Class 10th Maths - Surface Areas and Volumes Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
By QB365 on 09 Sep, 2022
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 10th Maths Subject - Surface Areas and Volumes, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Surface Areas and Volumes Case Study Questions With Answer Key
10th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Maths
-
Arun a 10th standard student makes a project on corona virus in science for an exhibition in his school. In this project, he picks a sphere which has volume 38808 cm3 and 11 cylindrical shapes, each of volume 1540 cm3 with length 10 cm.
Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
(i) Diameter of the base of the cylinder is(a) 7 cm (b) 14 cm (c) 12 cm (d) 16 cm (ii) Diameter of the sphere is
(a) 40 cm (b) 42 cm (c) 21 cm (d) 20 cm (iii) Total volume of the shape formed is
(a) 85541 cm3 (b) 45738 cm3 (c) 24625 cm3 (d) 55748 cm3 (iv) Curved surface area of the one cylindrical shape is
(a) 850 cm2 (b) 221 cm2 (c) 440 cm2 (d) 540 cm2 (v) Total area covered by cylindrical shapes on the surface of sphere is
(a) 1694 cm2 (b) 1580 cm2 (c) 1896 cm2 (d) 1470 cm2 (a) -
Ajay is a Class X student. His class teacher Mrs Kiran arranged a historical trip to great Stupa of Sanchi. She explained that Stupa of Sanchi is great example of architecture in India. Its base part is cylindrical in shape. The dome of this stupa is hemispherical in shape, known as Anda. It also contains a cubical shape part called Hermika at the top. Path around Anda is known as Pradakshina Path.

Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
(i) Find the lateral surface area of the Hermika, if the side of cubical part is 8 m.(a) 128 m2 (b) 256 m2 (c) 512 m2 (d) 1024 m2 (ii) The diameter and height of the cylindrical base part are respectively 42 m and 12 m. If the volume of each brick used is 0.01 m3, then find the number of bricks used to make the cylindrical base.
(a) 1663200 (b) 1580500 (c) 1765000 (d) 1865000 (iii) If the diameter of the Anda is 42 m, then the volume of the Anda is
(a) 17475 m3 (b) 18605 m3 (c) 19404 m3 (d) 18650 m3 (iv) The radius of the Pradakshina path is 25 m. If Buddhist priest walks 14 rounds on this path, then find the distance covered by the priest.
(a) 1860 m (b) 3600 m (c) 2400 m (d) 2200 m (v) The curved surface area of the Anda is
(a) 2856 m2 (b) 2772 m2 (c) 2473 m2 (d) 2652 m2 (a) -
One day Rinku was going home from school, saw a carpenter working on wood. He found that he is carving out a cone of same height and same diameter from a cylinder. The height of the cylinder is 24 ern and base radius is 7 cm. While watching this, some questions came into Rinkus mind. Help Rinku to find the answer of the following questions.
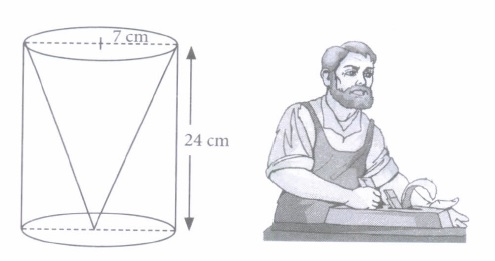
(i) After carving out cone from the cylinder,(a) Volume of the cylindrical wood will decrease. (b) Height of the cylindrical wood will increase. (c) Volume of cylindrical wood will increase. (d) Radius of the cylindrical wood will decrease. (ii) Find the slant height of the conical cavity so formed.
(a) 28 cm (b) 38 cm (c) 35 cm (d) 25 cm (iii) The curved surface area of the conical cavity so formed is
(a) 250 cm2 (b) 550 cm2 (c) 350 cm2 (d) 450 cm2 (iv) External curved surface area of the cylinder is
(a) 876 cm2 (b) 1250 cm2 (c) 1056 cm2 (d) 1025 cm2 (v) Volume of conical cavity is
(a) 1232 cm3 (b) 1248 cm3 (c) 1380 cm3 (d) 999 cm3 (a) -
To make the learning process more interesting, creative and innovative, Amayras class teacher brings clay in the classroom, to teach the topic - Surface Areas and Volumes. With clay, she forms a cylinder of radius 6 ern and height 8 cm. Then she moulds the cylinder into a sphere and asks some questions to students.
(i) The radius of the sphere so formed is(a) 4 cm (b) 6 cm (c) 7 cm (d) 8 cm (ii) The volume of the sphere so formed is
(a) 905.14 cm3 (b) 903.27 cm3 (c) 1296.5 cm3 (d) 1156.63 cm3 (iii) Find the ratio of the volume of sphere to the volume of cylinder.
(a) 2:1 (b) 1:2 (c) 1:1 (d) 3: 1 (iv) Total surface area of the cylinder is
(a) 528 cm2 (b) 756 cm2 (c) 625 cm2 (d) 636 cm2 (v) During the conversion of a solid from one shape to another the volume of new shape will
(a) be increase (b) be decrease (c) remain unaltered (d) be double (a) -
A carpenter used to make and sell different kinds of wooden pen stands like rectangular, cuboidal, cylindrical, conical. Aarav went to his shop and asked him to make a pen stand as explained below. Pen stand must be of the cuboidal shape with three conical depressions, which can hold 3 pens. The dimensions of the cuboidal part must be 20 cm x 15 cm x 5 cm and the ffrlog radius and depth of each conical depression must be 0.6 cm and 2.1 cm respectively.
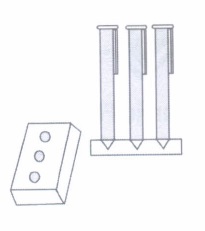
Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
(i) The volume of the cuboidal part is(a) 1250 cm3 (b) 1500 cm3 (c) 1625 cm3 (d) 1500 cm3 (ii) Total volume of conical depressions is
(a) 2.508 cm3 (b) 1.5 cm3 (c) 2.376 cm3 (d) 3.6 cm3 (iii) Volume of the wood used in the entire stand is
(a) 631.31 cm3 (b) 3564 cm3 (c) 1502.376 cm3 (d) 1497.624 cm3 (iv) Total surface area of cone of radius r is given by
\((a) \pi r l+\pi r^{2}\) \((b) 2 \pi r l+\pi r^{2}\) \((c) \pi r^{2} l+\pi r^{2}\) \((d) \pi r l+2 \pi r^{3}\) (v) If the cost of wood used is Rs 5 per cm3, then the total cost of making the pen stand is
(a) Rs 8450.50 (b) Rs 7480 (c) Rs 9962.14 (d) Rs 7488.12 (a) -
Meera and Dhara have 12 and 8 coins respectively each of radius 3.5 cm and thickness 0.5 cm. They place their coins one above the other to form solid cylinders .

Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
(i) Curved surface area of the cylinder made by Meera is(a) 144 cm2 (b) 132 cm2 (c) 154 cm2 (d) 142 cm2 (ii) The ratio of curved surface area of the cylinders made by Meera and Dhara is
(a) 2: 5 (b) 3: 2 (c) 1: 2 (d) 2: 7 (iii) The volume of the cylinder made by Dhara is
(a) 154 cm3 (b) 144 cm3 (c) 132 cm3 (d) 142 cm3 (iv) The ratio of the volume of the cylinders made by Meera and Dhara is
(a) 1:2 (b) 2: 5 (c) 3: 2 (d) 4: 3 (v) When two coins are shifted from Meeras cylinder to Dhara's cylinder, then
(a) Volume of two cylinder become equal (b) Volume of Meera's cylinder> Volume of Dharas cylinder (c) Volume of Dhara's cylinder> Volume of Meeras cylinder (d) None of these (a) -
Ankit wants a beautiful ceramic cuboidal flower vase for the decoration of his room. So, he visit to ceramicists and explained him about, what kind of flower vase he wants. According to his requirement, the ceramicists carved out a sphere of maximum size from a cuboidal ceramic block of dimensions 24 cm by 24 cm by 27 cm.

Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
(i) What is the maximum radius of the sphere that can be carved out from the block of ceramic?(a) 23 cm (b) 17 cm (c) 9 cm (d) 12 cm (ii) What is the volume of the complete block of ceramic?
(a) 15552 cm3 (b) 12646 cm3 (c) 15292 cm3 (d) 12898 cm3 (iii) What is the volume of the ceramic carved out?
(a) 1940.4 cm3 (b) 7241.14 cm3 (c) 14553.5 cm3 (d) None of these (iv) What is the volume of the cuboidal vase thus formed?
(a) 8853.73 cm3 (b) 1153.37 cm3 (c) 8310.86 cm3 (d) None of these (v) What is the surface area of the sphere carved out?
(a) 15540 cm2 (b) 1810.28 cm2 (c) 2702 cm2 (d) 1838 cm2 (a) -
Pankaj's father has to purchase a new water tank to store water for irrigation of their fields. For this purpose, they visit to a shop. The shopkeeper has three types of water tanks as shown below.
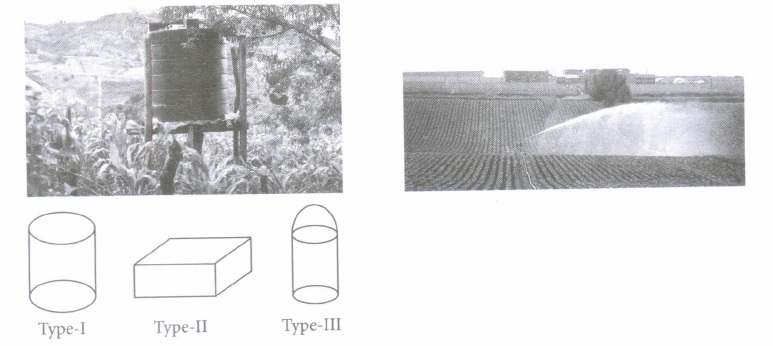
Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
(i) If the radius of type- I tank is 1.5 m and its height is 3.5 m, then find the capacity of tank type- I. (Take \(\pi\): = 3.14)(a) 24727.5 litres (b) 10000 litres (c) 13200 litres (d) 90400 litres (ii) Find the capacity of type- II tank having dimensions 5 m x 4 m x 3.5 m
(a) 72000 litres (b) 70000 litres (c) 250000 litres (d) 404000 litres (iii) How much more water type- III tank contains than tank of type- I, if its base radius is 2.5 m and total height is 5.5 m? [Take \(\pi\) = 3.14]
(a) 12394.5 litres (b) 32200.5 litres (c) 29000.5 litres (d) 66852.5 litres (iv) If Pankaj's father bought type- II tank and wants to cover it with a cloth costs Rs 45 per m2, then find the total cost of cloth used (if cloth is covered on all its faces).
(a) Rs 4495 (b) Rs 1500 (c) Rs 4635 (d) Rs 1750 (v) Find the ratio of the total surface area of type- I and type-Il tanks.
(a) 728: 275 (b) 275: 729 (c) 51: 325 (d) 471: 1030 (a) -
Emily purchased a spinner from a shop, which is of the shape as shown in the figure, in which right circular cone and hemisphere lie on opposite sides of a common base of length 3.5 m. Cylindrical box circumscribing them in this position. Now, answer the following questions.
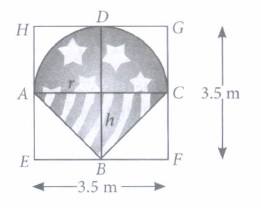
(i) What will be the volume of the cone?(a) 6.5 m3 (b) 2.9 m3 (c) 40 m3 (d) 5.614 m3 (ii) Volume of hemispherical part is
(a) 11.23 m3 (b) 6.03 m3 (c) 8 m3 (d) 9.5 m3 (iii) Volume of cyiinder that circumscribe the cone and hemisphere, is
(a) 31 m3 (b) 17.19 m3 (c) 17.5 m3 (d) 33.69 m3 (iv) Find the additional space enclosed by the cylinder.
(a) 3.14 m3 (b) 0.13 m3 (c) 2.14 cm3 (d) 16.846 m3 (v) Find the ratio of the curved surface areas of cone and hemisphere.
\((a) 1: \sqrt{2}\) \((b) 1: 5\) \((c) 1: \sqrt{5}\) \((d) 1: 3\) (a) -
Pinki's class teacher explained the students about the benefits of drinking fruit juice in the morning. So, Pinki went to a juice stall with her friend Bipin. On the stall, they observed that shopkeeper has three types of glasses of inner diameter 4.6 cm to serve customers. The height of each glass is 11 cm. Seeing this, certain questions came into their mind. Help Pinki and Bipin to solve these questions.
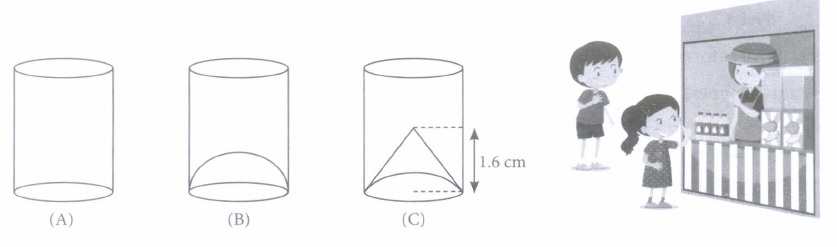
(i) Volume of the type (A) glass is(a) 275 cm3 (b) 250 cm3 (c) 182.88 cm3 (d) 208 cm3 (ii) Volume of type (B) glass is
(a) 208.6cm3 (b) 150.5 cm3 (c) 152.4 cm3 (d) 157.39 cm3 (iii) How much more juice can be filled in type (A) glass than glass of type (C)?
(a) 10.48 mL (b) 9.10 mL (c) 98.12 mL (d) 8.6 mL (iv) Which glass has minimum capacity?
(a) Type (A) (b) Type (B) (c) Type (C) (d) All glasses have same capacity (v) Which mathematical concept has been used in above problem?
(a) Curved surface area (b) Total surface area (c) Volume (d) None of these (a) -
Anjali join four cubical open boxes of edge 20 cm each to make a pot for planting saplings of pudina in her kitchen garden, The saplings are cylindrical in shape with diameter 14.2 cm and height 11 cm.
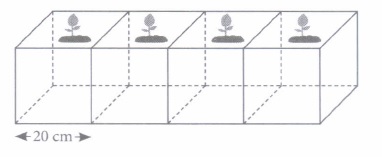
On the basis of above information, answer the following questions.
(i) If Anjali wants to paint the outer surface of the pot, then how much area she needs to paint?(a) 6400 cm2 (b) 5600 cm2 (c) 4200 cm2 (d) 2025 cm2 (ii) What is the volume of the pot formed?
(a) 32000 cm3 (b) 20250 cm3 (c) 40000 cm3 (d) 10125 cm3 (iii) If Anjali decorates the four walls of the pot with coloured square paper of side 10 cm each, then how many pieces of papers would be required?
(a) 120 (b) 54 (c) 160 (d) 40 (iv) Find the volume of 1 sapling.
(a) 1742.75 cm3 (b) 4548.16 cm3 (c) 1764.08 cm3 (d) None of these (v) If Anjali planted 4 saplings in the pot with some soil and compost up to the brim of the pot, then how much soil and compost are there in the pot?
(a) 12612 cm3 (b) 25029 cm3 (c) 21975 cm3 (d) None of these (a) -
Ritu packed a football as a gift for her brother's birthday in a cuboidal box whose diameter is same as that of length of base of the box having length, breadth and height respectively 23 cm, 23 cm and 28 cm.
(i) The volume of the football is(a) 3581 cu.cm (b) 6373.19 cu.cm (c) 6451 cu.cm (d) 9807 cu.crn (ii) Ritu covers the box with a wrapping sheet. The area of the wrapping sheet that covers the box exactly is
(a) 3634 sq.cm (b) 2533 sq.cm (c) 2584 sq.cm (d) 3813 sq.cm (iii) The volume of the box is
(a) 25733 cu.crn (b) 18573 cu.cm (c) 14812 cu.cm (d) 77536 cu.crn (iv) Half of the remaining volume of the box is filled with thermocol balls. Find the volume of thermocol balls used.
(a) 36150.9 cu.cm (b) 4219.405 cu.crn (c) 2764 cu.cm (d) 4048.05 cu.cm (v) The surface area of the football is
(a) 691.03 sq.cm (b) 12772 sq.cm (c) 15544 sq.cm (d) 1662.57 sq.cm (a) -
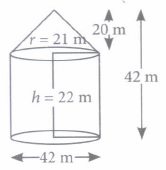
Alok and his family went for a vacation to Iaipur, There they had a stay in tent for a night. Alok found that the tent in which they stayed is in the form of a cone surmounted on a cylinder. The total height of the tent is 42 m, diameter of the base is 42 m and height of the cylinder is 22 m.

Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
(i) How much canvas is needed to make the tent?(a) 3280 m2 (b) 4464 m2 (c) 4818 m2 (d) None of these (ii) If each person needs 126 m2 of floor, then how many persons can be accommodated in the tent?
(a) 17 (b) 11 (c) 19 (d) 15 (iii) Find the cost of the canvas used to make the tent, if the cost of 100 m2 of canvas is Rs 425.
(a) Rs 12944 (b) Rs 18244 (c) Rs 24724 (d) Rs 20476.50 (iv) Find the volume of the tent.
(a) 27248 m3 (b) 32496 m3 (c) 39732 m3 (d) 15874 m3 (v) Find the number of persons that can be accommodated in tent, if each person needs 1892 m3 of space.
(a) 21 (b) 31 (c) 18 (d) 42 (a) -
Isha's father brought an ice-cream brick, empty cones and scoop to pour the ice-cream into cones for all the family members. Dimensions of the ice-cream brick are (30 x 25 x 10) cm3 and radius of hem i-spherical scoop is 3.5 cm. Also, the radius and height of cone are 3.5 cm and 15 cm respectively.

Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
(i) The quantity of ice-cream in the brick (in litres) is(a) 3 (b) 7.5 (c) 2.5 (d) 4.5 (ii) Volume of hemispherical scoop is
(a) 40.6 cm3 (b) 2509 cm3 (c) 89.83 cm3 (d) 20 cm3 (iii) Volume of a cone is
(a) 148 cm3 (b) 250.05 cm3 (c) 145.83 cm3 (d) 192.5 cm3 (iv) The minimum number of scoops required to fill one cone upto brim is
(a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 5 (v) The number of cones that can be filled upto brim using the whole brick is
(a) 15 (b) 39 (c) 40 (d) 42 (a) -
Arpana is studying in X standard. While helping her mother in kitchen, she saw rolling pin made of steel and empty from inner side, with two small hemispherical ends as shown in the figure.
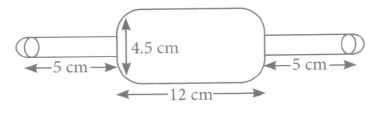
(i) Find the curved surface area of two identical cylindrical parts, if the diameter is 2.5 cm and length of each part is 5 cm.(a) 475 cm2 (b) 78.57 cm2 (c) 877 cm2 (d) 259.19 cm2 (ii) Find the volume of big cylindrical part.
(a) 190.93 cm3 (b) 75 cm3 (c) 77 cm3 (d) 83.5 cm3 (iii) Volume of two hemispherical ends having diameter 2.5 cm, is
(a) 4.75 cm3 (b) 8.18 cm3 (c) 2.76 cm3 (d) 75 cm3 (iv) Curved surface area of two hemispherical ends, is
(a) 17.5cm2 (b) 7.9cm2 (c) 19.64 cm2 (d) 15.5 cm2 (v) Find the difference of volumes of bigger cylindrical part and total volume of the two small hemispherical ends.
(a) 175.50 cm3 (b) 182.75 cm3 (c) 76.85 cm3 (d) 96 cm3 (a)
Case Study
*****************************************
Answers
Surface Areas and Volumes Case Study Questions With Answer Key Answer Keys
-
(i) (b): We know that, volume of cylinder \(=\pi r^{2} h\)
\(\Rightarrow 1540=\frac{22}{7} \times r^{2} \times 10 \)
\(\Rightarrow \frac{154 \times 7}{22}=r^{2} \Rightarrow r^{2}=49 \Rightarrow r=7 \mathrm{~cm}\)
\(\therefore\) Diameter of the base of cylinder \(=2 r=2 \times 7=14 \mathrm{~cm}\)
(ii) (b): We know that, volume of sphere \(=\frac{4}{3} \pi r^{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow 38808=\frac{4}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times r^{3} \)
\(\Rightarrow r^{3}=\frac{38808 \times 3 \times 7}{4 \times 22}=441 \times 21=(21)^{3} \Rightarrow r=21 \mathrm{~cm}\)
\(\therefore\) Diameter of sphere = 42 cm.
(iii) (d): Total volume of shape formed = Volume of cylindrical shapes + Volume of sphere
= 11 x 1540 + 38808 = 16940 + 38808 = 55748 cm3
(iv) (c): Curved surface area of one cylindrical shape \(=2 \pi r h \)
\(=2 \times \frac{22}{7} \times 7 \times 10=440 \mathrm{~cm}^{2}\)
(v) (a): Area covered by cylindrical shapes on the surface of sphere
\(=11 \times \pi r^{2}=11 \times \frac{22}{7} \times 7 \times 7=1694 \mathrm{~cm}^{2}\) -
(i) (b): Lateral surface area of Hermika which is cubical in shape = 4a2 = 4 x (8)2 = 256 m2
(ii) (a): Diameter of cylindrical base = 42 m
\(\therefore\) Radius of cylindrical base (r) = 21 m
Height of cylindrical base (h) = 12 m
\(\therefore\) Number of bricks used \(=\frac{\frac{22}{7} \times 21 \times 21 \times 12}{0.01}\)
= 1663200
(iii) (c) : Given, diameter of Anda which is
hemispherical in shape = 42 m
\(\Rightarrow\) Radius of Anda (r) = 21 m
\(\therefore \quad \text { Volume of } A n d a =\frac{2}{3} \pi r^{3}=\frac{2}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times 21 \times 21 \times 21 \)
\(=44 \times 21 \times 21=19404 \mathrm{~m}^{3}\)
(iv) (d): Given, radius of Pradakshina Path (r) = 25 m
\(\therefore\) Perimeter of path = \(2\pi r\)
\(=\left(2 \times \frac{22}{7} \times 25\right) \mathrm{m}\)
· . Distance covered by priest \(=14 \times 2 \times \frac{22}{7} \times 25\)
= 2200 m
(v) (b):\(\because\) Radius of Anda (r) = 21 m
\(\therefore\) Curved surface area of Anda = \(2\pi r^{2}\)
\(=2 \times \frac{22}{7} \times 21 \times 21=2772 \mathrm{~m}^{2}\) -
(i) (a)
(ii) (d): Slant height of conical cavity \(l=\sqrt{h^{2}+r^{2}}\)
\(=\sqrt{(24)^{2}+(7)^{2}}=\sqrt{576+49}=\sqrt{625}=25 \mathrm{~cm}\)
(iii) (b): Curved surface area of conical cavity = \(\pi r l\)
\(=\frac{22}{7} \times 7 \times 25=550 \mathrm{~cm}^{2}\)
(iv) (c) : External curved surface area of cylinder
\(=2 \pi r h=2 \times \frac{22}{7} \times 7 \times 24=1056 \mathrm{~cm}^{2}\)
(v) (a): Volume of conical cavity \(=\frac{1}{3} \pi r^{2} h\)
\(=\frac{1}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times 7 \times 7 \times 24=1232 \mathrm{~cm}^{3}\) -
(i) (b): Since, volume of sphere = volume of cylinder
\(\Rightarrow \frac{4}{3} \pi R^{3}=\pi r^{2} h\)
where R, r are the radii of sphere and cylinder respectively.
\(\Rightarrow R^{3}=\frac{6 \times 6 \times 8 \times 3}{4}=(6)^{3} \Rightarrow R=6 \mathrm{~cm}\)
\(\therefore\) Radius of sphere = 6 cm
(ii) (a): Volume of sphere \(=\frac{4}{3} \pi R^{3}\)
\(=\frac{4}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times 6 \times 6 \times 6=905.14 \mathrm{~cm}^{3}\)
(iii) (c): \(\because\) Volume of sphere = Volume of cylinder
\(\therefore\) Required ratio = 1 : 1
(iv) (a): Total surface area of the cylinder \(=2 \pi r(r+h)\)
\(=2 \times \frac{22}{7} \times 6(6+8)=2 \times \frac{22}{7} \times 6 \times 14=528 \mathrm{~cm}^{2}\)
(v) (c) -
(i) (b): Volume of cuboidal part = 1 x b x h = (20 x 15 x 5) cm3 = 1500 cm3
(ii) (c): Radius of conical depression, r = 0.6 cm
Height of conical depression, h = 2.1 cm
\(\therefore\) Total volume of conical depressions \(=3 \times \frac{1}{3} \pi r^{2} h\)
\(=\frac{22}{7} \times 0.6 \times 0.6 \times 2.1=\frac{2.376}{1000}-2.376 \mathrm{~cm}^{3}\)
(iii) (d): Volume of wood used in the entire stand = Volume of cuboidal part - Total volume of conical depressions
= 1500 - 2.376 = 1497.624 cm3
(iv) (a)
(v) (d): Cost of wood per cm3 = Rs 5
\(\therefore\) Total cost of making the pen stand
= Rs (5 x 1497.624) = Rs 7488.12 -
We have, radius of each coin = 3.5 cm
\(=\frac{35}{10} \mathrm{~cm}=\frac{7}{2} \mathrm{~cm}\)
Thickness of each coin \(=0.5 \mathrm{~cm}=\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{~cm}\)
So,height of cylinder made by Meera (h1) \(=12 \times \frac{1}{2}=6 \mathrm{~cm}\)
and height of cylinder made by Dhara (h2)
\(=8 \times \frac{1}{2}=4 \mathrm{~cm}\)
(i) (b): Curved surface area of cylinder made by Meera \(=2 \times \frac{22}{7} \times \frac{7}{2} \times 6=132 \mathrm{~cm}^{2}\)
(ii) (b): Required ratio
\(=\frac{\text { Curved surface area of cylinder made by Meera }}{\text { Curved surface area of cylinder made by Dhara }}\)
\(=\frac{2 \pi r h_{1}}{2 \pi r h_{2}}=\frac{h_{1}}{h_{2}}=\frac{6}{4}=\frac{3}{2} \text { i.e., } 3: 2\)
(iii) (a): Volume of cylinder made by Dhara \(=\pi r^{2} h_{2}\)
\(=\frac{22}{7} \times \frac{7}{2} \times \frac{7}{2} \times 4=154 \mathrm{~cm}^{3}\)
(iv) (c): Required ratio
\(=\frac{\text { Volume of cylinder made by Meera }}{\text { Volume of cylinder made by Dhara }} \)
\(=\frac{\pi r^{2} h_{1}}{\pi r^{2} h_{2}}=\frac{h_{1}}{h_{2}}=\frac{6}{4}=\frac{3}{2} \text { i.e., } 3: 2\)
(v) (a): When two coins are shifted from Meera's cylinder to Dhara's cylinder, then length of both cylinders become equal. So, volume of both cylinders become equal -
(i) (d): Let r be the radius of the sphere. Then, diameter of sphere = 24 cm
\(\therefore \quad \text { Radius }(r)=\frac{24}{2}=12 \mathrm{~cm}\)
(ii) (a): Volume of ceramic block = 1 x b x h = 24 x 24 x 27 = 15552 cm3
(iii) (b): Volume of ceramic carved out \(=\frac{4}{3} \pi r^{3}\)
\(=\frac{4}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times(12)^{3}=7241.14 \mathrm{~cm}^{3}\)
(iv) (c): Volume of cuboidal vase = Volume of ceramic block - Volume of sphere
= 15552 - 7241.14 = 8310.86 cm3
(v) (b): Surface area of the sphere carved out \(=4 \pi r^{2}\)
\(=4 \times \frac{22}{7} \times(12)^{2}=1810.28 \mathrm{~cm}^{2}\) -
(i) (a): Type- I tank is cylindrical in shape with r = 1.5 m and h = 3.5 m.
\(\therefore \quad \text { Required volume } =\pi r^{2} h=\left(3.14 \times 1.5^{2} \times 3.5\right) \mathrm{m}^{3} =24.7275 \mathrm{~m}^{3}\)
Now, 1 m3 = 1000 litres
\(\therefore \quad Capacity of type-I tank =(24.7275 \times 1000) litres =24727.5 litres\)
(ii) (b): Capacity of type- II tank = 1 x b x h
= 5 x 4 x 3.5 m3 = 70 m3 = (70 x 1000) litres
= 70000 litres
(iii) (d): Volume of type-III tank
\(=\pi r^{2} h+\frac{2}{3} \pi r^{3}=3.14 \times(2.5)^{2}\left[(5.5-2.5)+\frac{2}{3}(2.5)\right]\)
= 91.58 m3 = 91.58 x 1000 litres = 91580 litres
\(\therefore\) Required difference = 91580 - 24727.5
= 66852.5 litres
(iv) (c): TSA of type-II tank = 2 (lb + bh + hI)
= 2 (5 x 4 + 4 x 3.5 + 3.5 x 5)
= 2(20 + 14 + 17.5) = 103 m2
\(\therefore\) Cost of cloth required = Rs (45 x 103) = Rs 4635
(v) (d): Required ratio \(=\frac{2 \pi r\left(r+h^{\prime}\right)}{2(l b+b h+h l)}\)
\(=\frac{2 \times 3.14 \times 1.5(1.5+3.5)}{103}=\frac{471}{1030} \text { i.e., } 471: 1030\) -
(i) (d): Volume of cone \(=\frac{1}{3} \pi r^{2} h\)
\(= \frac{1}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times \frac{3.5}{2} \times \frac{3.5}{2} \times \frac{3.5}{2}\)
\(\left[\because r=\frac{3.5}{2} \text { and } h=3.5-\frac{3.5}{2}=\frac{3.5}{2}\right] \)
\(= 5.614 \mathrm{~m}^{3}\)
(ii) (a): Volume of hemisphere \(=\frac{2}{3} \pi r^{3}\)
\(=\frac{2}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times \frac{3.5}{2} \times \frac{3.5}{2} \times \frac{3.5}{2}=11.23 \mathrm{~m}^{3}\)
(iii) (d): Volume of cylinder that circumscribe the cone and hemisp here \(=\frac{22}{7} \times \frac{3.5}{2} \times \frac{3.5}{2} \times 3.5\)
= 33.69 m3
(iv) (d): Additional space enclosed by cylinder
= Volume of cylinder - (volume of cone + volume of hemisphere)
= ;33.69- (11.23 + 5614) = 16.846 m3
(v) (a): Required ratio
\(=\frac{\text { Curved surface area of cone }}{\text { Curved surface area of hemisphere }}=\frac{\pi r \sqrt{r^{2}+h^{2}}}{2 \pi r^{2}} \\ \)
\(=\frac{\sqrt{2 r^{2}}}{2 r}=\frac{\sqrt{2} r}{2 r}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \text { i.e., } 1: \sqrt{2}\) -
Diameter of each glass = 4.6 cm
\(\therefore\) Radius of each glass = 2.3 cm
Height of each glass = 11 cm
(i) (c): Volume of type (A) glass \(=\pi r^{2} h\)
\(=\frac{22}{7} \times 2.3 \times 2.3 \times 11=182.88 \mathrm{~cm}^{3}\)
(ii) (d): Volume of type (B) glass
= Volume of type (A) glass - Volume of hemisphere
\(=182.88-\frac{2}{3} \pi r^{3}=182.88-\frac{2}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times 2.3 \times 2.3 \times 2.3 \)
\(=182.88-25.49=157.39 \mathrm{~cm}^{3}\)
(iii) (d) : Volume of type (C) glass = Volume of type (A) glass - Volume of cone
\(=182.88-\frac{1}{3} \pi r^{2} h=182.88-\frac{1}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times 2.3 \times 2.3 \times 1.6 \)
\(=182.88-8.86=174.02 \mathrm{~cm}^{3}\)
\(\therefore\) Required difference = 182.88 - 174.02
= 8.86 cm3 = 8.86 mL
(iv) (b) : Glass of type B has minimum capacity.
(v) (c) -
(i) (b): Area to be painted = Area of 14 square faces = 14 x (20)2 = 5600 cm2
(ii) (a): Height of pot = 20 cm
Length of pot = 20 x 4 = 80 cm
Breadth of pot = 20 cm
\(\therefore\) Volume of pot = 20 x 80 x 20 = 32000 cm3
(iii) (d) : Required area = 2(l + b) x h
= 2(80 + 20) x 20 = 4000 cm2
Side of coloured square paper = 10 cm
\(\therefore\) Number of pieces of paper required \(=\frac{4000}{10 \times 10}=40\)
(iv) (a) : We have,
\(\text { Radius }(r)=\frac{14.2}{2} \mathrm{~cm}=7.1 \mathrm{~cm}\)
\(\text { Height }(h)=11 \mathrm{~cm} \)
\(\therefore \quad \text { Volume of each sapling }=\pi r^{2} h=\frac{22}{7} \times(7.1)^{2} \times 11 \)
\(=1742.75 \mathrm{~cm}^{3}\)
(v) (b): Total volume of pot = 32000 cm3
Volume of 4 saplings = 1742.75 x 4 = 6971 cm3
So, volume of compost and soil = 32000 - 6971 = 25029 cm3 -
Diameter of football = Length of base of the box =23cm
\(\therefore\) Radius of football \(=\left(\frac{23}{2}\right) \mathrm{cm}\)
(i) (b): Volume of the football \(=\frac{4}{3} \pi r^{3}\)
\(=\frac{4}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times \frac{23}{2} \times \frac{23}{2} \times \frac{23}{2}=6373.19 \mathrm{~cm}^{3}\)
(ii) (a): Area of wrapping sheet = Total surface area of the cuboidal box
= 2(lb + bh + hl) = 2(23 x 23 + 23 x 28 + 28 x 23)
= 2(529 + 644 + 644) = 3634 cm2
(iii) (c) : Volume of the box = I x b x h = 23 x 23 x 28 = 14812 cm3
(iv) (b) : Volume of thermocal balls used
\(=\frac{1}{2} \text { (Volume of box - Volume of football) } \)
\(=\frac{1}{2}(14812-6373.19)=\frac{1}{2} \times 8438.81=4219.405 \mathrm{~cm}^{3}\)
(v) (d): Surface area of the football = \(4 \pi r^{2}\)
\(=4 \times \frac{22}{7} \times \frac{23}{2} \times \frac{23}{2}=1662.57 \mathrm{~cm}^{2}\) -
(i) (c) : Required area of canvas = Curved surface area of cone + Curved surface area of cylinder
\(=\pi r l+2 \pi r h=\pi r(l+2 h) \)
\(=\frac{22}{7} \times 21(29+44)=4818 \mathrm{~m}^{2} \)
\(\because l=\sqrt{r^{2}+h_{1}^{2}} =\sqrt{(21)^{2}+(20)^{2}} \)
\(=\sqrt{841}=29 \mathrm{~m} \)
(ii) (b): Area of floor \(=\pi r^{2}\)
\(=\frac{22}{7} \times 21 \times 21=1386 \mathrm{~m}^{2}\)
Number of persons that can be accommodated in the tent \(=\frac{1386}{126}=11\)
(iii) (d) : Since, cost of 100 m2 of canvas = Rs 425
\(\therefore\) Cost of 1 m 2 of canvas = Rs 4.25
Thus, cost of 4818 m2 of canvas = Rs 20476.50
(iv) (c) : Volume of tent = Volume of cone + Volume of cylinder
\(=\frac{1}{3} \pi r^{2} h_{1}+\pi r^{2} h=\pi r^{2}\left(\frac{1}{3} h_{1}+h\right)\)
\(=\frac{22}{7} \times(21)^{2}\left[\frac{20}{3}+22\right]=\frac{9702}{7} \times \frac{86}{3}=39732 \mathrm{~m}^{3}\)
(v) (a): Required rrumber of persons
\(=\frac{\text { Volume of tent }}{\text { Space required by one person }}=\frac{39732}{1892}=21\) -
(i) (b): Quantity of ice-cream in the brick
= volume of the brick = (30 x 25 x 10) cm3= 7500 cm3
\(=\frac{7500}{1000} l \quad\left[\because 1 l=1000 \mathrm{~cm}^{3}\right] \)
\(=7.5 \mathrm{l}\)
(ii) (c): Volume of hemispherical scoop \(=\frac{2}{3} \pi r^{3}\)
\(=\frac{2}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times(3.5)^{3}=\frac{1886.5}{21}=89.83 \mathrm{~cm}^{3}\)
(iii) (d) : Volume of cone \(=\frac{1}{3} \pi r^{2} h\)
\(=\frac{1}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times 3.5 \times 3.5 \times 15=\frac{4042.5}{21}=192.5 \mathrm{~cm}^{3}\)
(iv) (a) : Number of scoops required to fill one cone
\(=\frac{\text { Volume of a cone }}{\text { Volume of a scoop }}=\frac{192.5}{89.83}=2.14 \approx 2\)
(v) (b): Number of cones that can be filled using the whole brick \(=\frac{\text { Volume of brick }}{\text { Volume of } 1 \text { cone }}\)
\(=\frac{7500}{192.5}=38.96 \approx 39\) -
(i) (b):Curved surface area of two identical cylindrical parts \(=2 \times 2 \pi r h=2 \times 2 \times \frac{22}{7} \times \frac{2.5}{2} \times 5\)
= 78.57 cm2
(ii) (a): Volume of big cylindrical part \(=\pi r^{2} h\)
\(=\frac{22}{7} \times \frac{4.5}{2} \times \frac{4.5}{2} \times 12=190.93 \mathrm{~cm}^{3}\)
(iii) (b) :Volume of two hemispherical ends \(=2 \times \frac{2}{3} \pi r^{3}\)
\(=\frac{2 \times 2}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times\left(\frac{2.5}{2}\right)^{3}=8.18 \mathrm{~cm}^{3}\)
(iv) (c) : Curved surface area of two hemispherical ends \(=2 \times 2 \pi r^{2}=2 \times 2 \times \frac{22}{7} \times \frac{2.5}{2} \times \frac{2.5}{2}=19.64 \mathrm{~cm}^{2}\)
(v) (b): Difference of volume of bigger cylinder to two small hemispherical ends = 190.93 - 8.18 = 182.75 cm3

























