Class 10th Science - Metals and Non-Metals Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
By QB365 on 09 Sep, 2022
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 10 Science Subject - Metals and Non-Metals, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Metals and Non-Metals Case Study Questions With Answer Key
10th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Science
-
The chemical reactivity of an element depends upon its electronic configuration. All elements having less than eight electrons in the outermost shell show chemical reactivity. During chemical reactions, atoms of all elements tend to achieve a completely filled valence shell. Metals are electropositive in nature. They have tendency to lose one or more electrons present in the valence shell of their atoms to form cations and achieve nearest noble gas configuration. The compounds formed by the transfer of electrons from one element to other are known as ionic or electrovalent compounds.
(i) The electronic configurations of three elements X, Y and Z are:
X : 2 Y: 2, 8, 7 Z : 2, 8, 2
Which of the following is correct regarding these elements?(a) X is a metal. (b) Y is a metal. (c) Z is a non-metal (d)Yis a non-metal and Z is a metal (ii) Element X reacts with element Y to form a compound Z. During the formation of compound Z, atoms of X lose one electron each whereas atoms of Y gain one electron each. Which of the following properties is not shown by compound Z?
(a) High melting point (b) Low melting point (c) Occurrence as solid (d) Conduction of electricity in molten state (iii) Which of the following is correct representation of formation of magnesium chloride?
(d) None of these (iv) The electronic configuration of sodium ion is
(a) 2,8,8 (b) 2,8,2. (c) 2,6 (d) 2,8. (v)Which of the following represents an electropositive element?
(a) 2,8,6 (b) 2,8,8 (c) 2,8,8,1 (d) 2, 7 (a) -
The arrangement of metals in a vertical column in the decreasing order of their reactivities is called the reactivity series or activity series of metals. The most reactive metal is at the top position of the reactivity series. The least reactive metal is at the bottom of the reactivity series.
Hydrogen, though a non-metal, has been included in the activity series of metals only for comparison. Apart from it, the hydrogen atom also has tendency to lose its valence electron and form cation which behaves like metal.
\(\mathrm{H} \rightarrow \mathrm{H}^{+}+e^{-}\)
(i) Which metal can be displaced by copper from its salt solution?(a) Zinc (b) Silver (c) Iron (d) Lead (ii) An element 'X after reacting with acids liberates hydrogen gas and can displace lead and mercury from their salt solutions. The metal 'X is
(a) copper (b) gold (c) calcium (d) hydrogen. (iii) the most reactive metal is
(a) potassium (b) barium (c) zinc (d) calcium (iv) The metal which does not liberate hydrogen gas after reacting with acid is
(a) zinc (b) lead (c) iron (d) gold (v) Which of the following metals does not react with water at all?
(I) Sodium
(II) Copper
(III) Aluminium
(IV) Lead(a) I and III only (b) IV only (c) II and IV only (d) I, II, III and IV (a) -
Metals as we know, are very useful in all fields, industries in particular. Non-metals are no less in any way. Oxygen present in air is essential for breathing as well as for combustion. Non-metals form a large number of compounds which are extremely useful, e.g., ammonia, nitric acid, sulphuric acid, etc.
Non-metals are found to exist in three states of matter. Only solid non-metals are expected to be hard however, they have low density and are brittle. They usually have low melting and boiling points and are poor conductors of electricity.
(i)____________ is a non-metal but is lustrous(a) Phosphorus (b) Sulphur (c) Bromine (d) Iodine (ii) Which of the following is known as 'King of chemicals'?
(a) Urea (b) Ammonia X (c) Sulphuric acid (d) Nitric acid (iii) Which of the following non-metals is a liquid?
(a) Carbon (b) Bromine (c) Iodine (d) Sulphur (iv) Hydrogen is used
(a) for the synthesis of ammonia (b) for the synthesis of methyl alcohol (c) in welding torches (d) all of these (v) Generally, non-metals are bad conductors of electricity but 'X' which is a form of carbon is a good conductor of electricity and is an exceptional non-metal. 'X'is
(a) diamond (b) graphite (c) coal (d) coke. (a) -
Ionic compound is a chemical compound in which ions are held together by ionic bonds. An ionic bond is the type of chemical bond in which two oppositely charged ions are held through electrostatic forces. We know that, metal atoms have loosely bound valence electrons in their valence shell and non-metal atoms need electrons in their valence shell to attain noble gas configuration. The metal atom loses the valence electrons while non-metal atom accepts these electrons. By losing electrons, metal atoms change to cations and by accepting electrons, non-metals form anions. Ionic compounds are generally solid and exist in the form of crystal. They have high melting and boiling points.
(i) Which of the following can change to a cation?(a) Fluorine (b) Oxygen (c) Potassium (d) Neon (ii) Which of the following can change to an anion?
(a) Iodine (b) Magnesium (c) Calcium (d) Xenon (iii) Ionic compounds are soluble in _____________.
(a) Kerosene (b) Petrol (c) Water (d) None of these (iv) Which of the following statements is correct about ionic compounds?
I. They conduct electricity in solid state.
II. They conduct electricity in solutions.
III. They conduct electricity in molten state.(a) I only (b) II only (c) III only (d) II and III only (v) Select the incorrect statement.
(a) Ionic compounds are generally brittle (b) Ions are the fundamental units of ionic compounds (c) Formation of ionic bonds involve sharing of electrons (d) NaCl is an ionic compound. (a) -
An element is a pure substance made up of same kind of atoms. At present, nearly 118 elements are known but all of them do not occur free in nature, some of them have been synthesized by artificial methods. Based on their properties, they are mainly classified as metals and non-metals. Metals are those elements which lose electrons and form positive ions i.e., they are electropositive in nature. They are generally hard, good conductors of heat and electricity, malleable, ductile and have striking lustre. They have a significant role to play in our daily life.
(i) Metals which are of vital importance to the national defence, energy and industry sector are called strategic metals. Which of the following is a strategic metal?(a) Titanium (b) Zirconium (c) Manganese (d) All of these (ii) Which metal is the best conductor of electricity?
(a) Silver (b) Platinum (c) Nickel (d) Iron (iii) Which of the following metals is not a coinage metal?
(a) Copper (b) Silver (c) Iron (d) Gold (iv) Which of the following are the most malleable metals?
(I) Sodium
(II) Gold
(III) Potassium
(IV) Silver(a) (I) and (IV) (b) (II) and (III) (c) (III) and (IV) (d) (II) and (IV) Identify the correct statement(s).
(I) The wires that carry current in our homes have a coating of PVC or a rubber like material.
(II) School bells are made of metals.
(III) Metals do not conduct electricity.
(IV) Metals which produce a sound on striking a hard surface are said to be non-sonorous.(a) (I) and (III) (b) (I) and (II) (c) (III) and (IV) (d) Only (II) (a) -
The chemical properties of metals are mostly linked with the electron releasing tendency of their atoms. Greater the tendency, more will be the reactivity of the metal. They react with oxygen, water, hydrogen, acids, etc. Since they can lose electrons, they act as reducing agents. Some reactions of metals are given as :
Metal + Oxygen \(\longrightarrow\) Metal oxide
Metal + Water \(\longrightarrow\)7 Metal hydroxide + Hydrogen ..
Metal + Acid(dilute)\(\longrightarrow\)7 Metal salt + Hydrogen
Metal X + Salt solution of metal Y \(\longrightarrow\)7 Salt solution of X + Y (Displacement reaction).
(i) Metals such as _________ and __________ react so vigorously that they catch fire if kept in the open. Hence, to protect them and to prevent accidental fires, they are kept immersed in _____________.(a) phosphorus, magnesium, water (b) sodium, potassium, kerosene oil (c) sodium, potassium, water (d) tin, lead, alcohol (ii) Which of the following pairs will give displacement reaction?
(a) NaCl solution and copper metal (b) MgCl2 solution and aluminium metal (c) FeSO4 solution and silver metal (d) AgNO3 solution and copper metal (iii) There are four metals K, L, M and N. Identify them by using the hints given below.
K forms basic oxide.
L forms amphoteric oxide.
Oxide of M dissolves in water to form alkali.
N does not react with water at all.\({ (a) } K \rightarrow \mathrm{Zn}, L \rightarrow \mathrm{Al}, M \rightarrow \mathrm{Na}, N \rightarrow \mathrm{Fe}\) \({ (b) } K \rightarrow \mathrm{Fe}, L \rightarrow \mathrm{Na}, M \rightarrow \mathrm{K}, N \rightarrow \mathrm{Zn}\) \({ (c) } K \rightarrow \mathrm{K}, L \rightarrow \mathrm{Cu}, M \rightarrow \mathrm{Pb}, N \rightarrow \mathrm{Na}\) \({ (d) } K \rightarrow \mathrm{Cu}, L \rightarrow \mathrm{Zn}, M \rightarrow \mathrm{K}, N \rightarrow \mathrm{Pb}\) (iv) Which metal does not react with dilute hydrochloric acid?
(a) Iron (b) Sodium (c) Zinc (d) Copper (v) Food cans are coated with tin and not with zinc because
(a) zinc is costlier than tin (b) zinc has a higher melting point than tin (c) zinc is more reactive than tin (d) zinc is less reactive than tin. (a) -
On the basis of reactivity of different metals with oxygen, water and acids as well as displacement reactions, the metals have been arranged in the decreasing order of their reactivities. This arrangement is known as activity series or reactivity series of metals.
The basis of reactivity is the tendency of metals to lose electrons. If a metal can lose electrons easily to form positive ions, it will react readily with other substances. Therefore, it will be a reactive metal. On the other hand, if a meal loses electrons less rapidly to form a positive ion, it will react slowly with other substances. Therefore, such a metal will be less reactive.
(i) Which of the following metals is less reactive than hydrogen?(a) Copper (b) Zinc (c) Magnesium (d) Lead (ii) Which of the following metals is more reactive than hydrogen?
(a) Mercury (b) Platinum (c) Iron (d) Gold (iii) Which of the following metals reacts vigorously with oxygen?
(a) Zinc (b) Magnesium (c) Sodium (d) Copper (iv) Which of the following represents the correct order of reactivity for the given metals?
\({ (a) } \mathrm{Na}>\mathrm{Mg}>\mathrm{Al}>\mathrm{Cu}\) \({ (b) } \mathrm{Mg}>\mathrm{Na}>\mathrm{Al}>\mathrm{Cu}\) \({ (c) } \mathrm{Na}>\mathrm{Mg}>\mathrm{Cu}>\mathrm{Al}\) \({(d) } \mathrm{Mg}>\mathrm{Al}>\mathrm{Na}>\mathrm{Cu}\) (v) Hydrogen gas is not evolved when a metal reacts with nitric acid. It is because HNO3 is a strong oxidising agent. It oxidises the H2 produced to water and itself gets reduced to any of the nitrogen oxides (N2O, NO, NO2 ). But ___________ and ___________ react with very dilute HNO3 to evolve H2 gas.
(a) Pb, Cu (b) Na, K (c) Mg, Mn (d) AI, Zn (a) -
Non-metals are highly electronegative in nature. They have a tendency to gain electrons in their valence shell to achieve nearest noble gas configuration. Thus, they form anions and act as good oxidising agents.
\(X \quad+n e^{-} \longrightarrow X^{n-}\)
(non-metal atom) (anion)
They react with air or oxygen on heating to form oxides which react with water to form acids. Thus, nonmetal oxides are acidic in nature. Non-metals do not react with dilute acids at all. This is because they are electronegative and therefore, cannot displace hydrogen from acids but they form covalent hydrides when heated with hydrogen.
(i) The acid formed when sulphur trioxide reacts with water is(a) sulphurous acid (b) sulphuric acid (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these (ii) An element 'X' forms an oxide XO2 , which is a very useful gas used in the process of photosynthesis. The element 'X' is
(a) sulphur (b) nitrogen (c) carbon (d) phosphorus (iii) Non-metals generally act as
(a) oxidising agents (b) reducing agents (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these (iv) Which of the following elements produces basic oxide on reacting with oxygen?
(a) Chlorine (b) Sulphur (c) Phosphorus (d) Magnesium (v) Which of the following is a covalent hydride?
(a) CH4 (b) NH3 (c) H2S (d) All of these (a) -
Although there is no sharp line of distinction between metals and non-metals yet there are some distinctive differences. The main points of differences are:
Property Metals Non-metals Electronic structure They have 1 to 3 electrons in the outermost shell of their atoms They have 4 to 8 electrons in the outermost shell of their atoms. State of existence They are mostly solid at room temperature except mercury and gallium which are liquid. They are either solids or gases at room temperature (except bromine which is a liquid). Density They have high density. They have low density. Nature of ions They are electropositive elements and hence, lose one or more electrons to form positive ions. They are electronegative elements and
hence, gain one or more electrons to form negative ions.Nature of chlorides They generally combine with chlorine to form solid ionic chlorides which conduct electricity in the aqueous solution or in the molten state. They combine with chlorine to form covalen chlorides. These are either gases or liquids. Non-metal chlorides do not contain ions, therefore, they do not conduct electricity. Nature of oxides They form basic oxides, though some oxides are amphoteric also. They form acidic or neutral oxides. Displacement of hydrogen from acids Metals which lie above hydrogen in the reactivity series displace hydrogen from acids. They do not displace hydrogen from acids. (i) Match column-I with column-Il and select the correct option using the given code
Column-I Column-II P. A metal that forms amphoteric oxides (I) Ga Q. A metal which melts when keep on our palm (II) Au R. A metal that has highest density (III) Al S. A metal which cannot displace hydrogen from acids (IV) Os (a) P-(II), Q-(I), R-(lII), S-(lV) (b) P-(III), Q-(I), R-(IV), S-(lI) (c) P-(lV), Q-(II), R-(lII), S-(I) (d) P-(lII), Q-(II), R-(I), S-(lV) (ii) State True (T) or False (F) for the following statements.
(I) Non-metals react with acids to give a salt and hydrogen gas.
(II) Zinc oxide is amphoteric in nature.
(III) Copper oxide is basic in nature.
(IV) Hydrogen gas is evolved when a metal reacts with dilute acid.
(V) Copper reacts vigorously with dilute HCl.(I) (II) (III) (IV) (V) (a) F F F T T (b) T F T F F (c) F T F F T (d) F T T T F (iii) Tick (✓) the correct statements and cross (x) the incorrect statements.
(I) Non-metals are either solids or gases except mercury which is a liquid.
(II) Sodium is a metal and can lose its electrons easily.
(III) Most non-metals produce acidic oxides when dissolved in water. Most metals produce basic oxides on reaction with water.
(IV) Graphite is a conductor of electricity.(I) (II) (III) (IV) (a) ✓ メ ✓ メ (b) メ ✓ メ ✓ (c) メ ✓ ✓ ✓ (d) メ ✓ ✓ メ (iv) An element X (atomic number 12) reacts with another element Y (atomic number 17) to form a compound Z. Which of the following statements are true regarding this compound?
I. Molecular formula of Z is XY2
II. It is soluble in water.
III. X and Yare joined by sharing of electrons.
IV. It would conduct electricity in the molten state.(a) II and III only (b) I and II only (c) I, III and IV only (d) I, II and IV only (v) Which of the following metals form an amphoteric oxide?
(a) Zn (b) Ca (c) Na (d) Cu (a) -
Sample pieces of five metals P, Q, R, S and T are added to the tabulated solutions separately. The results observed are shown in the table given below:
Metal Solutions CuSO4 ZnSO4 FeSO4 AgNO3
P No change No change No change A coating on metal Q Brown coating ___ Grey deposit A coating on metal R No change No change No change No change S ___ No change No change Brown deposit T Brown deposit New coating New coating New coating Based on the observations recorded in the table answer the following questions:
(i) Which is the most reactive metal?(a) Q (b) R (c) S (d) T (ii) Which is the least reactive metal?
(a) P (b) R (c) T (d) Q (iii) Activity series of elements is
(a) the arrangement of elements in increasing order of reactivity. (b) the arrangement of elements in decreasing order of reactivity. (c) the arrangement of oxides of elements in increasing order of reactivity (d) none of these. (iv) Which of the following metal is least reactive?
(a) Zn (b) Cu (c) Ag (d) Fe (v) Decreasing order of reactivity is
(a) P>Q>R >S>T (b) Q>T>R>S>P (c) T>Q>S>P>R (d) S>R>Q>T>P (a) -
Metallic Character
The ability of an atom to donate electrons and form positive ion (cation) is known as electropositivity or metallic character. Down the group, metallic character increases due to increase in atomic size and across the period, from left to right electropositivity decreases due to decrease in atomic size.
Non-Metallic Character
The ability of an atom to accept electrons to form a negative ion (anion) is called non- metallic character or electronegativity. The elements having high electro-negativity have a higher tendency to gain electrons and form anion. Down the group, electronegativity decreases due to increase in atomic size and across the period, from left to right electronegativity increases due to decrease in atomic size.
(i) Which of the following correctly represents the decreasing order of metallic character of Alkali metals plotted in the graph?
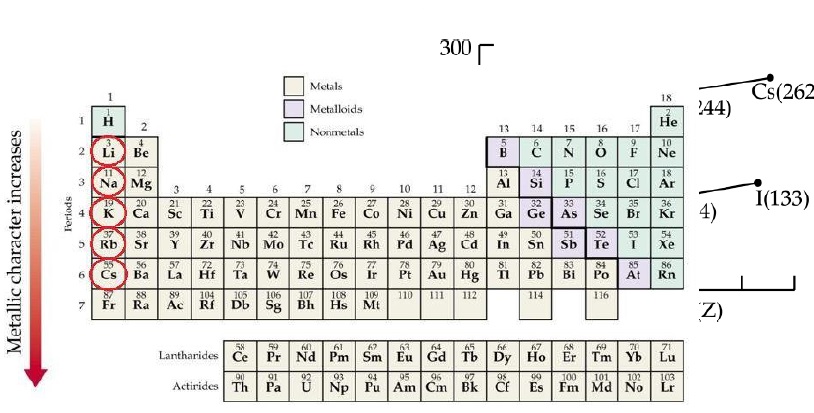
(a) Cs > Rb > Li > Na > K (b) K > Rb > Li > Na > Cs (c) Cs > Rb > K > Na > Li (d) Cs > K > Rb > Na > Li (ii) Hydrogen is placed along with Alkali metals in the modern periodic table though it shows non-metallic character
(a) as Hydrogen has one electron & readily loses electron to form negative ion
(b) as Hydrogen can easily lose one electron like alkali metals to form positive ion
(c) as Hydrogen can gain one electron easily like Halogens to form negative ion
(d) as Hydrogen shows the properties of non-metals
(iii) Which of the following has highest electronegativity?(a) F (b) C (c) Br (d) I (iv) Identify the reason for the gradual change in electronegativity in halogens down group.
(a)Electronegativity increases down the group due to decrease in atomic size
(b)Electronegativity decreases down the group due to decrease in tendency to lose lectrons
(c)Electronegativity decreases down the group due to increase in atomic radius/ tendency to gain electron decreases
(d)Electronegativity increases down the group due to increase in forces of attractions between nucleus & valence electrons
(v) Which of the following reason correctly justifies that “Fluorine (72pm) has smaller atomic radius than Lithium (152pm)”?
(a) F and Li are in the same group. Atomic size increases down the group
(b) F and Li are in the same period. Atomic size increases across the period due to increase in number of shells
(c) F and Li are in the same group. Atomic size decreases down the group
(d) F and Li are in the same period and across the period atomic size/radius decreases from left to right.(a)
Case Study
*****************************************
Answers
Metals and Non-Metals Case Study Questions With Answer Key Answer Keys
-
(i) (d)
(Ii) (b): '2' is an ionic compound
\({ (iii) }(\mathrm{a}): \mathrm{Mg} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Mg}^{2+}+2 e^{-}\) \(\mathrm{Cl}+e^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Cl}^{-}\) \(\mathrm{Mg}^{2+}+2 \mathrm{Cl}^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{MgCl}_{2}\)
2,8,2 2,8 2,8,7 2,8,8
\((\text { iv })(\mathrm{d}): \mathrm{Na} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Na}^{+}+e^{-}\)
2,8,1 2,8
(v) (c): (a) and (d) represent electronegative elements and (b) represents a noble gas. -
(i) (b) : Copper is more reactive than silver thus, it can displace silver from its salt solution.
(ii) (c): Calcium is more reactive than lead and mercury.
(iii) (a) :Potassium is present at the top of the activity series.
(iv) (d): Gold is below hydrogen in the reactivity series so, it does not liberate hydrogen gas on reaction with acids.
(v) (c): Metals such as lead, copper, silver and gold do not react with water at all. -
(i) (d) : Iodine is a lustrous non-metal
(ii) (c): H2 SO4 is known as 'King of Chemicals
(iii) (b): Bromine exists as a liquid.
(iv) (d)
(v) (b): Graphite conducts electricity because of the delocalised electrons in its structure -
(i) (c): Potassium, being a metal, can change to cation by losing its valence electron.
(ii) (a): Iodine, being a non-metal, can change to anion by gaining electron.
(iii) (c): Ionic compounds are generally soluble in water and insoluble in kerosene and petrol.
(iv) (d): Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity in solid state as ions are very closely packed and are free to move.
(v) (c): Formation of ionic bonds involve complete transfer of electrons from metal atom to non-metal atom. -
(i) (d): Titanium, zirconium and manganese are used in defence equipments as they are light and durable and therefore, are called strategic metals.
(ii) (a)
(iii) (c): Copper, silver and gold are called coinage metals because they are used in making coins, jewellery etc.
(iv) (d)
(v) (b): Metals conduct electricity. Metals which produce a sound on striking a hard surface are said to be sonorous. -
(i) (b)
(Ii) (d): As copper is more reactive than silver, it displaces silver from silver nitrate solution.
(iii) (d): CuO is basic in nature, ZnO is amphoteric in nature.
Oxide of potassium dissolves in water to form alkali.\(\mathrm{K}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(s)}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(l)} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{KOH}_{(a q)}\) Pb does not react with water at all. Thus, K, L, M and N are Cu, Zn, K and Pb respectively.
(iv) (d)
(v) (c): Zinc being more reactive than tin can react with food elements kept in food cans. -
(i) (a): Copper is placed below hydrogen in activity series therefore, it is less reactive than hydrogen.
(ii) (c): Iron is placed above hydrogen in activity series therefore, it is more reactive than hydrogen.
(iii) (c)
(iv) (a)
(v) (c) -
\({ (i) }(\mathrm{b}): \mathrm{SO}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \longrightarrow \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}+\text { heat }\)
(ii) (c): Carbon forms CO2 on reaction with oxygen. During photosynthesis plants take in CO2 ,
(iii) (a): Non-metals act as oxidising agents since they can accept electrons.
(iv) (d): Magnesium, being a metal, produces basic oxide on reaction with oxygen.
\(2 \mathrm{Mg}+\mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{MgO}\)
(v) (d): Carbon, nitrogen and sulphur are non-metals hence, they form covalent hydrides. -
(i) (b)
(ii) (d)
(iii) (c)
(iv) (d): An element (X) with atomic number 12 is Mg. Element (Y) with atomic number 17 is Cl. Therefore, compound (Z) will be MgCI2. It is soluble in water. It is an ionic compound and it conducts electricity in the molten state.
(v) (a) -
(i) (d): The most reactive metal is T.
(ii) (b): The least reactive metal is R.
(iii) (b)
(iv) (c)
(v) (c): T> Q> S> P> R -
(i) (c) Cs > Rb > K > Na > Li
As we move down the group atomic radius increases so the metallic character also increases.
Hence the order is Li < Na < K < Rb < Cs
(ii) (b) as Hydrogen can easily lose one electron like alkali metals to form positive ion
(iii) (a) F
(iv) (c)Electronegativity decreases down the group due to increase in atomic radius/ tendency to gain electron decreases
(v) (d) F and Li are in the same period and across the period atomic size/radius decreases from left to right.
Case Study

























