac { Q_{ q } }{ x^{ 2 } } =-\frac { 1 }{ 4\pi \varepsilon _{ 0 } } .\frac { Q^{ 2 } }{ 4x^{ 2 } } \)
\(\\ q=-\frac { Q }{ 4 } \) -
Yes, the man will get an electric shock, if he touches the metal slab next morning because the steady discharging current in the atmosphere charges up the aluminum sheet. As a result, its voltage rises gradually. This rise in voltage depends on the capacitance of the capacitor formed by aluminum slab and ground.
-
Dielectric constant of water is much greater than that of mica because of the following reason
(i) water has a symmetrical shape as compared to mica
(ii) water has permanent dipole moment. -
The insulating porcelain of the spark plugs accumulates a film of dirt.
The surface dirt is hygroscopic and picks up moisture from the air. Therefore, in humid weather, the insulating porcelain of the plugs becomes quasi-conductor.
This allows an appreciable proportion of the spark to leak across the surface of the plug instead of discharging across the gap.






































