Class 10th Maths - Some Applications of Trigonometry Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
By QB365 on 09 Sep, 2022
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 10th Maths Subject - Some Applications of Trigonometry, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Some Applications of Trigonometry Case Study Questions With Answer Key
10th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Maths
-
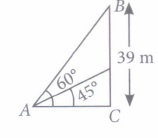
There are two temples on each bank of a river. One temple is 50 m high. A man, who is standing on the top of 50 m high temple, observed from the top that angle of depression of the top and foot of other temple are 30° and 60° respectively. (Take \(\sqrt{3}\) = 1.73)
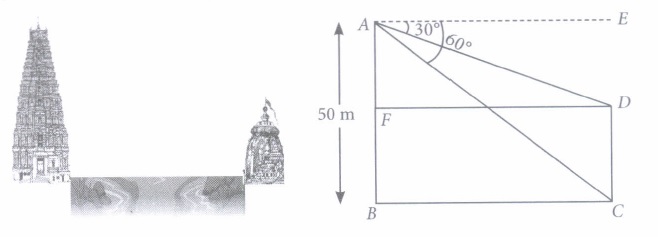
Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
(i) Measure of \(\angle\)ADF is equal to(a) 45° (b) 60° (c) 30° (d) 90° (ii) Measure of \(\angle\)ACB is equal to
(a) 45° (b) 60° (c) 30° (d) 90° (iii) Width of the river is
(a) 28.90 m (b) 26.75 m (c) 25 m (d) 27 m (iv) Height of the other temple is
(a) 32.5 m (b) 35 m (c) 33.33 m (d) 40 m (v) Angle of depression is always
(a) reflex angle (b) straight (c) an obtuse angle (d) an acute angle (a) -
There are two windows in a house. First window is at the height of 2 m above the ground and other window is 4 m vertically above the lower window. Ankit and Radha are sitting inside the two windows at points G and F respectively. At an instant, the angles of elevation of a balloon from these windows are observed to be 60° and 30° as shown below
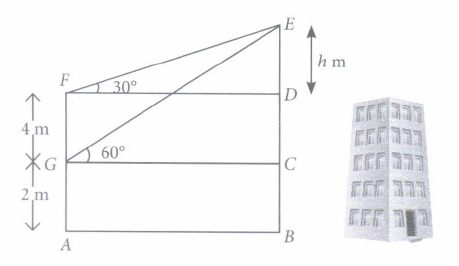
Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
(i) Who is more closer to the balloon?(a) Ankit (b) Radha (c) Both are at equal distance (d) Can't be determined (ii) Value of DF is equal to
\((a) \frac{h}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}\) \((b) h \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\) \((c) \frac{h}{2} \mathrm{~m}\) \((d) 2 h \mathrm{~m}\) (iii) Value of h is
(a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 5 (iv) Height of the balloon from the ground is
(a) 4 m (b) 6 m (c) 8 m (d) 10 m (v) If the balloon is moving towards the building, then both angle of elevation will
(a) remain same (b) increases (c) decreases (d) can't be determined (a) -
A circus artist is climbing through a 15 m long rope which is highly stretched and tied from the top of a vertical pole to the ground as shown below. Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
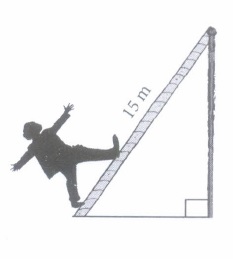
(i) Find the height of the pole, if angle made by rope to the ground level is 45°.\((a) 15 \mathrm{~m}\) \((b) 15 \sqrt{2} \mathrm{~m}\) \((c) \frac{15}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}\) \((d) \frac{15}{\sqrt{2}} \mathrm{~m}\) (ii) If the angle made by the rope to the ground level is 45°, then find the distance between artist and pole at ground level.
\((a) \frac{15}{\sqrt{2}} \mathrm{~m}\) \((b) 15 \sqrt{2} \mathrm{~m}\) \((c) 15 \mathrm{~m}\) \((d) {15}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}\) (iii) Find the height of the pole if the angle made by the rope to the ground level is 30°.
(a) 2.5 m (b) 5 m (c) 7.5 m (d) 10 m (iv) If the angle made by the rope to the ground level is 30° and 3 m rope is broken, then find the height of the pole
(a) 2m (b) 4m (c) 5m (d) 6m (v) Which mathematical concept is used here?
(a) Similar Triangles (b) Pythagoras Theorem (c) Application of Trigonometry (d) None of these (a) -
There is fire incident in the house. The house door is locked so, the fireman is trying to enter the house from the window. He places the ladder against the wall such that its top reaches the window as shown in the figure .
Based on. the above information, answer the following questions.
(i) If window is 6 m above the ground and angle made by the foot ofladder to the ground is 30°, then length of the ladder is(a) 8m (b) 10m (c) 12m (d) 14m (ii) If fireman place the ladder 5 m away from the wall and angle of elevation is observed to be 30°, then length of the ladder is
(a) 5 m \((b) \frac{10}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}\) \((c) \frac{15}{\sqrt{2}} \mathrm{~m}\) (d) 20 m (iii) If fireman places the ladder 2.5 m away from the wall and angle of elevation is observed to be 60°, then find the height of the window. (Take \(\sqrt{3}\) = 1.73)
(a) 4.325 m (b) 5.5 m (c) 6.3 m (d) 2.5 m (iv) If the height of the window is 8 m above the ground and angle of elevation is observed to be 45°, then horizontal distance between the foot of ladder and wall is
(a) 2 m (b) 4 m (c) 6 m (d) 8 m (v) If the fireman gets a 9 m long ladder and window is at 6 m height, then how far should the ladder be placed?
(a) 5 m (b) 3\(\sqrt{5}\)m (c) 3 m (d) 4 m (a) -
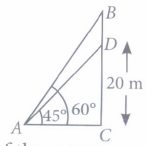
An electrician has to repair an electric fault on the pole of height of8 m. He needs to reach a point 2 m below the top of the pole to undertake the repair work.
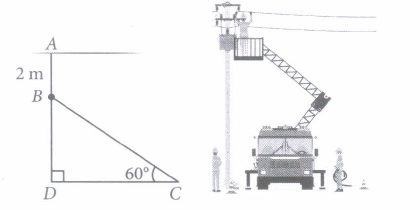
Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
(i) Length of BD is(a) 10 m (b) 6 m (c) 4 m (d) 4 m (ii) What should be the length of ladder, so that it makes an angle of 60° with the ground?
\((a) 4\sqrt{3} {~m}\) \((b) 2\sqrt{3} {~m}\) \((c) 3\sqrt{3} {~m}\) \((d) 5\sqrt{3} {~m}\) (iii) The distance between the foot ofladder and pole is
\((a) 6\sqrt{3} {~m}\) \((b) 4\sqrt{3} {~m}\) \((c) 3\sqrt{3} {~m}\) \((d) 2\sqrt{3} {~m}\) (iv) What will be the measure of \(\angle\)BCD when BD and CD are equal?
(a) 30° (b) 45° (c) 60° (d) 75° (v) Find the measure of \(\angle\)DBC.
(a) 15° (b) 60° (c) 30° (d) 45° (a) -
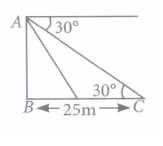
Rohit is standing at the top of the building observes a car at an angle of 30°, which is approaching the foot of the building with a uniform speed. 6 seconds later, angle of depression of car formed to be 60°, whose distance at that instant from the building is 25 m.
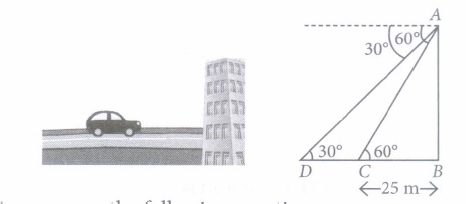
Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
(i) Height of the building is\((a) 25\sqrt{2} {~m}\) (b) 50 m \((a) 25\sqrt{3} {~m}\) (d) 25 m (ii) Distance between two positions of the car is
(a) 40 m (b) 50 m (c) 60 m (d) 75 m (iii) Total time taken by the car to reach the foot of the building from starting point is
(a) 4 sec. (b) 3 sec. (c) 6 sec. (d) 9 sec. (iv) The distance of the observer from the car when it makes an angle of 60° is
(a) 25 m (b) 45 m (c) 50 m (d) 75 m (v) The angle of elevation increases
(a) when point of observation moves towards the object (b) when point of observation moves away from the object (c) when object moves away from the observer (d) None of these (a) -
A boy is standing on the top of light house. He observed that boat P and boat Q are approaching to light house from opposite directions. He finds that angle of depression of boat P is 45° and angle of depression of boat Q is 30°. He also knows that height of the light house is 100 m.
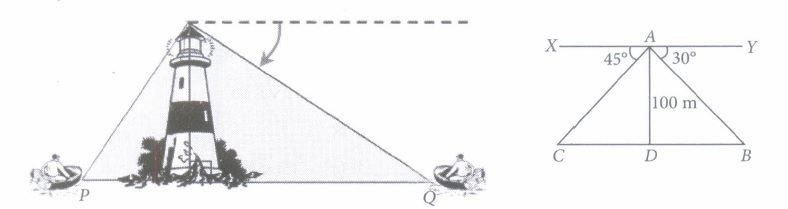
Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
(i) Measure of \(\angle\)ACD is equal to(a) 30° (b) 45° (c) 60° (d) 90° (ii) If \(\angle\)YAB = 30°, then \(\angle\)ABD is also 30°, Why?
(a) vertically opposite angles (b) alternate interior angles (c) alternate exterior angles (d) corresponding angles (iii) Length of CD is equal to
(a) 90 m (b) 60 m (c) 100 m (d) 80 m (iv) Length of BD is equal to
(a) 50 m (b) 100 m (c) 100\(\sqrt{2}\) m (d) 100\(\sqrt{3}\) m (v) Length of AC is equal to
(a)100\(\sqrt{2}\) m (b) 100\(\sqrt{3}\) m (c) 50 m (d) 100 m (a) -
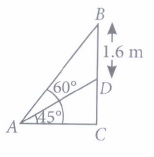
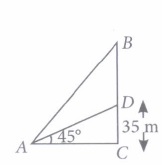
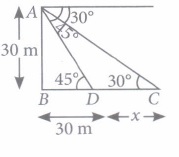
In an exhibition, a statue stands on the top of a pedestal. From the point on ground where a girl is clicking the photograph of the statue the angle of elevation of the top of the statue is 60° and from the same point, the angle of elevation of the top of pedestal is 45°.
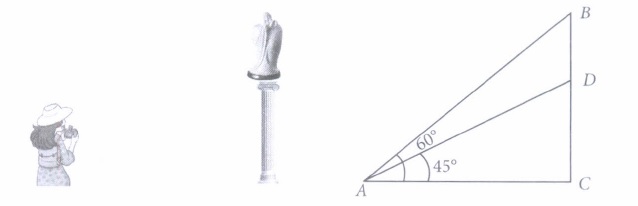
Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
(i) If the height of the pedestal is 20 m, then the distance between girl and the foot of the pedestal is(a) 20m (b) 40m (c) 60m (d) 80m (ii) If the height of the pedestal is 20 m, then the height of the statue is
\((a) 20 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\) \((b) 20(\sqrt{3}-1) \mathrm{m}\) \((c) 20(\sqrt{3}+1) \mathrm{m}\) \((d) 10(\sqrt{3}-1) \mathrm{m}\) (iii) If the height of the statue is 1.6 m, then height of the pedestal is
\((a) 0.8(\sqrt{3}-1) \mathrm{m}\) \((b) 1.6(\sqrt{3}+1) \mathrm{m}\) \((c) 0.8(\sqrt{3}) \mathrm{m}\) \((d) 0.8(\sqrt{3}+1) \mathrm{m}\) (iv) If the total height of the statue and pedestal is 39 m, then find the length of AC.
(a) 13 m (b) \(12\sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\) (c) \(13 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\) (d) \(15 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\) (v) If the height of the pedestal is 35 m, then length of AD is
(a) \(35\sqrt{2} \mathrm{~m}\) (b) \(40\sqrt{2} \mathrm{~m}\) (c) \(35 \sqrt{2+1} \mathrm{~m}\) (d) \(35 \sqrt{2-1} \mathrm{~m}\) (a) -
Teewan, Arun and Pankaj were celebrating the festival of Diwali in open ground with firecrackers. There is a pedestal in the ground. All of sudden Teewan stands on pedestal and release sky lantern from the top of pedestal.
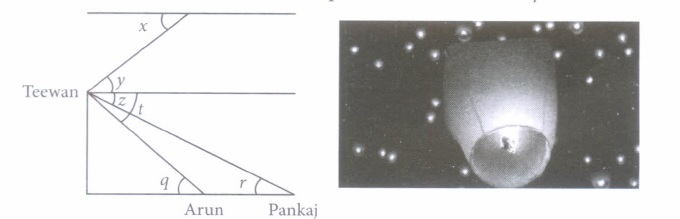
Based on the above information answer the following questions. (Take \(\sqrt{3}\) = J .73)
(i) Which one is a pair of angle of depression?\((a) (\angle x, \angle y)\) \((b) (\angle y, \angle z)\) \((c) (\angle z, \angle t)\) \((d) (\angle r, \angle q)\) (ii) If the position of Pankaj is 25 m away from the base of pedestal and Zr = 30°, then find the height of pedestal.
(a) 14.45m (b) 15.5m (c) 16.36m (d) 17.36m (iii) If the height of pedestal is 30 m, \(\angle\)t = 45° and \(\angle\)z = 30°, then the horizontal distance between Arun and Pankaj is
(a) 24.5 m (b) 19.5 m (c) 20 m (d) 21.9 m (iv) If the vertical height of sky lantern from the top of pedestal is 12 m and \(\angle\)y = 30°, then distance between Teewan and sky lantern is
(a) 20 m (b) 16.97 m (c) 24 m (d) 19.86 m (v) If \(\angle\)q = 60° and position of Arun is 15 m away from the base of pedestal, then find the height of pedestal.
(a) 16.25 m (b) 25 m (c) 25.95 m (d) 26 m (a) -
Two hoardings are put on two poles of equal heights standing on either side of the road. From a point between them on the road the angle of elevation of the top of poles are 60° and 30° respectively. Height of the each pole is 20 m.
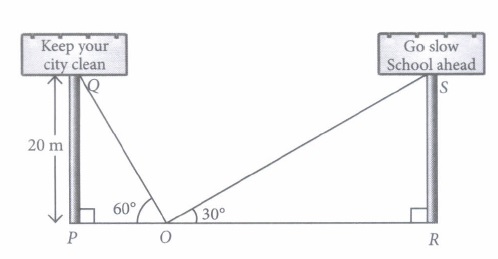
Based on the above information, answer the following questions. (Take \(\sqrt{3}\) = 1.73).
(i) Find the length of PO.(a) 20 m \((b) 20 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\) \((c) \frac{20}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}\) (d) None of these (ii) Find the length of RO.
(a) 20 m \((b) 20 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\) \((c) \frac{20}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}\) (d) None of these (iii) The width of the road is
(a) 31.23m (b) 35.68 m (c) 39.73 m (d) 46.24 m (iv) If the angle of elevation made by pole PQ is 45°, then the length of PO =
(a) 20 m \((b) 20 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\) \((c) \frac{20}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}\) (d) None of these (v) Angle formed by the line of sight with the horizontal when the point being viewed is above the horizontal level is known as
(a) angle of depression (b) angle of elevation (c) right Angle (d) reflex angle (a) -
Suppose a straight vertical tree is broken at some point due to storm and the broken part is inclined at a certain distant from the foot of the tree. Based on the above information, answer the following questions.

(i) If the top of upper part of broken tree touches ground at a distance 000 m (from the foot of the tree) and makes an angle of inclination 30°, then the height of remaining part of the tree is\((a) \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\) \((b) 30 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\) \((c) \frac{30}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}\) (d) 30 m (ii) If the top of broken part of a tree touches the ground at a point whose distance from foot of the tree is equal to height of remaining part, then its angle of inclination is
(a) 30° (b) 60° (c) 45° (d) None of these (iii) The angle of elevation are always
(a) obtuse angle (b) acute angle (c) right angle (d) reflex angle (iv) If \(A B=10 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}, A D=2 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}, \text { then } C D=\)
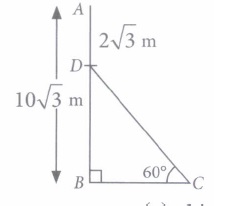
(a) 9 m (b) 11 m (c) 14 m (d) 16 m (v) If the height of a tree is 6 m, which is broken by wind in such a way that its top touches the ground and makes an angles 30° with the ground. At what height from the bottom of the tree is broken by the wind?
(a) 2 m (b) 4 m (c) 8 m (d) 10 m (a) -
One day while sitting on the bridge across a river Arun observes the angles of depression of the banks on opposite sides of the river are 30° and 60° respectively as shown in the figure. (Take \(\sqrt{3}\) = 1.73)

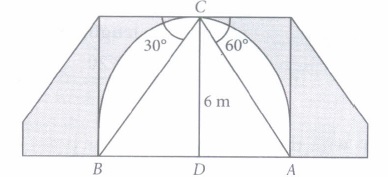
Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
(i) If the bridge is at a height of 6 m, then AD =(a) 6 m \((b) \frac{\sqrt{3}}{6} \mathrm{~m}\) \((c) 6 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\) \((d) \frac{6}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}\) (ii) BD =
(a) 6 m \((b) 6 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\) \((c) \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\) \((d) 10 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\) (iii) Width of the river is
(a) 10.85 m (b) 13.87 m (c) 15.85 m (d) 19.85 m (iv) The angles of elevation and depression are always
(a) acute angles (b) obtuse angles (c) right angles (d) straight angles (v) If BD = 21 m, then height of the bridge is
(a) 7 m (b) 21 m \((c) 7 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\) \((d) \frac{7}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}\) (a) -
Karan and his sister Riddhima visited at their uncle's place- Bir, Himachal Pradesh. During day time Karan, who is standing on the ground spots a para glider at a distance of 24 m from him at an elevation of 30°. His sister Riddhima is also standing on the roof of a 6 m high building, observes the elevation of the same paraglider as 45°. Karan and Riddhima are on the opposite sides of the paraglider.
Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
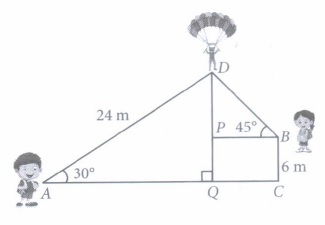
(i) The distance of paraglider from the ground is(a) 10 m (b) 12 m (c) 18 m (d) 22 m (ii) The value of PD is
(a) 6 m (b) 7 m (c) 8 m (d) 9 m (iii) The distance between the paraglider and the Riddhima is
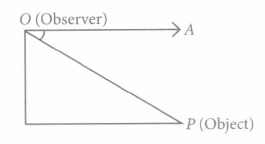
(a) Reflex angle (b) Angle of elevation (c) Straight angle (d) Angle of depression (v) If A and B are two objects and the eye of an observer is at point 0, then the line of sight will be
(a) OA (b) OB (c) Both (a) and (b) (d) None of these (a) -
A boy 4 m tall spots a pigeon sitting on the top of a pole of height 54 m from the ground. The angle of elevation of the pigeon from the eyes of boy at any instant is 60°. The pigeon flies away horizontally in such a way that it remained at a constant height from the ground. After 8 seconds, the angle of elevation of the pigeon from the same point is 45°
Based on the above information, answer the following questions. (Take \(\sqrt{3}\) = 1.73 )
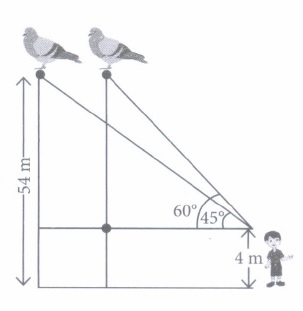
(i) Find the distance of first position of the pigeon from the eyes of the boy.(a) 54 m (b) 100 m \((c) \frac{100}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}\) \((d) 100 \sqrt{3}\) (ii) If the distance between the position of pigeon increases, then the angle of elevation
(a) Increases (b) decreases (c) remains unchanged (d) can't say (iii) Find the distance between the boy and the pole.
(a) 50 m \((b) \frac{50}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}\) \((c) 50 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\) \((d) 60 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\) (iv) How much distance the pigeon covers in 8 seconds?
(a) 12.13 m (b) 19.60 m (c) 21.09 m (d) 26.32 m (v) Find the speed of the pigeon
(a) 2.63 m/sec (b) 3.88 m/sec (c) 6.7 m/sec (d) 9.3 m/sec (a) -
Aditi purchase a wooden bar stool for her living room with square top of side 2 m and having height of 6 m above the ground. Also each leg is inclined at an angle of 60° to the ground as shown in the figure (not drawn to scale).
Based on the above information, answer the following questions. (Take \(\sqrt{3}\) = 1.73)
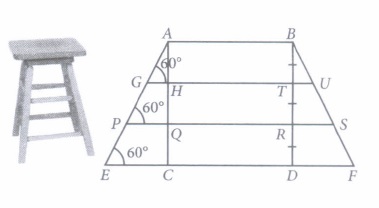
(i) Find the length of the each leg(a) 5.9 m (b) 6.93 m (c) 7.3 m (d) 8.2 m (ii) Find the length of GH.
(a) 0.53 m (b) 1 m (c) 1.15 m (d) 2.73 m (iii) The length of second step is
(a) 4.3 m (b) 4.99 m (c) 5.68 m (d) 6.78 m (iv) The length of PQ =
(a) 1.56 m (b) 2.31 m (c) 3.34m (d) 5.68m (v) The length of first step is
(a) 4.78 m (b) 5.34 m (c) 6.62 m (d) 7.82 m (a)
Case Study
*****************************************
Answers
Some Applications of Trigonometry Case Study Questions With Answer Key Answer Keys
-
(i) (c) : Since AE || FD
\(\therefore\) \(\angle\)EAD = \(\angle\)ADF = 30° [Alternate interior angles]
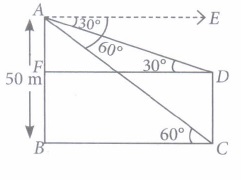
(ii) (b): Since, AE || BC
\(\therefore\) \(\angle\)EAC = \(\angle\)ACB = 60° [Alternate interior angles]
(iii) (a) : In \(\Delta\)ABC,
\(\begin{array}{l} \tan 60^{\circ}=\frac{A B}{B C} \Rightarrow \sqrt{3}=\frac{50}{B C} \\ \Rightarrow \quad B C=\frac{50}{\sqrt{3}}=28.90 \mathrm{~m} \end{array}\)
(iv) (c): In \(\Delta\)ADF, \(\tan 30^{\circ}=\frac{A F}{F D}\)
\(\Rightarrow \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{A B-B F}{F D} \Rightarrow \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{50-C D}{\frac{50}{\sqrt{3}}}\)
\(\left[\because F D=B C=\frac{50}{\sqrt{3}}\right] \)
\(\Rightarrow \frac{50}{3}=50-C D \Rightarrow C D=50-\frac{50}{3}=\frac{100}{3}=33.33 \mathrm{~m}\)
(v) (d) -
(i) (b): The person who makes small angle of elevation is more closer to the balloon.
\(\therefore\) Radlra is more closer to the balloon.
(ii) (b): \(\text { In } \Delta E F D, \tan 30^{\circ}=\frac{E D}{D F}\)
\(\Rightarrow \quad \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{h}{D F} \)
\(\Rightarrow \quad D F=h \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\)
(iii) (a): In \(\Delta\)GCE,
\(\begin{array}{l} \tan 60^{\circ}=\frac{E C}{G C}=\frac{h+4}{D F} \\ \Rightarrow \quad \sqrt{3}=\frac{h+4}{\sqrt{3} h} \Rightarrow 3 h=h+4 \Rightarrow h=2 \end{array}\)
(iv) (c): Height of the balloon from the ground = BE = BC + CD + DE = 2 + 4 + 2 = 8 m
(v) (b) -
(i) (d): Let h be the height of the pole.
In \(\Delta\)ABC,
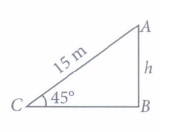
\( \frac{h}{15}=\sin 45^{\circ} \Rightarrow \frac{h}{15}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\)
\(\Rightarrow \quad h =\frac{15}{\sqrt{2}} \mathrm{~m}\)
(ii) (a): Let x be the required distance.
In \(\Delta\)ABC,
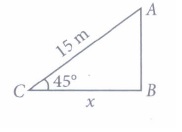
\(\frac{x}{15}=\cos 45^{\circ}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\)
\(\Rightarrow \quad x=\frac{15}{\sqrt{2}} \mathrm{~m}\)
(iii) (c) : Let h be the height of the pole.
In right triangle ABC,
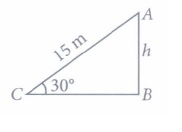
\(\frac{h}{15}=\sin 30^{\circ}=\frac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow \quad h=\frac{15}{2}=7.5 \mathrm{~m}\)
(iv) (d): If 3 m rope is broken, then the length of the rope is 12 m.
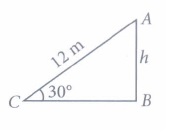
\(\text { In } \Delta A B C, \frac{h}{12}=\sin 30^{\circ}=\frac{1}{2} \)
\(\Rightarrow \quad h=\frac{12}{2}=6 \mathrm{~m}\)
(v) (c) -
(i) (c) : Let AC be the length of the ladder.
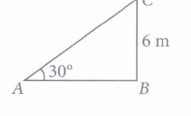
\(\text { In } \Delta A B C, \frac{B C}{A C}=\sin 30^{\circ} \)
\(\Rightarrow \frac{6}{A C}=\frac{1}{2} \Rightarrow A C=12 \mathrm{~m}\)
(ii) (b): \(\text { In } \Delta A B C, \frac{A B}{A C}=\cos 30^{\circ}\)
\(\Rightarrow \frac{5}{A C}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \Rightarrow A C=\frac{10}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}\)
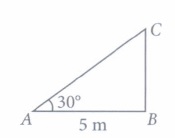
(iii) (a) : Let BC be the height of window from ground.
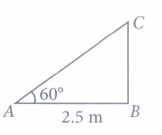
\(\text { In } \Delta A B C, \frac{B C}{A B}=\tan 60^{\circ} \)
\(\Rightarrow \frac{B C}{2.5}=\sqrt{3} \)
\(\Rightarrow B C=2.5 \times 1.73=4.325 \mathrm{~m}\)
(iv) (d): Let AB be the horizontal distance between the foot of ladder and wall.
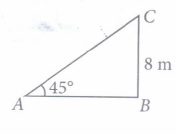
\(\text { In } \Delta A B C, \frac{B C}{A B}=\tan 45^{\circ} \)
\(\Rightarrow \quad \frac{8}{A B}=1 \Rightarrow A B=8 \mathrm{~m}\)
(v) (b): Let the required distance be x.
\(\text { In } \Delta A B C,(9)^{2}=x^{2}+(6)^{2}\)
[By Pythagoras theorem]
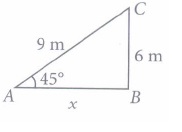
\(\Rightarrow 81-36=x^{2} \Rightarrow 45=x^{2} \)
\(\Rightarrow \quad x=3 \sqrt{5} \mathrm{~m}\) -
(i) (b): Total height of pole = 8 m
\(\therefore\) BD = AD - AB = (8 - 2)m = 6 m
(ii) (a): \(\text { In } \Delta B D C, \frac{B D}{B C}=\sin 60^{\circ}\)
\(\Rightarrow \quad \frac{6}{B C}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \)
\(\Rightarrow \quad B C=\frac{12}{\sqrt{3}} \times \frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}=4 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\)
(iii) (d): \(\text { In } \triangle B D C\)
\(\frac{B D}{C D}=\tan 60^{\circ} \Rightarrow \frac{6}{C D}=\sqrt{3} \Rightarrow C D=\frac{6}{\sqrt{3}} \times \frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}=2 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\)
(iv) (b) : \(\text { If } \Delta B C D\)
\(\frac{B D}{C D}=\tan \theta \Rightarrow 1=\tan \theta \quad[\because B D=C D] \)
\(\Rightarrow \quad \theta=45^{\circ}\)
(v) (c) : \(\operatorname{In} \Delta B D C, \angle B+\angle D+\angle C=180^{\circ}\)
\(\therefore \quad \angle B=180^{\circ}-60^{\circ}-90^{\circ}=30^{\circ}\) -
(i) (c): \(\text { In } \Delta A B C, \frac{A B}{B C}=\tan 60^{\circ}\)
\(\Rightarrow \quad A B=25 \times \sqrt{3}\)
\(\therefore\) Height of building is 25\(\sqrt{3}\) m .
(ii) (b): \(\text { In } \Delta A B D, \frac{A B}{B D}=\tan 30^{\circ}\)
\(\Rightarrow \frac{25 \sqrt{3}}{B D}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \Rightarrow B D=75 \mathrm{~m}\)
\(\therefore\) Distance between two positions of car = (75 - 25) m = 50m.
(iii) (d): Time taken to cover 50 m distance = 6 sec.
\(\therefore\) Time taken to cover 25 m distance = 3 sec.
\(\therefore\) Total time taken by car = 6 sec + 3 sec = 9 sec
(iv) (c): \(\text { In } \Delta A B C, \frac{B C}{A C}=\cos 60^{\circ}\)
\(\Rightarrow \quad \frac{25}{A C}=\frac{1}{2} \)
\(\Rightarrow A C=50 \mathrm{~m}\)
(v) (a) -
(i) (b): \(\angle X A C=45^{\circ}\)
\(\therefore \quad \angle A C D=45^{\circ}\) [Alternate interior angles]
(ii) (b)
(iii) (c) : \(\text { In } \Delta A C D\)
\(\frac{A D}{D C}=\tan 45^{\circ} \)
\(\Rightarrow \frac{100}{D C}=1 \Rightarrow D C=100 \mathrm{~m}\)
(iv) (d): \(\text { In } \Delta A B D, \frac{A D}{B D}=\tan 30^{\circ}\)
\(\Rightarrow \quad \frac{100}{B D}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \)
\(\Rightarrow \quad B D=100 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\)
(v) (a): \(\text { In } \Delta A D C\)
\(\frac{A D}{A C}=\sin 45^{\circ} \Rightarrow \frac{100}{A C}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \Rightarrow A C=100 \sqrt{2} \mathrm{~m}\) -
(i) (a): \(\text { In } \triangle A C D\)
\(\tan 45^{\circ}=\frac{C D}{A C}=1 \)
\(\therefore \quad A C=C D=20 \mathrm{~m}\)
(ii) (b): Let, BD = h m be the height of the statue.
\(\text { In } \Delta A B C, \tan 60^{\circ}=\frac{B C}{A C} \Rightarrow \frac{B D+C D}{A C}=\sqrt{3} \)
\(\Rightarrow \frac{20+h}{20}=\sqrt{3}[\text { using }(\mathrm{i})] \Rightarrow h=20(\sqrt{3}-1) \mathrm{m}\)
(iii) (d): Since, in \(\triangle A C D, \angle D A C=45^{\circ}\)
\(\therefore \quad A C=C D(\operatorname{say} x) \)
\(\text { In } \Delta B A C, \tan 60^{\circ}=\frac{B C}{A C} \)
\(\Rightarrow \frac{1.6+x}{x}=\sqrt{3} \)
\(\Rightarrow 1.6=x(\sqrt{3}-1)\)
\(\Rightarrow \quad x=\frac{1.6}{\sqrt{3}-1} \times \frac{\sqrt{3}+1}{\sqrt{3}+1}=0.8(\sqrt{3}+1) \mathrm{m}\)
(iv) (c): \(\text { In } \triangle A B C\)
\(\tan 60^{\circ}=\frac{B C}{A C} \Rightarrow \frac{39}{A C}=\sqrt{3} \)
\(\Rightarrow A C=\frac{39}{\sqrt{3}} \times \frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}=13 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\)
(v) (a): \(\text { In } \Delta A C D, \sin 45^{\circ}=\frac{C D}{A D}\)
\(\Rightarrow \quad \frac{35}{A D}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \)
\(\Rightarrow A D=35 \sqrt{2} \mathrm{~m}\) -
(i) (c)
(ii) (a): Let AB be the height of pedestal.
\(\text { In } \Delta A B C, \)
\(\tan 30^{\circ}=\frac{A B}{B C} \)
\(\Rightarrow \quad A B=\frac{25}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{25}{1.73}=14.45 \mathrm{~m}\)
(iii) (d): Let x be the distance between Arun and Pankaj.
\(\text { In } \Delta A B \dot{D}, \tan 45^{\circ}=\frac{A B}{B D}\)
\(\Rightarrow B D=30 \mathrm{~m}\)
\(\text { Now, in } \Delta \overline{A B C} \text { , }\)
\(\tan 30^{\circ}=\frac{A B}{B C}\)
\(\Rightarrow \frac{30}{30+x}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=30(\sqrt{3}-1)=30 \times 0.73=21.9 \mathrm{~m}\)
(iv) (c): \(\text { In } \triangle A R S\)
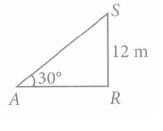
\(\sin 30^{\circ}=\frac{R S}{A S} \)
\(\Rightarrow \quad \frac{12}{A S} =\frac{1}{2} \Rightarrow A S=12 \times 2=24 \mathrm{~m}\)
(v) (c): \(\text { In } \Delta A B D, \frac{A B}{B D}=\tan 60^{\circ}\)
\(\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow \frac{A B}{15}=\sqrt{3} \\ \Rightarrow A B=15 \times 1.73=25.95 \mathrm{~m} \end{array}\) -
(i) (c): \(\text { In } \Delta O P Q\), we have
\(\tan 60^{\circ}=\frac{P Q}{P O} \)
\(\Rightarrow \sqrt{3}=\frac{20}{P O} \)
\(\Rightarrow P O=\frac{20}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}\)
(ii) (b): In \(\Delta\)ORS, we have
\(\tan 30^{\circ}=\frac{R S}{O R} \Rightarrow \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{20}{O R} \Rightarrow O R=20 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\)
(iii) (d): Clearly, width of the road = PR
\(\begin{array}{l} =P O+O R=\left(\frac{20}{\sqrt{3}}+20 \sqrt{3}\right) \mathrm{m} \\ =20\left(\frac{4}{\sqrt{3}}\right) \mathrm{m}=\frac{80}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}=46.24 \mathrm{~m} \end{array}\)
(iv) (a): \(\text { In } \Delta O P Q \text { , if } \angle P O Q=45^{\circ} \text { , then }\)
\(\tan 45^{\circ}=\frac{P Q}{P O} \Rightarrow 1=\frac{20}{P O} \Rightarrow P O=20 \mathrm{~m}\)
(v) (b) -
(i) (c): Let AB be the tree of height h m and let it broken at height of x m, as shown in figure. Clearly CD = AC = (h - x) m
Now, in \(\Delta\)CBD, we have
\( \tan 30^{\circ}=\frac{x}{30} \)
\(\Rightarrow \quad x=\frac{30}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}\)
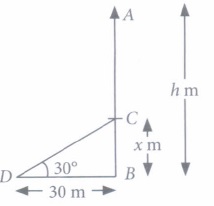
Thus, the height of remaining part of the tree is \(\frac{30}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}\)
(ii) (c): In this case, BD = BC = x m
\(\therefore\) If \(\theta\) be the angle of inclination, then
\( \tan \theta=\frac{B C}{B D}=1 \)
\(\Rightarrow \tan \theta=\tan 45^{\circ} \)
\(\Rightarrow \theta=45^{\circ}\)
(iii) (b): The angle of elevation and depression are always acute angles.
(iv) (d): Clearly, BD = AB - AD
\(=(10 \sqrt{3}-2 \sqrt{3}) \mathrm{m}=8 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\)
Now, in \(\Delta\)BCD,we have
\(\sin 60^{\circ}=\frac{B D}{D C} \)
\(\Rightarrow \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}=\frac{8 \sqrt{3}}{D C} \Rightarrow D C=16 \mathrm{~m}\)
(v) (a): Here, h = 6 m, \(\theta\) = 30°
\(\therefore\) DC = AC = (6 - x) m
Now, in \(\Delta\)BCD,we have
\(\sin 30^{\circ}=\frac{B C}{C D} \)
\(\Rightarrow \frac{1}{2}=\frac{x}{6-x} \)
\(\Rightarrow 6-x=2 x\)
\(\Rightarrow 3 x=6 \Rightarrow x=2\)
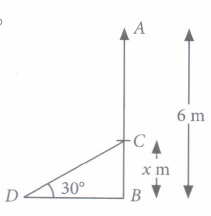
-
(i) (d): Clearly, \(\angle\)DAC = 60°
So,in \(\Delta\)ADC, we have
\(\tan 60^{\circ}=\frac{C D}{A D} \Rightarrow \sqrt{3}=\frac{6}{A D} \)
\(\Rightarrow A D=\frac{6}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}\)
(ii) (b): Clearly, \(\angle\)DBC = 30°
So, in \(\Delta\)BDC,we have
\(\tan 30^{\circ}=\frac{C D}{B D} \)
\(\Rightarrow \quad \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{6}{B D} \)
\(\Rightarrow B D=6 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\)
(iii) (b): Width of the river = AB = AD + BD
\(\begin{array}{l} =\frac{6}{\sqrt{3}}+6 \sqrt{3} \\ =6\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}+\sqrt{3}\right)=6\left(\frac{4}{\sqrt{3}}\right)=\frac{24}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}=13.87 \mathrm{~m} \end{array}\)
(iv) (a): The angle of elevation and angle of depression are always acute angles.
(v) (c): In \(\Delta\)BCD,if BD = 21m, then
\( \tan 30^{\circ}=\frac{C D}{B D} \)
\(\Rightarrow \quad \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{C D}{21} \Rightarrow C D=\frac{21 \sqrt{3}}{3}=7 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}\) -
(i) (b): In the right \(\Delta\)ADQ, we have
\(\sin 30^{\circ}=\frac{D Q}{A D} \Rightarrow \frac{1}{2}=\frac{D Q}{24}\)
\(\Rightarrow \quad D Q=12 \mathrm{~m}\)
Thus, distance of paraglider from the ground is 12 m.
(ii) (a): We have PQ = BC = 6 m
Now, as DQ = 12 m
\(\therefore\) DP = DQ - PQ = 12 - 6 = 6 m
(iii) (c) : In right \(\Delta\)BDP,we have
\(\sin 45^{\circ}=\frac{D P}{B D} \Rightarrow \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{6}{B D}\)
\(\Rightarrow \quad B D=6 \sqrt{2} \mathrm{~m}\)
Thus, the distance of paraglider from the girl is 6\(\sqrt{2}\) m.
(iv) (d): \(\angle\)AOP given in figure, is the angle of depression.
(v) (c): If A and B are two objects and the eye of an observer is at point 0, then line of sight will be both OA and OB. -
(i) (c): Distance of first position of pigeon from the eyes of boy = AC
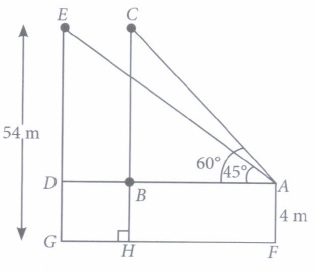
\(\text { In } \triangle A B C \text { , } \)
\(\sin 60^{\circ}=\frac{B C}{A C} \Rightarrow A C=\frac{C H-B H}{\sin 60^{\circ}}=\frac{54-4}{\sqrt{3} / 2}=\frac{100}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}\)
(ii) (b): If the distance increases, then the angle of elevation decreases.
(iii) (b): Distance between boy and pole = AB
\(\text { Now, in } \triangle A B C \text { , }\)
\(\tan 60^{\circ}=\frac{B C}{A B} \Rightarrow \sqrt{3} A B=50 \Rightarrow A B=\frac{50}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}\)
(iv) (c): \(\text { In } \Delta A E D, \tan 45^{\circ}=\frac{E D}{A D}\)
\(\Rightarrow A D=B C=50 \mathrm{~m} \quad A D \quad(\because E D=B C)\)
Now, distance between two positions of pigeon = EC = BD = AD-AB
\(=\left(50-\frac{50}{\sqrt{3}}\right) \mathrm{m}=\frac{50(1.73-1)}{1.73}=21.09 \mathrm{~m}\)
(v) (a): \(\text { Speed of pigeon }=\frac{\text { Distance covered }}{\text { Time taken }} \)
\(=\left(\frac{21.09}{8}\right) \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{sec}=2.63 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{sec}\) -
Given, side of square top = 2 m
\(\therefore\) AB = HT = QR = CD = 2 m
Also, A C and BD are perpendicular to the ground.
So, AH = HQ = QC. (By B.P.T. Theorem)
(i) (b):\(\text { In } \triangle A E C\)
\(\sin 60^{\circ}=\frac{A C}{A E} \Rightarrow \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}=\frac{6}{A E} \Rightarrow A E=6.93 \mathrm{~m}\)
\(\therefore\) Length of each leg i.e., AE = BF = 6.93 m.
(ii) (c): \(\text { In } \Delta A G H, \tan 60^{\circ}=\frac{A H}{G H} \Rightarrow \sqrt{3}=\frac{2}{G H}\)
\(\Rightarrow G H=1.15 \mathrm{~m}\)
(iii) (a) :Length of second step = GH + HT + TU
= 1.15 + 2 + 1.15 = 4.3 m
(iv) (b):\(\text { In } \Delta A P Q\)
\(\tan 60^{\circ}=\frac{A Q}{P Q} \Rightarrow \sqrt{3}=\frac{4}{P Q} \Rightarrow P Q=\frac{4}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}=2.31 \mathrm{~m}\)
(v) (c): Length of first step = PQ + QR + RS
=2.31 + 2 + 2.31 = 6.62 m

























