Class 12th Chemsitry - Aldehydes , Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
By QB365 on 08 Sep, 2022
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 12 Chemsitry Subject - Aldehydes , Ketones and Carboxylic Acids, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Aldehydes , Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Case Study Questions With Answer Key
12th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Chemistry
-
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
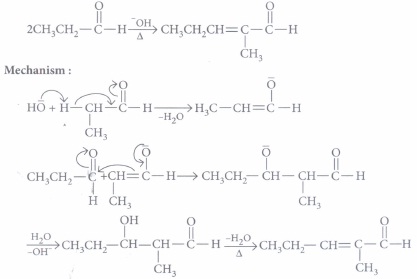
The addition reaction of enol or enolate to the carbonyl functional group of aldehyde or ketone is known as aldol addition. The \(\beta\)-hydroxyaldehyde or \(\beta\)-hydroxyketone so obtained undergo dehydration in second step to produce a conjugated enone. The first part of reaction is an addition reaction and the second part is an elimination reaction. Carbonyl compound having \(\alpha\)-hydrogen undergoes aldol condensation reaction.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
(i) Condensation reaction is the reverse of which of the following reaction?(a) Lock and key hypothesis (b) Oxidation (c) Hydrolysis (d) Glycogen formation (ii) Which of the following compounds would be the main product of an aldol condensation of acetaldehyde and acetone?
(a) CH3CH=CHCHO (b) CH3CH=CHCOCH3 (c) (CH3)2C=CHCHO (d) (CH3)2C=CHCOCH3 (ii) Which combination of carbonyl compounds gives phenyl vinyl ketone by an aldol condensation?
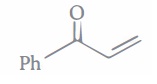
(a) Acetophenone and Formaldehyde (b) Acetophenone and acetaldehyde (c) Benzaldehyde and acetaldehyde (d) Benzaldehyde and acetone (iv) Which of the following will undergo aldol condensation?
(a) HCHO (b) CH3CH2OH (c) C6H5CHO (d) CH3CH2CHO (a) -
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :
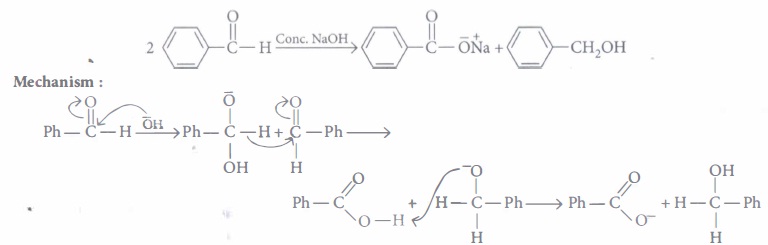
When an aldehyde with no a-hydrogen reacts with concentrated aqueous NaOH, half the aldehyde is converted to carboxylic acid salt and other half is converted to an alcohol. In other words, half of the reactant is oxidized
and other half is reduced. This reaction is known as Cannizzaro reaction
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer :
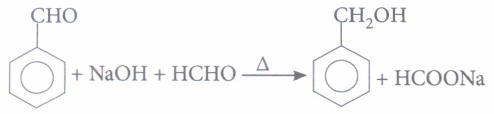
(i) A mixture of benzaldehyde and formaldehyde on heating with aqueous NaOH solution gives(a) benzyl alcohol and sodium formate (b) sodium benzoate and methyl alcohol (c) sodium benzoate and sodium formate (d) benzyl alcohol and methyl alcohol. (ii) Which of the following compounds will undergo Cannizzaro reaction?
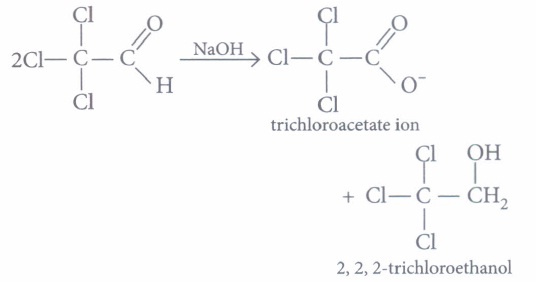
(a) CH3CHO (b) CH3COCH3 (c) C6H5CHO (d) C6H5CH2CHO (iii) Trichloroacetaldehyde is subjected to Cannizzaro's reaction by using NaOH. The mixture of the products contains sodium trichloroacetate ion and another compound. The other compounds is
(a) 2, 2, 2-trichloroethanol (b) trichloromethanol (c) 2, 2, 2-trichloropropanol (d) chloroform (iv) Which of the following reaction will not result in the formation of carbon-carbon bonds?
(a) Cannizzaro reaction (b) Wurtz reaction (c) Reimer- Tiemann reaction (d) Friedel-Crafts acylation (a) -
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions
A tertiary alcohol H upon acid catalysed dehydration gives a product I. Ozonolysis of I leads to compounds J and K. Compound J upon reaction with KOH gives benzyl alcohol and a compound L, whereas K on reaction with KOH gives only M.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer :
(i) Compound H is formed by the reaction of
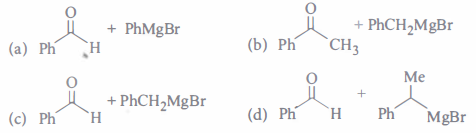
(ii) The structures of compound J, Kand L, respectively, are(a) PhCOCH3 , PhCH2COCH3 and PhCH2COO-K+ (b) PhCHO, PhCH2CHO and PhCOO-K+ (c) PhCOCH3, PhCH2CHO and CH3 COO-K+ (d) PhCHO, PhCOCH3 and PhCOO-K+ (iii) When (J) is treated with acetic anhydride, in the presence of corresponding salt of an acid, the product obtained is
(a) cinnamic acid (b) crotonic acid (c) maleic acid (d) benzylic acida (iv) Which of the following statements is correct for compound (K)?
(a) It reacts with alkaline KMnO4 followed by acidic hydrolysis and forms benzoic acid. (b) It reacts with iodine and NaOH to form triiodomethane. (c) It is prepared by the reaction of benzene with benzoyl chloride in presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride (d) It reacts with freshly prepared ammoniacal silver nitrate solution (a) -
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :
Carboxylic acids dissociate in water to give carboxylate ion and hydronium ion.
RCOOH + H2O \(\longrightarrow\) RCOO- + H3O+
The acidity of carboxyl group is due to the presence of positive charge on oxygen which liberates proton. The carboxylate ion formed is resonance stabilised.
Carboxylic acids are stronger acids than phenols. Electron withdrawing groups (EWG) increase the acidity of carboxylic acids by stabilising the conjugate base through delocalisation of negative charge by inductive and/ or resonance effects. Electron donating group (EDG) decrease the acidity by destabilising the conjugate base.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer :
(i) Which of the following reactions is showing the acidic property of carboxylic acid?
(ii) Which one of the following is the correct order of acidic strength?(a) CF3COOH > CHCl2COOH > HCOOH > C6H5CH2COOH > CH3COOH (b) CH3COOH > HCOOH > CF3COOH > CHCl2COOH > C6H5CH2COOH (c) HCOOH > C6H5CH2COOH > CF3COOH > CHCl2COOH > CH3COOH (d) CF3COOH > CH3COOH > HCOOH > CHCl2COOH > C6H5CH2COOH (iii) Which of the following acids has the smallest dissociation constant?
(a) CH3CHFCOOH (b) FCH2CH2COOH (c) BrCH2CH2COOH (d) CH3CHBrCOOH (iv) The correct order of acidity for the following compounds is
(a) I > II > III > IV (b) III > I > II > IV (c) III> IV > II> I (d) I > III > IV > II (a) -
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Aldehydes and ketones having acetyl groupare oxidised by sodium hypohalate (NaOX) or halogen and alkali (X2 + OH-) to corresponding sodium salt having one carbon atoms less than the carbonyl compound and give a haloform.
Sodium hypoiodite (NaOI) when treated with compounds containing CH3CO - group gives yellow precipitate of iodoform. Haloform reaction does not affect a carbon-carbon double bond present in the compound.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:(a) Isopropyl alcohol (b) Propionaldehyde (c) Ethylphenyl ketone (d) Benzyl alcohol (ii) Which of the following compounds is not formed in iodoform reaction of acetone?
(a) CH3COCH2I (b) ICH2COCH2I (c) CH3COCHI2 (d) CH3COCI3 (iii) For the given set of reactions
starting compound A corresponds to
(iv) An organic compound 'A' has the molecular formula C3H6O. It undergoes iodoform test. When saturated with HCI it gives 'B' of molecular formula C9H14O. 'A' and 'B' respectively are(a) propanal and mesityl oxide (b) propanone and mesityl oxide (c) propanone and 2,6-dimethyl-2,5-hepta-dien-4-one (d) propanone and propionaldehyde (a) -
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
(A), (B) and (C) are three non-cyclic functional isomers of a carbonyl compound with molecular formula C4H8O. Isomers (A) and (C) give positive Tollen's test whereas isomer (B) does not give Tollen's test but gives positive iodoform test. Isomers (A) and (B) on reduction with Zn(Hg)/conc. HCI give the same product (D).
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
(i) Compound A is
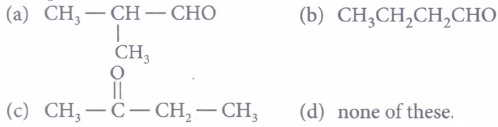
(ii) Compound (B) can be obtained by\({ (a) } \ \mathrm{CH}_{3}-\mathrm{C} \equiv \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{CH}_{2}-\mathrm{CH}_{3} \frac{\text { dil. } \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}+\mathrm{HgSO}_{4}}{333 \mathrm{~K}}\) \((b) \ \left(\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{CH}_{2} \mathrm{COO}\right)_{2} \mathrm{Ca} \stackrel{\text { Dry distill }}{\longrightarrow}\) \((c) \ \mathrm{CH}_{3}-\mathrm{C} \equiv \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{CH}_{3} \frac{\mathrm{B}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{6} / \mathrm{THF}}{\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2} / \mathrm{NaOH}}\) \((d) \ \mathrm{CH}_{3}-\mathrm{CH}=\mathrm{CH}-\mathrm{CH}_{3} \frac{\mathrm{O}_{3}}{\mathrm{Zn} / \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}}\) (iii) Out of (A), (B) and (C) isomers, which one is least reactive towards addition of HCN ?
(a) A (b) B (c) C (d) All are equally reactive (iv) What will be the product when (B) reacts with ethylene glycol in presence ofHCI gas?
 (a)
(a) -
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
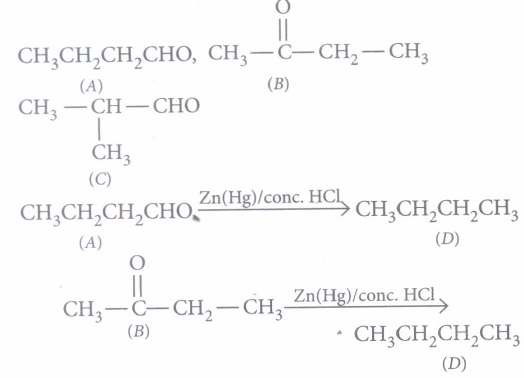
Aldehydes and ketones are reduced to primary and secondary alcohols respectively by NaBH4 or LiAIH4 as well as catalytic hydrogenation. The carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones is reduced to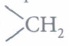 group on treatment with Zn-Hg and cone, HCI (Clemmensen reduction) or with hydrazine followed by NaOH or KOH in highly boiling solvent such, as ethylene glycol (Wolff- Kishner reduction).
group on treatment with Zn-Hg and cone, HCI (Clemmensen reduction) or with hydrazine followed by NaOH or KOH in highly boiling solvent such, as ethylene glycol (Wolff- Kishner reduction).
Aldehydes differ from ketones in their oxidation reactions. Aldehydes are easily oxidised to carboxylic acids on treatment with HNO3, KMnO4, K2Cr2O7 etc. Even mild oxidising agents mainly Tollens' reagent and Fehling's solution also oxidise aldehydes. Ketones are generally oxidised under vigorous conditions i.e., strong oxidising agents and at elevated temperatures, to give mixture of carboxylic acids having lesser number of C-atoms than the parent ketone.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
(i) Which of the following cannot be made by reduction of ketone or aldehyde with NaBH4 in methanol?(a) 1-Butanol (b) 2-Butanol (c) 2-Methyl-I-propanol (d) 2-Methyl-2-propanol (ii) The carbonyl compound producing an optically active product by reaction with LiAlH4 is
(a) propanone (b) butanone (c) 3-pentanone (d) benzophenone (iii) A substance C4H10O(X) yields on oxidation a compound C4H8O which gives an oxime and a positive iodoform test. The substance X on treatment with cone. H2S04 gives C4Hs. The structure of the compound (X) is
(a) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH (b) CH3CH(OH)CH2CH3 (c) (CH3)3COH (d) CH3CH2-O-CH2CH3 (iv) In the oxidation
 of by acidified K2Cr2O7, the products are
of by acidified K2Cr2O7, the products are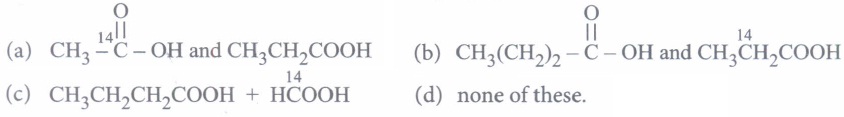 (a)
(a) -
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Carboxylic acids having an a-hydrogen atom when treated with chlorine or bromine in the presence of small amount of red phosphorus gives a-halo carboxylic acids. The reaction is known as Hell- Volhard-Zelinsky reaction.
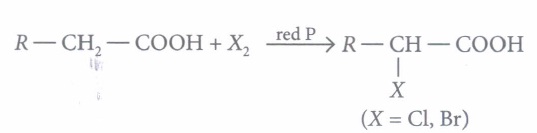
When sodium salt of carboxylic acid is heated with soda lime it loses carbon dioxide and gives hydrocarbon with less number of C-atoms.

In these questions (i - iv), a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
(i) Assertion: (CH3)3CCOOH does not give H.V.Z reaction.
Reason: (CH3)3CCOOH does not have \(\alpha\)-hydrogen atom.
(ii) Assertion: H.V.Z. reaction involves the treatment of carboxylic acids having \(\alpha\)-hydrogens with Cl2 or Br2 in presence of small amount of redphosphorus.
Reason : Phosphorus reacts with halogens to form phosphorus trihalides.
(iii) Assertion: C6H5COCH2COOH undergoes decarboxylation easily than C6H5COCOOH.
Reason : C6H5COCH2COOH is a 13-ketoacid.
(iv) Assertion: On heating 3-methylbutanoic acid with soda lime, isobutane is obtained.
Reason: Soda lime is a mixture of NaOH + CaO in the ratio 3 : 1.(a) -
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Fehling's reagent: Fehling's reagent is a mixture of two solutions. Fehling's solution A is aqueous copper sulphate solution. Fehling's solution B is alkaline sodium potassium tartarate (Rochelle salt).
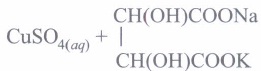
It is a mild oxidising agent. It is weaker than Tollens' reagent. It oxidises only aliphatic aldehydes to carboxylate ions and'itself gets reduced to reddish brown precipitate of cuprous oxide.
Aromatic aldehydes do not respond to Fehling's test. This reaction is used for the test of aliphatic aldehydes known as Fehling's reagent test.
In these questions ( i - iv) a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
(i) Assertion: Fehling's solution can be used to distinguish between acetaldehyde and acetone.
Reason: Fehling's reagent is a mixture of two solutions.
(ii) Assertion: Aromatic aldehydes can be distinguished from aliphatic aldehydes by Fehling's solution.
Reason: Aromatic 'aldehydes reduce Fehling's solution, but aliphatic aldehydes do not.
(iii) Assertion: CH3CHO and C6H5CH2CHO cannot be distinguished chemically by Fehling's solution.
Reason: CH3CHO and C6H5CH2CHO can be distinguished by iodoform test.
(iv) Assertion: Formaldehyde, when heated with Fehling's reagent produces a reddish brown ppt. of Cu.
Reason: Fehling's reagent oxidises formaldehyde to formate ion.(a) -
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic addition reactions .
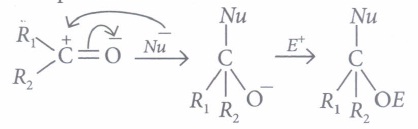
Carbonyl carbon is electron deficient hence acts as an electrophile. Nucleophile attacks on the electrophilic carbon atom of the carbonyl group from a direction perpendicular to the plane of the molecule.
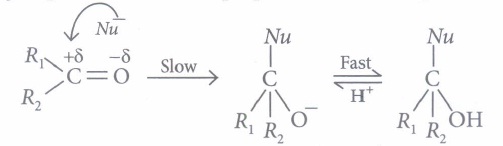
In this process, hybridisation of carbon atom changes from sp2 to sp3 and a tetrahedral alkoxide ion is formed as intermediate. This intermediate captures proton from the reaction medium to give the neutral product. Aldehydes are generally more reactive than ketones in nucleophilic addition reactions.
In these questions ( i - iv), a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
(i) Assertion: Benzaldehyde is more reactive than ethanal towards nucleophilic attack.
Reason: The overall effect of -land +R effect of phenyl group decreases the electron density on the carbon atom of >C=O group in benzaldehyde
(ii) Assertion: (CH3)3CCOC(CH3)3 and acetone can be distinguished by the reaction with NaHSO3.
Reason: HSO3 is the nucleophile in bisulphite addition.
(iii) Assertion: Ease of nucleophilic addition of the compounds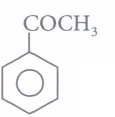 (I). CH3CHO(II) and CH3COCH3(III) is I > II > III.
(I). CH3CHO(II) and CH3COCH3(III) is I > II > III.
Reason : Aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic addition reactions.
(iv) Assertion: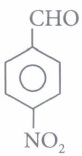 is more reactive towards nucleophilic addition reaction than
is more reactive towards nucleophilic addition reaction than 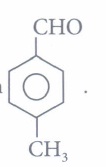
Reason : Reactivity of carbonyl group is due to electrophilic nature of carbonyl carbon.(a) -
Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic acids and their derivatives are collectively called carboxyl compounds which are widely spread both in plants and animal kingdom. They play an important role in biological processes. They are responsible for fragrance and flavour of naturally occurring compounds e.g., Vanilline (from vanilla beans), salicylaldehyde (from meadowsweet), cinnamaldehyde (from cinnamon) and isoamyl acetate (from banana) have pleasant flavour.
Acetone and acetic acid are widely used as solvents. Various carboxylic acids are used to prepare drugs (Analgesics, antipyretics etc.).
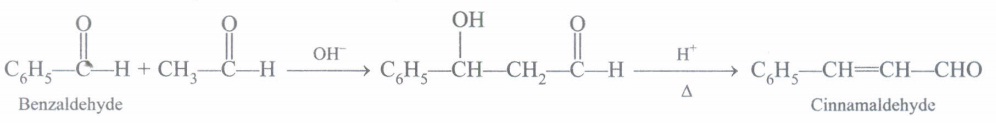
(a) Convert benzaldehyde to Cinnamaldehyde?
(b) What is IUPAC name of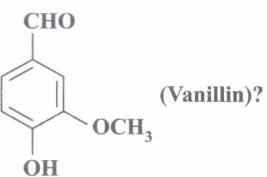
(c) Write the structural formula of Isoamyl acetate.
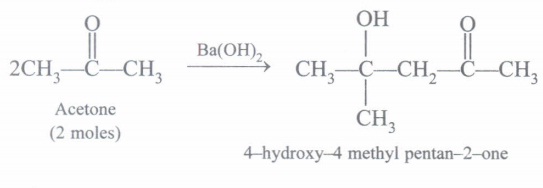
(d) What happens when 2 moles of acetone are condensed in presence of Ba(OH)2? Write chemical equation.
(e) What happens when acetic acid is heated with P2O5?(a) -
Study the table in whick pka of various is given. Answer the questions based on table and related studied concepts.
Compounds pka Acetic acid 4.76 HCOOH 3.75 CH3CH2COOH 4.38 CICH2COOH 2.87 FCH2COOH 2.59 CH2 = CH-COOH 4.30 Benzoic acid 4.19 p- Toluic acid 4.38 Salicylic acid 2.98 p-nitro benzoic acid 3.44 p-methoxy benzoic acid 4.88 p-chloro benzoic acid 3.99 p-hydroxy benzoic acid 4.58 (a) Why is HCOOH stronger than CH3 COOH?
(b) Why is p-hydroxy benzoic acid more acidic than p-methoxy benzoic acid?
(c) Why is salicylic acid stronger than benzoic acid?
(d) What happens when salicylic acid is heated with zinc dust?
(e) Give one use of salicylic acid.(a) -
The following table has boiling points of different classes of compounds. Study the table and answer the questions based on table and related studied concepts.
Compound Boiling point Ethanal 20.2°C Ethanol 78°C Acetone 56.2 °C Acetic acid 118°C Acetic anhydride 139.8 oc Diethyl ether 34.6°C Acetamide 222°C Ethyl acetate 77.1 oc (a) Why diethyl ether has lower boiling point than C2H5OH?
(b) Why acetic anhydride has high boiling point than acetic acid?
(c) Why amides have higher boiling point among-acid derivatives?
(d) Why does aqueous solution of CH3 COOH conducts electricity but ethanol does not?
(e) How will you distinguish between ethanol and acetone by suitable chemical test?(a)
Case Study
*****************************************
Answers
Aldehydes , Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Case Study Questions With Answer Key Answer Keys
-
(i) (c) : Condensation reaction is the reverse of hydrolysis, which splits a chemical entity into two parts through the action of the polar water molecule
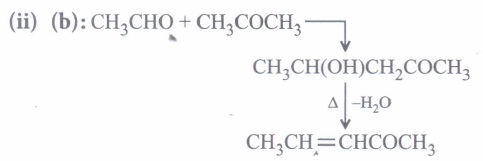
(iii) (a)
(iv) (d) -
(i) (a): It is an example of cross Cannizzaro reaction where aromatic aldehyde gets reduced to alcohol and aliphatic aldehyde gets oxidised to its sodium salt (both aldehydes must not contain any \(\alpha\)-hydrogen).
(ii) (c)
(iii) (a): The Cannizzaro product of given reaction yields 2, 2, 2-trichloroethanol.
(iv) (a): C-C bond is not formed in Cannizzaro reaction while other reactions result in the formation of C-C bond. -
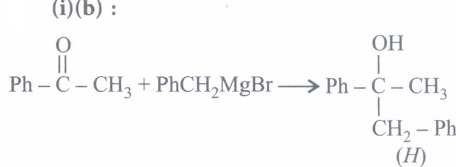
(iv) (b) -
(i) (d): All the reactions are showing the acidic properties of carboxylic acid. Carboxylic acid forms the sodium salts with all i.e., alkali metals, NaOH and Na2CO3 etc. and removes the acidic proton from the carboxylic acid.
(ii) (a): In general, greater the +I effect of the group attached to the carboxyl group, lesser will be the acidic strength and greater the -I effect ofthe group, greater will be acidic strength. As number of halogen atoms and electronegativity of halogen atom increases, acidic strength increases. Thus, correct order of acidic strength is
CF3COOH> CHCl2COOH > HCOOH > C6H5CH2COOH > CH3COOH
(iii) (c) : Stronger -I group attached closer to - COOH makes the acid stronger, i.e., acid has the larger dissociation constant. - Br shows poor (-I) effect and also far away from -COOH group i.e., option (c) has smallest dissociation constant.
(iv) (a): Due to ortho-effect, (I) and (II) are stronger acids than (III) and (IV). Due to two ortho-hydroxyl groups in (I), it is stronger acid than (II). (III) is a stronger acid than (IV) because at m-position, -OH group cannot exert its +R effect but can only exert its -I effect while at p-position, -OH group exerts its strong +R effect. Thus, the correct order of acidity is : I > II > III > IV. -
(i) (a): Iodoform test is given by the organic compounds having
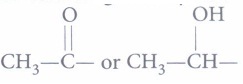
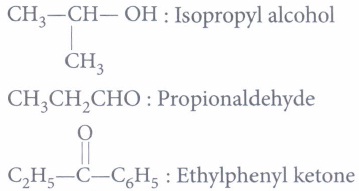
C6H5 - CH2-OH : Benzyl alcohol
Therefore, isopropyl alcohol will give positive iodoform test.
(ii) (b): Iodoform reaction of acetone occurs in following steps
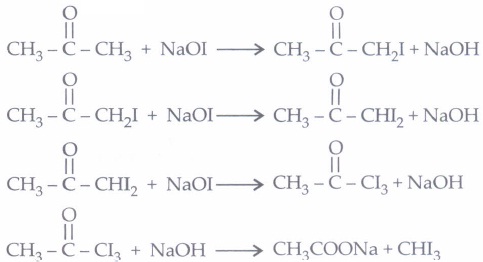
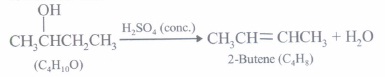
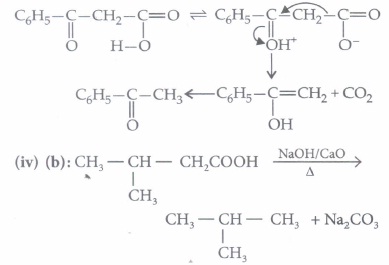
(iii) (c): Given reagents indicate the presence of -COCH3 group in the starting compound A. Further, since the -COOH group introduced in B due to iodoform reaction is absent in the final product, B should be a p-keto acid. Hence, A should have structure given in option (c).
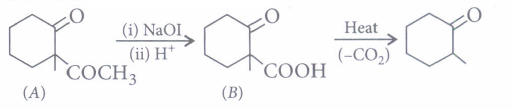
(iv) (c): Since compound A(C3H6O) undergoes iodoform test, it must be CH3COCH3 (propanone). Further, the compound 'B' obtained from 'A' has three times more the number of carbon atoms as in 'A' (propanone), 'B' must be phorone, i.e., 2,6-dimethyl-2, 5-heptadien -4-one.
\(\left(\mathrm{CH}_{3}\right)_{2} \mathrm{C}=\mathrm{O}+\mathrm{H}_{3} \mathrm{CCOCH}_{3}+\mathrm{O}=\mathrm{C}\left(\mathrm{CH}_{3}\right)_{2}\) \(\stackrel{\mathrm{HCl}}{\rightarrow}\left(\mathrm{CH}_{3}\right)_{2} \mathrm{C}=\mathrm{CHCOCH}=\mathrm{C}\left(\mathrm{CH}_{3}\right)_{2}\)
A, propanone(3 molecules) 2,6-dimethyl- 2,5-heptadien-4-one -
(i) (b): As (A) and (C) gives positive Tollens' test thus these two should be aldehydes while (B) should be a ketone (does not give Tollen's test) with
group (as it gives positive iodoform test). Three isomers are.
(iii) (b): (B) is least reactive among the three isomers towards addition of HCN. Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones towards nucleophilic addition reactions.
(iv) (a): When butanone reacts with ethylene glycol in presence of HCl, it forms a ketal.
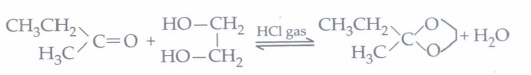
-
(i) (d): 2-Methyl-2-propanol is
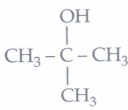 It cannot be obtained by reduction of an aldehyde or ketone with NaBH4·
It cannot be obtained by reduction of an aldehyde or ketone with NaBH4·
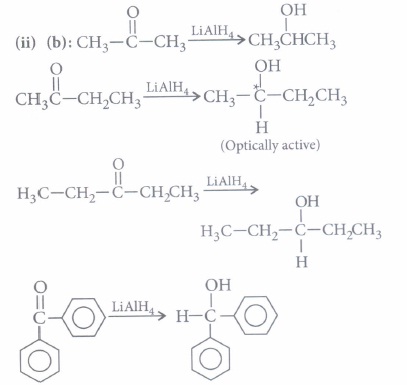
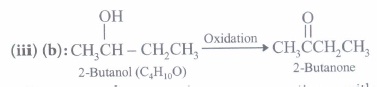
2-Butanone forms oxime on reaction with hydroxylamine (NH2OH) and also gives positive iodoform test.
-
(i) (a)
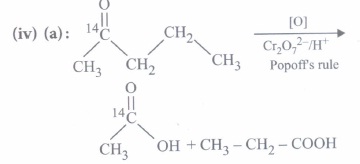
(ii) (c): Phosphorus converts a little .of the acid into acid chloride which is more reactive than the parent carboxylic acid. Thus, it is the acid chloride, not the acid itself, that undergoes chlorination at the \(\alpha\)-carbon.
(iii) (a): \(\beta\)-ketoacids are unstable acids. They readily undergo decarboxylation through a cyclic transition state.
(i) (b): All aliphatic aldehydes give red ppt. with
Fehling's solution, but ketones do not reduce Fehling's
solution.
(ii) (e): Aliphatic aldehydes reduce Fehling's solution,
but aromatic aldehydes do not. -
(i) (b): All aliphatic aldehydes give red ppt. with Fehling's solution, but ketones do not reduce Fehling's solution.
(ii) (c): Aliphatic aldehydes reduce Fehling's solution, but aromatic aldehydes do not.
(iii) (b): CH3CHO and C6H5CH2CHO both are aliphatic aldehydes, hence cannot be distinguished by Fehling's solution. CH3CHO contains CH3COgroup whereas C6H5CH2CHO does not contain any CH3CO- group. Thus, CH3CHO will give yellow ppt. with 12 and NaOH but C6H5CH2CHO will not.
(iv) (d): Formaldehyde when heated with Fehling's reagent, undergo oxidation to give formate ion and produce reddish brown ppt. of Cu2O.
\(\mathrm{HCHO}+2 \mathrm{Cu}^{2+}+5 \mathrm{OH}^{-} \rightarrow \mathrm{HCOO}^{-}+\mathrm{Cu}_{2} \mathrm{O}+3 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\\ \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \text { Reddish brown ppt. } \) -
(i) (a)
(ii) (b): \(\mathrm{HSO}_{3}^{-}\) is a bulky nucleophile, hence, cannot attack on sterically hindered ketones.
(iii) (d): Aromatic aldehydes and ketones are less reactive than the corresponding aliphatic analogues towards nucleophilic addition reactions due to the +R effect of benzene ring. Further, aldehydes are more reactive than ketones due to +I effect and steric effect of alkyl group. Therefore, the ease of nucleophilic addition will follow the order:
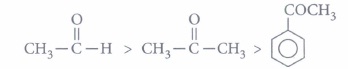
(iv) (b): Electron withdrawing group (-NO2) increases the reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reactions, whereas electron donating group (-CH3) decreases the reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reactions. -
(a)
(b) 4-hydroxy- 3-methoxy benzaldehyde
(c)
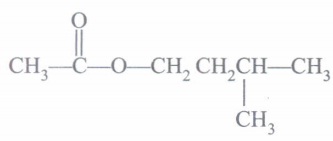
(d)
(e)
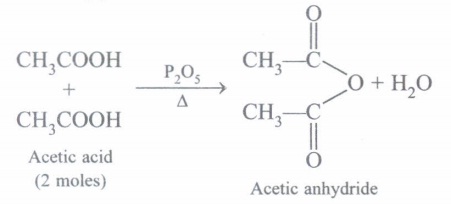
Acetic anhydride is formed. -
(a) It is because HCOO- is more stable than CH3COO-.
(b) It is because -OH has more -I effect than -OCH3 group.
(c) It is because salicylate is more stable than benzoate ion due to intra molecular H-bonding.
(d)
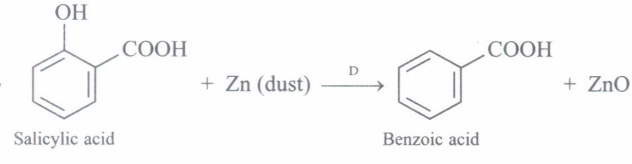
(e) It is used for preparation of Aspirin which is an important Analgesics, Antipyretic and prevents heart attack. -
(a) It is because diethyl ether have weaker dipole-dipole attraction than C2H5OH which has intermolecular H-bonding.
(b) It is because acetic anhydride has higher molar mass, more surface area, more van der Waals' forces of attraction than acetic acid.
(c) Most of amides are solids and have strong forces of attraction, hence higher boiling point.
(d) It is because acetic acid ionise in aqueous solution early where as ethanol does not.
(e) Add Ceric ammonium nitrate. Ethanol gives wine red colouration, Acetone does not.






































