Class 12th Biology - Organisms and Populations Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
By QB365 on 08 Sep, 2022
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 12 Biology Subject - Organisms and Populations, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Organisms and Populations Case Study Questions With Answer Key
12th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Biology
-
The graph given below shows the distribution of the major biomes of the world.
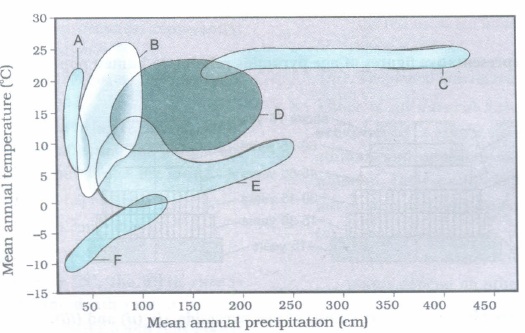
Answer the following questions based on the graph.
(a) Identify the biomes A, D, E, F.
(b) Which of the biomes shows the maximum range of
(i) Mean annual precipitation
(ii) Mean annual temperature?(a) -
The graph given below depicts the organismic response to changing external environmental conditions. According to their response, the organisms are grouped into two types.
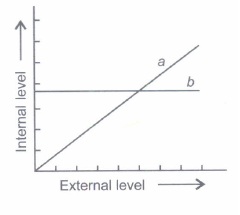
Answer the following questions.
(a) Name the group of organisms, which will show pattern A. Give an example.
(b) ame the group of organisms, which will show pattern B. Give an example.
(c) Define homeostasis.(a) -
Study the three representative figures of age pyramids relating to human population and answer the questions that follow:
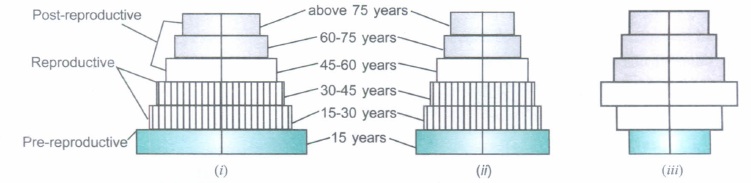
(a) Wrrte'the names given to the three kinds of age pyramids, (I), (il) and (iil).
(b) Give reason for each, why you have named them so.(a) -
'The population of a metro city experiences fluctuations in its population density over a period of time'.
(a) When does the population in a metro city tend to increase?
(b) When does the population in a metro city tend to decline?
(c) If 'N' is the population density at the time 't', write the population density at the time 't + l'.(Delhi 2020).(a) -
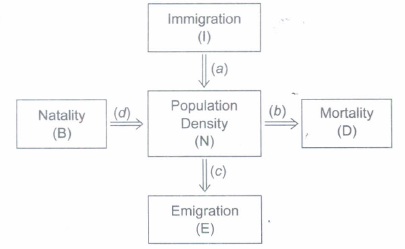
(I) Which of the above process(es) represent(s) an increase in population?
(ii) Which ofthe above process(es) represent(s) a decrease in population?
(iii) If a new habitat is just being colonised, out of the four process(es) affecting the population growth, which one contributes the most?(a) -
If in a population of size 'N', the birth rate is represented as 'b' and the death rate as 'd', the increase or decrease in 'N' during a unit time period 't' will be
dN/dt = (b - d) x N
The equation given above can also be represented as
dN/dt = r x N, where r = (b - d).
(a) What does 'r' represent in the above?
(b) Write anyone significance of calculating 'r' for any population.
(c) In a pond there are 100 frogs. 20 more were born in a year. Calculate the birth rate of this population.(a) -
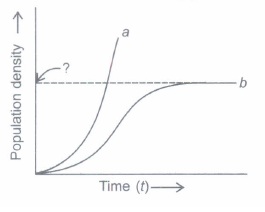
Study the population growth curves shown in the graph and answer the following questions.
(i) Identify the growth curves 'a' and 'b'.
(ii) Which one of them is considered more realistic and why?
(iii) What does the dotted line in the graph indicate?(a) -
There is no natural habitat on earth, which is occupied by a single species. In nature, plants, animals and microbes do not and cannot live in isolation. Interspecific interactions arise from the interaction of populations of two different species.
(a) Even a plant species, which makes its own food cannot live alone. Give two examples, where plants depend on other species for survival.
(b) Name the type of interspecific interaction seen in each of the following examples.
(i) Disappearance of smaller barnacles when Balanus dominated intertidal area of the sea coasts of Scotland.
(ii) Clown fish living among the stinging tentacles of sea anemone.
(iii) The Wasp species pollinating a fig inflorescence.
(iv) Cuscuta growing on hedge plants.(a) -
Study the table given below and answer the questions that follow:
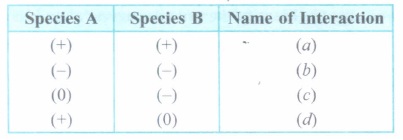
(+ = Beneficial interaction)
(- = Detrimental interaction)
(0 = Neutral interaction)
(i) Identify the type of interaction (a), (b), (c) and (d).
(ii) Why are predators 'prudent' in nature?(a) -
It is generally believed that competition occurs only when closely related species compete for the same resources that are limiting.
Give two examples to show that the above statement is not always true.(a) -
Read the following and answer the questions given below:
Unlike animals, plants cannot runaway for their defence, so, they have evolved on surprising variety of morphological and chemical defence against the herbivores. Thorns are the most common physical means of defence. Many plants secrete and store chemicals that make herbivore sick when they are eaten, inhibit feeding or digestion, disrupt its reproduction or even kill it. Some plants produce highly poisonous chemicals and that is why no cattle or goats browse on those plants. A large variety of chemical substances that we extract from plants on a commercial scale are produced by them actually as defence against grazer and browser.
(i) Why we never see cattle or goats browsing on weed Calotropis?(a) It produces highly poisonous tannins (b) It produces quinine which is bitter in taste. (c) It produces poisonous cardiac glycosides. (d) It bears prickles. (ii) Which of the following is most likely to sick by consuming chemicals produced by plants?
(a) Frog (b) Goat (c) Human (d) Pigeon (iii) Plant evolve different morphological and chemical defences against
(a) prey (b) predator (c) commensalism (d) mutualism (iv) Assertion: Some plant functions as predator in nature.
Reason: Phytophagous insects feed on plant sap.
(a) Both A and Rare true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) Both A and R are false(a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Kangaroo rat seldom drinks water. It has thick coat to minimise evaporative desiccation. The animal seldom comes out of its comparatively humid and cool burrow during the day time. 90% of its water requirement is met from metabolic water (water produced by respiratory breakdown of fats) while 10% is obtained from its food. Loss of water is minimised by producing nearly solid urine and faeces. As the animal faces acute water scarcity, it develops two types of adaptations: reducing water loss and ability to tolerate desert conditions.
(i) Kangaroo rat is a(a) partial regulators (b) partial conformer (c) regulator (d) conformer (ii) Metabolic water refers to
(a) water required for metabolic activities (b) water present in intercellular fluid (c) water produced during oxidation of fat or carbohydrate (d) water taken in, to promote metabolism. (iii) Desert animals minimise water loss by
(a) producing highly concentrated urine (b) promoting maximum reabsorption of water in kidney tubules (c) possessing one of the longest loop of Henle in kidney tubules (d) all of these. (iv) Assertion : Kangaroo rat can tolerate and thrive in wide temperature range and is known as stenothermal.
Reason: Kangaroo rats go into hibernation during winter to escape cold weather.(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion. (b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion. (c) Assertion is true but reason is false. (d) Both assertion and reason are false. (v) The adaptations in an organism are meant for
(a) optimum primary production (b) optimum life span (c) optimum mobility (d) optimum survival and reproduction. (a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Organism P has thick lips and tongue so that it can easily feed on the commonly available spiny plants. Organism Q has thick layer of insulating fat under the skin. It was strong hooves to walk steadily on steep surfaces and lives in burrows during winters. Organism R has bright colours and sticky pads on its fingers and toes. It lives on trees.
(i) Which of the following is correct habitat for organisms P regarding its adaptation?(a) Grassland biome (b) Desert biome (c) Tropical rainforest (d) Tropical deciduous forest (ii) Which of the following is correct match regarding organism Q and its habitat?
(a) Tundra - Polar bear (b) Tropical rain forest - Deer (c) Grassland - Bighorn sheep (d) Desert - Camel (iii) Which of the following is incorrect regarding organisms R's habitat?
(a) The vegetation shows stratification (b) Epiphytic growth is rich (c) Standing crop is highest (d) Deep rooted shrubs are common due to abundant sunlight. (iv) The dominant plants in habitat where P lives could be
(a) Opuntia (b) Nymphaea (c) Deodar (d) both (a) and (c). (v) Organisms P,Q and R respectively most likely occur in
(a) F, B and A (b) C, A, E (c) A, F and C (d) B, D and A. (a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
During teaching about various environmental factors, a teacher draw a figure that depicts like history strategies for three plant species (X, Y and Z) along 3 axes - strength of competition with other organisms, level of disturbance in the habitat and level of environmental stress in the habitat. Species X grows in habitats where competition among species is high but disturbance and stress are low. Species Y grows in habitats with high environmental stress but with low intraspecies competition. Species Z grows in highly disturbed habitats with low environmental stress.
(i) Which of the following is correct regarding plant type X?(a) It has slow growth rate. (b) It lives in area with high probability of severe environmental changes. (c) It has good competitive ability at low population densities near the carrying capacity. (d) None of these (ii) Environmental stress occurs through
(a) very low temperature (b) drought (c) nutrient deficiency (d) all of these. (iii) Select the correct option regarding plant type X, Y and Z.
(a) X type of plants are likely to be trees. (b) Y type of plants could be desert plants. (c) Z type of plants could be herbaceous plant. (d) All of these (iv) Y type of plants grow under high stress and
(a) produce large number of seeds in a short time after rains (b) have rapid growth (c) produce less number of seed in a long time after rain (d) both (a) and (b). (v) Assertion: Plant growth rate is high in area of high stress and high disturbance.
Reason: High stress and high disturbance promote breeding capacity in plants.(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion. (b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion. (c) Assertion is true but reason is false. (d) Both assertion and reason are false. (a) -
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v) given below:
Regular change in temperature that occurs at specific intervals of time is called thermoperiodicity. It is of two types-diurnal and seasonal thermoperiodicity. Diurnal periodicity refers to temperatures of day and night. It determines periods of annual activity. In season periodicity different temperature prevails in different seasons of the year. They favour different aspects of plant and animal life termed as phenology. For example in wheat, leaf growth requires a temperature of 10°-25° C. Apple requires temperature below 7°C for a period of 800 hrs before flowering and fruiting can occur. Low temperature is required for germination of some seeds as well as flowering in some plants. It also determines growth, reproduction, colour and morphology of animals. Both low and high temperature cause stress in organisms which is overcome by particular adaptations.
(i) Some plants require low temperature treatment for flowering. This phenomenon is known as(a) photoperiodism (b) vernalisation (c) thermoperiodism (d) none of these. (ii) Animals found in arctic zones are called
(a) microtherms (b) megatherms (c) mesotherms (d) hekistotherms. (iii) Which of the following parts of wheat plant grows maximum in temperature around 10°-25°C ?
(a) Root (b) Seeds (c) Leaf (d) Stem (iv) "Different temperatures prevail in different seasons of the year:' It represents
(a) diurnal thermoperiodicity (b) seasonal periodicity (c) homeostasis (d) thermoregulation. (v) Assertion: Low and high temperature causes stress in organisms.
Reasons: Organisms show specific adaptations to overcome stressful condition.(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion. (b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion. (c) Assertion is true but reason is false. (d) Both assertion and reason are false.
(a)
Case Study
*****************************************
Answers
Organisms and Populations Case Study Questions With Answer Key Answer Keys
-
(a) A ~ Desert,
D - Temperate forest
E - Coniferous forest
F - Arctic and Alpine tundra.
(b) (i) -Tropical forest
(ii) - Grassland. -
(a) Pattern A - Conformers
e.g. Amphibians
(b) Pattern B - Regulaters
e.g. Mammals
(c) Homeostasis is the process of maintaining a constant internal environment despite the varying external environmental conditions. -
(a) (i) Expanding
(ii) Stable
(iii) Declining.
(b) (i) The number of individuals in the pre-reproductive age group is more than that in the reproductive age group.
(ii) The number of individuals in the pre-reproductive and reproductive age groups is almost same.
(iii) The number of individuals in the pre-reproductive age group is much less than that in the reproductive age group. -
(a) When the sum total of immigration (I) and natality (B) is more than the sum total of emigration (E) and mortality (D), the population increases.
(b) When the sum total of emigration (E) and mortality (D) is more than the sum total of immigration (I) and natality (B), the population declines.

-
(i) (a) - immigration and (d) natality.
(ii) (b) - Mortality and (c) emigration.
(iii) Immigration. -
(a) 'r ' represents the 'intrinsic rate of natural increase'.
(b) It is an important parameter for assessing the impacts of any biotic and abiotic factor on population growth.
(c) The birth rate is 20/100 or 0.5/frog/year. -
(i) - 'a' is exponential growth curve.
- 'b' is logistic growth curve.
(ii) Logistic growth curve is more realistic because the resources are finite and will become limiting sooner or later.
(iii) The dotted line represents the carrying capacity. -
(a) Plants depend on
(i) the soil microbes to break down the organic matter in soil to return the inorganic nutrients for their absorption.
(ii) animals for pollination, without which fruits and seeds cannot be formed.
(b) (i) Competition
(ii) Commensalism
(iii) Mutualism
(iv) Parasitism -
(i) (a) - Mutualism
(b) - Competition
(c) - Amensalism
(d) - Commensalism
(ii) If a predator is too efficient and overexploits its prey, then the prey might become extinct and following it, the predator may face extinction for lack of food; hence, predators are prudent in nature. -
(i) Competition can occur between two unrelated species, when they compete for the same resource, e.g. the visiting flamingoes compete with the resident fishes for zooplanktons in some shallow lakes in South America.
(ii) Resources need not be limiting; in interference competition, the feeding efficiency of one species might be reduced due to the interfering and inhibitory presence of the other species, e.g the abingdon tortoise became extinct within a decade after goats were introduced into Galapagos Islands. -
(i) (c)
(ii) (b)
(iii) (b)
(iv) (b) -
(i) (c) : Kangaroo rat is a regulator that performs homeostasis through thermoregulation osmoregulation by physiological adjustments and behavioural changes.
(ii) (c)
(iii) (d)
(iv) (d) : Organisms that can tolerate and thrive in wide temperature range are known as eurythermal. Kangaroo rats do not go into hibernation rather, they stay if}cool moist burrows during summer days.
(v) (d): Adaptation is an attribute of an organism (morphological, physiological and behavioural) that enables it to survive and reproduce in its habitat. Adaptations lead to the formation of some specialised and peculiar features which have evolved over a long period of time through natural selection. -
(i) (b) : P is camel adapted to desert conditions as it has thick lips and tongue so that it can easily feed on the commonly available spiny plants.
(ii) (a): Q is polar bear as it has thick insulating fat layer under the skin.
(iii) (d) : R could be poison dart frog as it has bright colours and sticky pads on its fingers and toes and its habitat is tropical rainforest. Deep rooted shrubs are not found in tropical rainforest. These are found in deserts.
(iv) (a) : Habitat of P is desert, so, the dominant plant is Opuntia.
(v) (c) -
(i) (a) : 'X type' of plants are competitors which live under condition of low stress and low disturbance and have good competitive ability at high population densities near the carrying capacity. Such plant have slow growth rate and prevail in non-seasonal tropics where there is low probability of severe environmental changes.
(ii) (d) : Environmental stress occurs through external conditions such as shading, drought, nutrient deficiency or very low temperature that limit production.
(iii) (d)
(iv) (a)
(v) (d): Plant growth rate is low in area of high stress and high disturbance. High stress and high disturbance cannot promote breeding capacity in plants. -
(i) (b)
(ii) (d) : Organisms living in tropical, subtropical, temperate and arctic zones are megatherms, mesotherms, microtherms and hekistotherms respectively.
(iii) (c)
(iv) (b) : Different temperatures prevail in different seasons of the year represent seasonal periodicity.
(v) (b)






































