Class 12th Biology - Ecosystem Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
By QB365 on 08 Sep, 2022
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 12 Biology Subject - Ecosystem, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Ecosystem Case Study Questions With Answer Key
12th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Biology
-
An ecosystem can be visualised as a functional unit in nature, where living organisms interact among themselves and with the surrounding physical environment also. The interaction of the biotic and abiotic components results in a physical structure that is characteristic of an ecosystem.
(a) Name the two features that define the structural aspect of an ecosystem.
(b) Mention the four common functional aspects of an ecosystem.(a) -
A pond is a shallow water body, which is fairly a self-sustainable unit that explains the complex interactions in an aquatic ecosystem. The water with all the dissolved inorganic and organic nutrients is the major abiotic component.
Name the three groups of biotic components in the pond and give an example for each.(a) -
The fallen parts of plants such as leaves, flowers, etc., faecal matter of animals, dead remains of animals, etc. are ultimately broken down into simpler inorganic nutrients, carbon dioxide and water.
1. Fragmentation, 2. Leaching, 3. Catabolism are some important steps in the process; they occur simultaneously.
(a) What term is given to the group of organisms that carry out the steps 1 and 3, respectively and give an example for each.
(b) Name the other two steps involved in the process.(a) -
Organisms occupy a specific place in their natural surroundings or in a community according to their feeding relationship with the other organisms. Based on the source of nutrition of food organisms occupy a particular place, called trophic level, in a food chain.
(a) What technical term is given to the organisms occupying the first, second and third trophic levels in a food chain?
(b) Choose an example for each of the above trophic levels, from the following list of organisms: Rabbit, Wolf, phytoplanktons, frog, snail, Hydrilla, jackal.(a) -
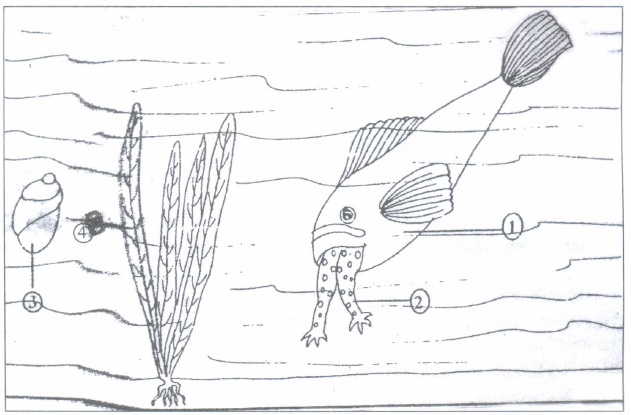
A part of an aquatic ecosystem is represented in the picture provided above.
(a) Mention the relationship between and with respect to population interaction
(c) Construct a food chain operating in this ecosystem.(a) -
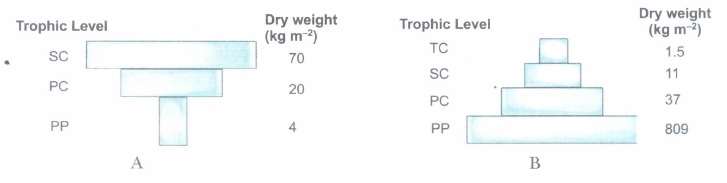
Pyramids of Biomass of two types are shown in the diagram given above.
Answer the following questions.
(a) Identify the type of ecosystems in which the pyramid of biomass A and B occur, respectively.
(b) Why is the pyramid A inverted and B upright?(a) -
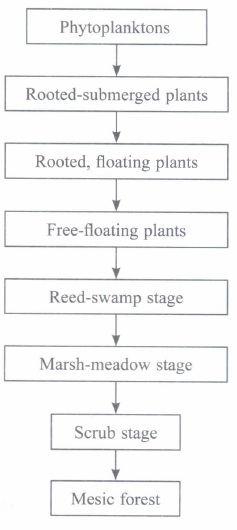
Over the years, it has been observed that some of the lakes are disappearing due to urbanisation. In the absence of human interference, depict through a flow chart, how the successional series progresses from hydric to mesic condition.
(a)
Case Study
*****************************************
Answers
Ecosystem Case Study Questions With Answer Key Answer Keys
-
(a) Structural aspects
(i) Species composition
(ii) Stratification
(b) Functional aspects
(i) Productivity
(ii) Decomposition
(iii) Energy flow
(iv) Nutrient cycling. -
The three groups of biotic components
(i) Producers - e.g. Phytoplanktons, some algae, submerged and floating plants.
(ii) Consumers - e.g. zooplanktons, sanils, fish.
(iii) Decomposers - e.g. some bacteria, fungi, flagellates. -
(a) Step 1: Detritivores, e.g. earthworm
Step 3: Decomposers, e.g. some fungi and bacteria
(b) Humification and mineralisation are the other two steps. -
(a) First trophic level - Producers
Second trophic level - Herbivores/Primary consumers
Third trophic level - Secondary consumers/Primary carnivores.
(b) First trophic level - Phytoplanktons, Hydrilla. Second trophic level - Rabbit, snail Third trophic level - Wolf, frog, jackal. -

-
(a) A - Aquatic/Marine/Sea ecosystem.
B - Grassland/Forest ecosystem.
(b) In a sea (A)
(i) The pyramid of biomass in a sea is inverted; this is because the biomass of consumers like fishes far exceeds that of the producers, i.e., phytoplanktons.
In a forest (B)
(i) The pyramid of biomass in a forest is upright; this is because, the biomass of producers is higher than that of primary consumers (herbivores) and that of herbivores is greater than that of carnivores. -