Class 12th Biology - Microbes in Human Welfare Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
By QB365 on 08 Sep, 2022
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 12 Biology Subject - Microbes in Human Welfare, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Microbes in Human Welfare Case Study Questions With Answer Key
12th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Biology
-
Microbes are the major components of biological systems on this earth. Microbes are omnipresent, i.e., they are present every where in the soil, water, air, inside the bodies of plants, animals and humans.
(a) Microbes are present even in such places, where no other life forms could possibly exist. Name two such places.
(b) Name two groups of microbes that can be grown on nutrient media to form colonies.
(c) Write the scientific name of the microbe employed in fermenting malted cereals and fruit juices.(a) -
Antibiotics produced by microbes are regarded as one of the most significant discoveries of the twentieth century. Antibiotics are the chemical substances which are produced by some microbes and can kill or retard the growth of other (diseasecausing) microbes.
(a) Name the scientist who discovered the first antibiotic and the organism he was working on.
(b) Name the first antibiotic and its source organism.
(c) Name the scientists who established the potential of the above as an effective antibiotic.(a) -
Large quantities of sewage is generated everyday in cities and towns, which is treated in Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs) to make it less polluted. Given below is the flow diagram of one of the stages of STP. Observe the given flow diagram and answer the questions accordingly.
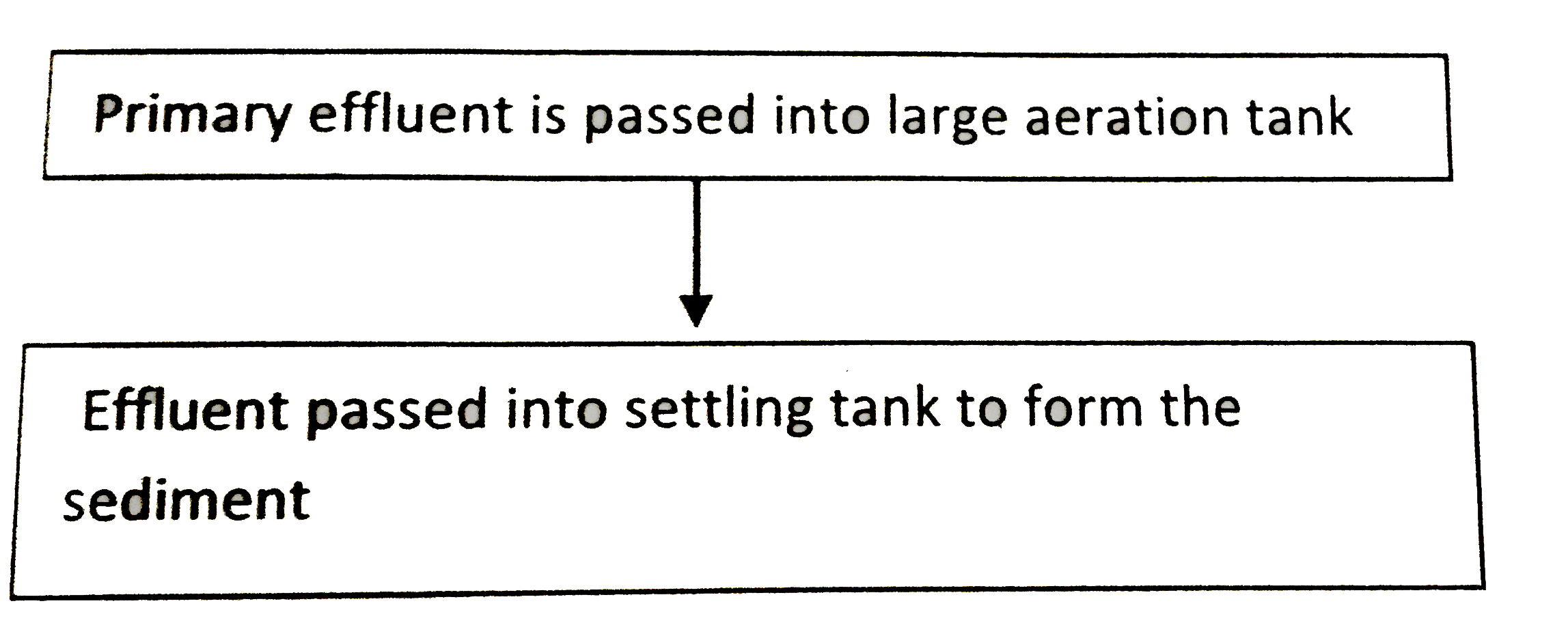
(a) Why is the primary effluent passed into large aeration tanks?
(b) Write the technical term used for the sediment formed. Mention its significance.
(c) Explain the final step that results in the formation of biogas in the large tank before the treated effluent is released into water bodies.(a) -
Rivers like Ganga, Cauvery, Yamuna, etc. are considered sacred rivers. Just because of this reason, the load of pollution in these rivers is increased as people throw into them many things in the name
of puja. Many factories also let their effluents into the rivers.
(a) What has the government done to check pollution in these rivers?
(b) What does the BOD test measure in the water bodies?(a) -
Cowdung and water is mixed and the slurry is fed into biogas plant for digestion by microbes. The person performing the process shares that there is no need to provide any inoculum to it.
(a) Give reason why no inoculum is needed.
(b) What is the role of the microbes at the source?
(c) Mention the condition under which they will be most active and effective.(a) -
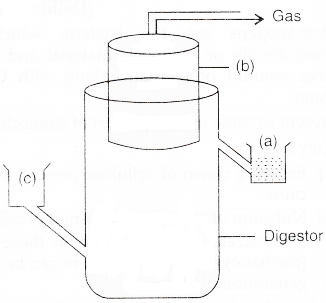
The diagram above is that of a typical biogas plant. Explain the sequence of events occurring in a biogas plant. Identify a, b and c.(a) -
In agriculture, there is a method of controlling pests that relies on natural predation rather than on chemicals. An organic farmer believes that the more biodiversity a landscape has, the more sustainable it is.
(a) Mention two disadvantages of using chemical methods to control pests.
(b) Give an example of a bacterium and a fungus that are used as biocontrol agents.
(c) An organic farmer does not eradicate the 'pests'. Give two reasons.(a) -
A farmer has been cultivating paddy in his field season after season. Of late, the yield has been decreasing though there is no occurrence of pests or disease. He has been advised to use Nostoe by the local centre of the Agricultural department. To his surprise, the yield started increasing.
(a) How does Nostoe help to increase the yield of paddy crops?
(b) Name two other organisms ofthe same category that can serve this purpose.(a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Microorganisms include bacteria, viruses, fungi and protozoa. In our mind, we presume, most of the time, that microbes are always harmful. Microbes are, of course, the causal agents of many infections diseases of plants and animals including humans but they also have lots of beneficial role. Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) are one of this kind of useful group. These are Gram positive, non-sporulating, either rod shaped or spherical bacteria. They produce lactic acid in milk products as major metabolic end product of carbohydrate fermentation. LAB are considered as natural fermentors. Lactobacillus is a common LAB which converts lactose sugar of milk into lactic acid, that causes coagulation and partial digestion of milk protein casein. Milk is then changed into curd, yoghurt and cheese. Lactobacillus is also used in probiotics which have potentially beneficial effect on gut ecosystem of humans. Some other pro biotic strain used belong to the Genus Bifidobacterium.
(i) Which of the following is not considered as microorganisms?(a) Bacteriophage (b) Streptococcus (c) Porphyra (d) Staphylococcus (ii) Select the incorrect option regarding the characteristics oflactic acid bacteria.
(a) They are rod-shaped or spherical (b) They are Gram positive (c) They take part in carbohydrate fermentation. (d) They are acid intolerant (iii) Which of the following is not a lactic acid producing bacteria?
(a) Streptococcus (b) Lactococcus (c) Saccharomyces (d) Enterococcus (iv) Probiotics are
(a) gut friendly live bacteria (b) acid balancing alternated bacteria (c) beneficial amount of dead bacteria (d) Gram negative attenuated bacteria (v) Assertion: Lactobacillus bacteria do not retain crystal violet stain while staining.
Reason: Lactobacillus have a very thin layer of peptidoglycan layer in their cell wall.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.(a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Discovery of penicillin by Alexander Fleming in 1928 marked the beginning of the remarkable era in medical field. Penicillin was the first antibiotic extracted from Penicillium notatum. Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial diseases. These can be broad spectrum which can kill diverse group of disease causing bacteria and narrow spectrum which is effective only against one group of pathogenic strain. Antibiotics can act as bactericides or bacteriostatic. Bactericidal antibiotics kill bacteria by - disruption of cell wall synthesis (e.g., penicillin, cephalosporin, etc.), inhibition of 50S ribosome function (e.g., erythromycin), inhibition of 30S ribosome function (e.g., streptomycin, neomycin), inhibition of amino acid-tRNA binding to ribosome (e.g., tetracyline), etc. Bacteriostatic antibiotics do not kill the bacteria rather they restrict the growth of bacteria. Penicillin belongs to B-Iactum group of antibiotics and it inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis by binding and inactivating protein. It inhibits transpeptidation of reaction and blocks cross-linking of the cell wall. It is used to treat tonsilitis, sore throat, gonorrhoea, rheumatic fever and some pneumonia types.
(i) The first antibiotic was extracted from a(a) lichen (b) fungus (c) eubacteria (d) actinomycetes (ii) Which of the following kills bacteria by interfering 50S ribosome function?
(a) Cephalosporin (b) Erythromycin (c) Streptomycin (d) Neomycin (iii) \(\beta \)-Iactum group of antibiotics kill the bacterial pathogen by
(a) disruption of plasma membrane (b) inhibition of translation of mRNA (c) disruption of cell wall (d) inhibition of transcription of mRNA. (iv) Penicillin is not used to treat
(a) pneumonia (b) tonsilitis (c) rheumatic fever (d) candidiasis (v) Assertion :Cephalosporins act by disruption of bacterial cell wall synthesis mechanism.
Reason: Cephalosporins are bacteriostatic antibiotics.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.(a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Enzymes are best known for their ability to catalise biochemical reactions without undergoing any change. A large number of enzymes are being used in biotechnological industry. Most of them are obtained from microbes. Proteases degrade proteins and polypeptides. Most of the commercially applicable proteases are alkaline and are biosynthesised mainly by bacteria such as Pseudomonas, Bacillus and some fungi like, Aspergillus. These enzymes are used in clearing beer, softening of bread and meat, degumming of silk, etc. Alkaline serine proteases have the largest applications in bio-industry. Alkaline proteases have shown their c,apability to work under high pH, temperature and in presence of inhibitory compounds. Another important group of enzymes is amylases. Amylolytic enzymes act on starch. These are obtained from Aspergillus, Rhizopus and Bacillus sp. These are used in softening and sweetening of bread, production of alcoholic beverages from starchy materials, clearing of turbidity in juices caused by starch, etc.
(I) Polypeptides are degraded by(a) amylases (b) proteases (c) pectinases (d) lipases (ii) Amylolytic enzymes are not obtained from
(a) Aspergillus (b) Rhizopus (c) Mucor (d) Bacillus (iii) Clearing of turbidity in juices caused by starch is achieved by
(a) amylases (b) proteases (c) rennet (d) both (a) and (b). (iv) Select the incorrect option from the following.
(a) Enzymes are proteinaceous substances. (b) Enzymes are substrate specific (c) Enzymes are large sized molecules. (d) Microbial enzymes can work only in normal temperature and pH. (v) A farmer harvests corns and prepares corn starch. He wants to prepare some corn syrup from this. For the conversion he needs to use enzyme ____________________.
(a) amylase (b) glucoamylases (c) glucoisomerases (d) all of these (a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Alcohols are important industrial solvents. Ethanol, methanol, propanol and butanol are produced commercially by fermentation activity of some fungi, majorly yeasts. During fermentation, yeast cells convert cereal derived sugars into ethanol and CO2. At the same time hundreds of secondary metabolites that influence the aroma and taste of alcohol are produced. Sugar concentration affects the rate of fermentation reactions. Yeast cannot grow in very strong sugar solution. In case of complex carbohydrate containing nutrient media, 1% malt or Rhizopus is used along with yeasts. Hydrolysis of starch is carried out at high temperature for 30 mins. The crushed food mixed with hot water for obtaining malt in called mash. The nutrient medium prior to fermentation in called wort. Wort is cooled down to appropriate temperature and inoculated with strain of yeast.
(i) The rate of alcohol production is measured on the basis of(a) amount of sugar present in the medium (b) amount of CO2 produced per unit time (c) amount of yeast added in the medium (d) all of these (ii) A number of chemicals are produced at the time of alcoholic fermentation with the change of nutrient media, pH and aeration. Select such by-product from the following.
(a) Phenylethanol (b) Amyl alcohol (c) Glycerol (d) All of these (iii) During alcoholic fermentation of cereals and potato, the crushed food mixed with hot water for obtaining malt is called
(a) juice (b) mash (c) wort (d) none of these (iv) Distilled alcohol with 95% ethanol content is called
(a) absolute alcohol (b) rectified spirit (c) gin (d) brandy. (v) Assertion: Rhizopus or 1% malt is used in the nutrient medium when it contains complex carbohydrates.
Reason: Yeast does not possess sufficient diastase or amylase.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.(a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Villagers in a place near Chambur started planning to make power supply for agricultural purposes from cow dung. They have started a biogas plant for the purpose. Study the flow chart for biogas production given below and answer the following questions.

(I) Biogas is composed of majorly(a) methane, CO2 and O2 (b) CO2, H2S and H (c) methane, CO2 (d) H2S, Hand O2. (ii) In the given flow chart, 'A' .denotes
(a) aerobic bacteria (b) methanogenic bacteria (c) cellulose degrading bacteria (d) yeast and protozoa. (iii) What is represented by 'B' in the flow chart?
(a) Carbohydrates (b) Protein polymers (c) Organic acids (d) Fat globules (iv) 'C' in the given flow chart causes
(a) aerobic breakdown of complex organic compounds (b) anaerobic digestion of complex organic compounds (c) fermentation of organic compounds (d) fermentation of monomers. (v) If 'A' is not added in the procedure
(a) methane will not be formed (b) CO2 will not be formed (c) organic compounds will not be converted to H2S (d) O2 will not be formed. (a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
In to day's world, more than 25% of human population is suffering from hunger and malnutrition. Scientists have developed techniques where microbes are grown on industrial scale as a source of good protein which can be grown from waste water, animal manure and even sewage. Single cell proteins are such products. The biomass or protein is extracted from pure or mixed cultures of algae, yeasts, fungi or bacteria. These are a very good source of food for human consumption.
(i) Why the name single cell protein is applied?(a) It contains only one type of protein. (b) It is obtained from unicellular edible microbes (c) It contains only one type of microorganism (d) All of these (ii) Which of the following is considered under single cell protein?
(a) Algae (b) Fungi (c) Cyanobacteria (d) All of these (iii) Microorganisms can be a useful food resource for increasing human population because
(a) these are easy to harvest (b) these can grow in water system (c) they have a high rate of multiplication thus producing huge biomass (d) they have high level of nucleic acid (iv) Single cell protein can be grown from
(a) waste water (b) animal manure (c) sewage (d) all of these. (v) Assertion: Production of single cell protein reduces pollution.
Reason: Single cell protein can be grown from waste water and even sewage.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false(a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Disposal of untreated sewage into the river or freshwater pond causes huge water pollution. Four water samples from different sources (A, B, C, D) are collected and tested for BOD value in a lab to assess their quality. The BOD values are presented in the given table. Water samples are collected from primary effluent, secondary effluent, untreated sewage and river water. Study the given table and answer the followingSample BOD A 20 mg/L B 5 mg/L C 300 mg/L D 400 mg/L (i) The source of sample 'C' is
(a) river water (b) primary effluent (c) secondary effluent (d) untreated sewage water (ii) If sewage in untreated condition is disposed off in a freshwater body then
(a) BOD and dissolved oxygen both will increase (b) BOD will increase and dissolved 0xygen will decrease (c) BOD will decrease and dissolved oxygen will increase (d) BOD and dissolved oxygen both will decrease. (iii) A large number of pathogenic microbes can be present in water sample of
(a) C (b) A (c) D (d) both (a) and (c). (iv) High value of BOD in sample D is due to
(a) high amount of organic wastes and aerobic microbes (b) high amount of inorganic wastes and anaerobic microbes (c) high amount of organic wastes and anaerobic microbes (d) high amount of inorganic wastes and aerobic microbes (v) River water is represented by the sample
(a) A (b) B (c) C (d) D (a)
Case Study
*****************************************
Answers
Microbes in Human Welfare Case Study Questions With Answer Key Answer Keys
-
(a) (i) Deep thermal vents, where the temperature may be as high as 100°C.
(ii) Under the layers of snow several metres thick.
(iii) Highly acidic environments.
(b) Bacteria and fungi can be grown on nutritive media.
(c) Saccharomyces cereviseae. -
(a) (i) Alexander Fleming
(ii) He was working on Staphylococcus bacterium.
(b) (i) Penicillin is the first antibiotic.
(ii) It is obtained from Penicillium notatum.
(c) Ernst Chain and Howard Florey established its full potential as an antibiotic. -
(a) It is to facilitate the vigorous growth of the useful aerobic microbes to form floes, which consume a large part of the organic matter.
(b) (i) Activated sludge
(ii) A small part of it is transferred to aeration tank as inoculum; it is used for production of biogas also.
(c) (i) The anaerobic microbes digest the floes in the anaerobic sludge digester and produce gases like carbon dioxide, methane and hydrogen sulphide that form biogas. -
(a) (i) The government has initiated Ganga Action Plan and Yamuna Action plan to save these rivers from pollution.
(ii) Under these plans, it is proposed to build a large number of sewage treatment plants so that only treated sewage would be discharged into the rivers.
(b) BOD test measures the rate of uptake of oxygen by the micro-organism in a sample of water; indirectly it is a measure of the amount of organic matter present in the water. -
(a) Cowdung contains the methanogens which act on the cellulosic material in the cowdung to produce biogds; hence, there is no need to provide inoculum.
(b) The microbes at the source (rumen of cattle) help in digestion of cellulose and thereby in their nutrition.
(c) Anaerobic condition. -
Bio Wastes are collected and a slurry of dungs is fed, a floating cover having gas outlet is placed over slurry which keeps on rising as the gas is produced in the tank, the spent slurry is removed through another outlet and may be used as fertilizer.
(a) sludge loader
(b) gas holder / CH4 and CO2
(c) dung and water. -
(a) Disadvantages of chemical methods.
(i) The chemicals kill both the beneficial and harmful organisms indiscriminately.
(ii) The chemicals are toxic and extremely harmful to humans and other animals.
(b) Bacterium - Bacillus thuringiensis
Fungus - Trichoderma sps.
(c) (i) According to an organic farmer, eradication of pests is impossible.
(ii) Some ofthe beneficial organisms that depend on the pests as food would not be able to survive. -
(a) Nostoc enriches soil fertility by
(i) fixing atmospheric nitrogen in the soil.
(ii) adding oranic matter to the soil through its photosynthetic activity.
(b) Anabaena and Oscillatoria. -
(i) (c) : Porphyra is a coldwater seaweed belongs to red algae.
(ii) (d) : LAB are acid tolerant bacteria.
(iii) (c): Sadharomyces cerevisiae, also known as Brewer's yeast, is used in alcoholic fermentation.
(iv) (a) : Probiotics are live bacteria which are beneficial for digestive system.
(v) (d) : Lactobacillus is a Gram positive bacteria. Gram positive bacteria have a very thick cell wall layer comprising of peptidoglycan. They retain crystal violet stain during Gram staining and appear violet in colour under microscope. -
(i) (b) : The first antibiotic was extracted from a fungus Penicillium notatum.
(ii) (b)
(iii) (c)
(iv) (d) : Penicillin is given to patients with an infection caused by bacteria including pneumonia, sore throat, gonorrhoea, etc. Candidiasis is a fungal disease.
(v) (c): Cephalosporins are bactericidal in nature. They kill the bacteria by disruption of cell wall synthesis. -
(i) (b) : Proteases are enzymes that degrade proteins and polypeptides
(ii) (c)
(iii) (a)
(iv) (d) : Enzymes obtained from microbes can work in extreme condition like high temperature and high pH.
(v) (d) : Amylase, glucoamylases and glucoisomerases are employed in conversion of corn starch to fructose rich corn syrup. -
(i) (b) : The fermentation rate of the yeast can be calculated by measuring the volume of CO2 and dividing it by the amount of time it took for that volume to form.
(ii) (d)
(iii) (b) : The crushed food mixed with hot water for obtaining malt is called mash. The nutrient medium prior to fermentation is called wort. Wort is added into the bioreactor tank, sterilised and then inoculated with yeast.
(iv) (b) : Alcoholic content in gin is 40%, brandy in 60-70%. These are hard liquors. Rectified spirit contains 95% alcohol and absolute alcohol is 100% alcohol. Rectified spirit and absolute alcohol are extensively used in laboratory works.
(v) (a) -
(I) (c) : Biogas is composed of methane (50-70%), carbon dioxide (30-40%) with traces of nitrogen, hydrogen sulphide and hydrogen.
(ii) (b)
(iii) (c) : In the second stage ofbiogas production, the simple soluble compounds or monomers are acted upon by fermentation causing microbes and converted into organic acids especially acetic acid.
(iv) (b)
(v) (a) -
(i) (b)
(ii) (d)
(iii) (c) : Microorganisms have a high rate of multiplication, which means a large quantity of biomass can be produced in a comparatively shorter duration.
(iv) (d)
(v) (a) -
(i) (b) : A - Secondary effluent, B - River water, C - Primary effluent, D - Untreated sewage water.
(ii) (b)
(iii) (d) : A number of pathogenic microbes mostly present in sewage water. They are removed during secondary or biological treatment. During primary treatment, small and large, floating and suspended solids are removed through filtration and sedimentation.
(iv) (a)
(v) (b)






































