Class 12th Chemsitry - Biomolecules Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
By QB365 on 08 Sep, 2022
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 12 Chemsitry Subject - Biomolecules, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Biomolecules Case Study Questions With Answer Key
12th Standard CBSE
-
Reg.No. :
Chemistry
-
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Pentose and hexose undergo intramolecular hemiacetal or hemiketal formation due to combination of the -OH group with the carbonyl group. The actual structure is either of five or six membered ring containing an oxygen atom. In the free state all pentoses and hexoses exist in pyranose form (resembling pyran). However, in the combined state some of them exist as five membered cyclic structures, called furanose (resembling furan).

The cyclic structure of glucose is represented by Haworth structure:
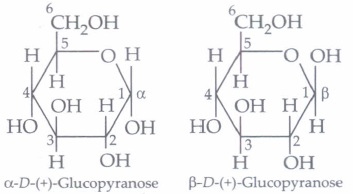
\(\alpha \) and \(\beta\) -D-glucose have different configuration at anomeric (C-l) carbon atom, hence are called anomers and the C-l carbon atom is called anomeric carbon (glycosidic carbon).
The six membered cyclic structure of glucose is called pyranose structure.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
(i) \(\alpha\) -D(+)-glucose and \(\beta\) -D( +)glucose are(a) enantiomers (b) conformers (c) epimers (d) anomers (ii) The following carbohydrate is
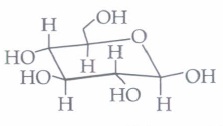
(a) a ketohexose (b) an aldohexose (c) an \(\alpha \)-furanose (d) an \(\alpha \)-pyranose (iii) In the following structure,
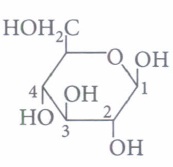
anomeric carbon is(a) C-l (b) C-2 (c) C-3 (d) C-4 (iv) The term anomers of glucose refers to
(a) isomers of glucose that differ in configurations at carbons one and four (C-l and C-4) (b) a mixture of (D)-glucose and (L)-glucose (c) enantiomers of glucose (d) isomers of glucose that differ in configuration at carbon one (C-l). (a) -
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
When a solution of an \(\alpha \) -amino acid is placed in an electric field depending on the pH of the medium, following three cases may happen.

(i) In alkaline solution,\(\alpha \) -amino acids exist as anion II, and there is a net migration of amino acid towards the anode.
(ii) In acidic solution, \(\alpha \) -amino acids exist as cation III, and there is a net migration of amino acid towards the cathode.
(iii) If II and III are exactly balanced there is no net migration; under such conditions anyone molecule exists as a positive ion and as a negative ion for exactly the same amount of time, and any small movement in the direction of one electrode is subsequently cancelled by an equal movement back toward the other electrode. The pH of the solution in which a particular amino acid does not migrate under the influence of an electric field is called the isoelectric point of that amino acid.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
(i)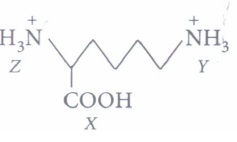
Arrange in order of increasing acid strengths.(a) X>Z>Y (b) Z (c) X>Y>Z (d) Z>X>Y (ii) In aqueous solutions, amino acids mostly exist as
\(\text { (a) } \mathrm{NH}_{2}-\mathrm{CH} R-\mathrm{COOH}\) \(\text { (b) } \mathrm{NH}_{2}-\mathrm{CH} R-\mathrm{COO}^{-}\) \(\text { (c) } \mathrm{NH}_{3} \mathrm{CH} R \mathrm{COOH}\) \(\text { (d) } \mathrm{H}_{3} \mathrm{NCH} R \mathrm{COO}^{-}\) (iii) Amino acids are least soluble
(a) at pH 1 (b) at pH 7 (c) at their isoelectric points (d) none of these. (iv) The \(pK_{a_{1}}\)and \(pK_{a_{2}}\) of an amino acid are 2.3 and 9.7 respectively. The isoelectric point of the amino acid is
(a) 12.0 (b) 7.4 (c) 6.0 (d) 3.7 (a) -
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Carbohydrates can exist in either of two conformations, as determined by the orientation of the hydroxyl group about the asymmetric carbon farthest from the carbonyl.
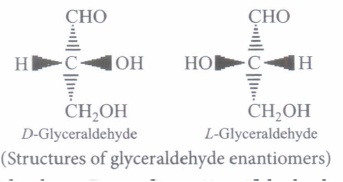
By convention, a monosaccharide is said to have D-configuration if the hydroxyl group attached to the asymmetric carbon atom adjacent to the - CH2OH group is on the right hand side irrespective of the positions of the other hydroxyl groups. On the other hand, the molecule is assigned L-configuration if the - OH group attached to the carbon adjacent to the - CH2OH group is on the left hand side.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
(i) D-Glyceraldehyde and L-Glyc~raldehyde are(a) epimers (b) enantiomers (c) anomers (d) conformational diasteriomers (ii) Which of the following monosaccharides, is the majority found in the human body?
(a) D-type (b) L-type (c) Both of these (d) None of these (iii) Monosaccharides contain
(a) always six carbon atoms (b) always five carbon atoms (c) always four carbon atoms (d) may contain 3 to 7 carbon atoms (iv) The correct corresponding order of names of four aldoses with configuration given below
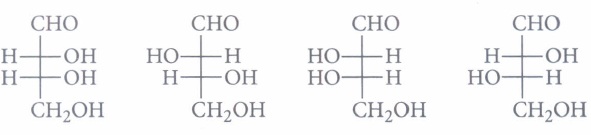
respectively, is(a) L-erythrose, L-threose, L-erythrose, D-threose (b) D-threose, D-erythrose, L-tl?repse, L-erythrose (c) L-erythrose, L-threose, D-erythrose, D-threose (d) D-erythrose, D-threose, L-erythrose, L-threose. (a) -
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones and those compounds which on hydrolysis give such compounds are also carbohydrates. The carbohydrates which are not hydrolysed are called monosaccharides. Monosaccharides with aldehydic group are called aldose and those which free ketonic groups are called ketose. Carbohydrates are optically active. Number of optical isomers = 2n
Where n = number of asymmetric carbons. Carbohydrates are mainly synthesised by plants during photosynthesis.
The monosaccharides give the characteristic reactions of alcohols and carbonyl group (aldehydes and ketones). It has been found that these monosaccharides exist in the form of cyclic structures. In cyclization, the -OH groups (generally C5 or C4 in aldohexoses and C5 or C6 in ketohexoses) combine with the aldehyde or keto group. As a result, cyclic structures of five or six membered rings containing one oxygen atom are formed, e.g., glucose forms a ring structure. Glucose contains one aldehyde group, one 1o alcoholic group and four 2o alcoholic groups in its open chain structure.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
(i) First member of ketos sugar is(a) ketotriose (b) ketotetrose (c) ketopentose (d) ketohexose (ii) In CH2OHCHOHCHOHCHOHCHOHCHO, the number of optical isomers will be
(a) 16 (b) 8 (c) 32 (d) 4 (iii) Some statements are given below:
1. Glucose is aldohexose.
2. Naturally occurring glucose is dextrorotatory.
3. Glucose contains three, chiral centres.
4. Glucose contains one 1o alcoholic group and four 2o alcoholic groups.
Among the above, correct statements are(a) 1 and 2 only (b) 3 and 4 only (c) 1,2 and 4 only (d) 1,2,3 and 4 (iv) Which of the following reactions of glucose can be explained only by its cyclic structure?
(a) Glucose forms cyanohydrin with HCN (b) Glucose reacts with hydroxylamine to form an oxime (c) Pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine (d) Glucose is oxidised by nitric acid to gluconic acid . (a) -
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
When a protein in its native form, is subjected to physical changes like change in temperature or chemical changes like change in pH, the hydrogenbonds are disturbed. Due to this, globules unfold and helix get uncoiled and protein loses its biological activity. This is called denaturation of protein.
The denaturation causes change in secondary and tertiary structures but primary structures remains intact. Examples of denaturation of protein are coagulation of egg white on boiling, curdling of milk, formation of cheese when an acid is added to milk.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
(i) Mark the wrong statement about denaturation of proteins(a) The primary structure of the protein does not change (b) Globular proteins are converted into fibrous proteins. (c) Fibrous proteins are converted into globular proteins. (d) The biological activity of the protein is destroyed. (ii) Which structure(s) of proteins remains(s) intact during denaturation process?
(a) Both secondary and tertiary structures (b) Primary structure only (c) Secondary structure only (d) Tertiary structure only (iii) Cheese is a
(a) globular protein (b) conjugated protein (c) denatured protein (d) derived protein (iv) Secondary structure of protein refers to
(a) mainly denatured proteins and structure of prosthetic groups (b) three-dimensional structure, especially the bond between amino acid residues that are distant from each other in the polypeptide chain (c) linear sequence of amino acid residues in the polypeptide chain (d) regular folding patterns of continuous portions of the polypeptide chain (a) -
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The sequence of bases along the DNA and RNA chain establishes its primary structure which controls the specific properties of the nucleic acid. An RNA molecule is usually a single chain of ribose-containing nucleotide. On the basis of X-ray analysis of DNA, J.D., Watson and F.H.C. crick (shared noble prize in 1962) proposed a three dimensional secondary structure for DNA. DNA molecule is a long and highly complex, spirally twisted, double helix, ladder like structure. The two polynucleotide chains or strands are linked up by hydrogen bonding between the nitrogeneous base molecules of their nucleotide monomers. Adenine (purine) always links with thymine (pyrimidine) with the help of two hydrogen bonds and guanine (purine) with cytosine (pyrimidine) with the help of three hydrogen bonds. Hence, the two strands extend in opposite directions, i.e., are antiparallel and complimentary.
In these questions (i-iv), a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
(i) Assertion: DNA molecules and RNA molecules are found in the nucleus of a cell.
Reason: There are two types of nitrogenous bases, purines and pyrimidines. Adenine (A) and guanine (G) are substituted purines; cytosine (C), thymine (T) and uracil (U) are substituted pyrimidines
(ii) Assertion: In both DNA and RNA, heterocyclic base and phosphate ester linkages are at C-1' and C-5' respectively of the sugar molecule.
Reason: Nucleotides and nucleosides mainly differ from each other in presence of phosphate units.
(iii) Assertion: The backbone ofRNA molecule is a linear chain consisting of an alternating units of a heterocylic base, D-ribose and a phosphate.
Reason: The segment of DNA which acts as the instruction manual for the synthesis of protein is ribose.
(iv) Assertion: The double helical structure of DNA was proposed by Emil Fischer.
Reason: A nucleoside is an N-glycoside of heterocyclic base.(a) -
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Proteins are high molecular mass complex biomolecules of amino acids. The important proteins required for our body are enzymes, hormones, antibodies, transport proteins, structural proteins, contractile proteins etc. Except for glycine, all a-amino acids have chiral carbon atom and most of them have L-configuration. The amino acids exists as dipolar ion called zwitter ion, in which a proton goes from the carboxyl group to the amino group. A large number of a-amino acids are joined by peptide bonds forming polypeptides. The pep tides having very large molecular mass (more than 10,000) are called proteins. The structure of proteins is described as primary structure giving sequence of linking of amino acids; secondary structure giving manner in which polypeptide chains are arranged and folded; tertiary structure giving folding, coiling or bonding polypeptide chains producing three dimensional structures and quaternary structure giving arrangement of sub-units in an aggregate protein molecule.
In these questions (i-iv), a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
(i) Assertion: All amino acids are optically active.
Reason: Amino acids contain asymmetric carbon atoms.
(ii) Assertion: In \(\alpha \) -helix structure, intramolecular H-bonding takes place whereas in \(\beta \) -pleated structure, intermolecular H-bonding takes place.
Reason: An egg contains a soluble globular protein called albumin which is present in the white part.
(iii) Assertion: Secondary structure of protein refers to regular folding patterns of continuos portions of the polypeptide chain.
Reason: Out of 20 amino acids, only 12 amino acids can be synthesised by human body.
(iv) Assertion: The helical structure of protein is stabilised by intramolecular hydrogen bond between -NH and carbonyl oxygen.
Reason: Sanger's reagent is used for the identification of N-terminal amino acid of peptide chain.(a) -
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Glucose is known as dextrose because it occurs in nature as the optically active dextrorotatory isomer. It is essential constituent of human blood. The blood normally contains 65 to 110 mg of glucose per 100 mL (hence named Blood sugar). The level may be much higher in diabetic persons. The urine of diabetic persons also contain considerable amount of glucose. In combined form, it occurs in cane sugar and polysaccharides such as starch and cellulose.
Glucose has an aldehyde group (-CHO), one primary alcoholic group (-CH2OH) and four secondary alcoholic groups (-CHOH) in their structure. Due to the presence five hydroxyl groups (-OH), glucose acetylation. Glucose also undergoes oxidation with mild oxidising agents like bromine water as well as with strong oxidising agents like nitric acid. Since glucose is readily oxidised, it acts as a strong reducing agent and reduces Tollen's reagent and Fehling solution. Glucose exists in two crystalline forms: \(\alpha \) -D-glucose and \(\beta \) -Dglucose undergoes If either of the two forms is dissolved in water and allowed to stand, the specific rotation of the solution changes gradually, until a constant value is obtained. This change is called mutarotation.
In these questions (i-iv), a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
(i) Assertion: A diabetic person carries a packet of glucose with him always.
Reason: Glucose increases the blood sugar level almost instantaneously.
(ii) Assertion: On oxidation with nitric acid, glucose as well as gluconic acid both yield saccharic acid.
Reason: The pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine indicating the absence of free -CHO group.
(iii) Assertion: Glucose reacts with acetyl chloride to form pentaacetyl glucose.
Reason: The formation of pentaacetyl derivative confirms the presence of five -OH groups in glucose.
(iv) Assertion: A certain compound gives negative test with ninhydrin and positive test with Benedict's solution, the compound is an amino acid.
Reason: Glucose is a monosaccharide.(a) -
Biomolecules are complex molecules which build up living organisms and required for their growth, maintenance and ability to reproduce. Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones which are major sources of energy. Monosachharides are simple sugars which cannot be hydrolysed. Oligosachharide, on hydrolysis give 2 to 10 molecules of monosachharides. Polysachharides like starch and cellulose on hydrolysis give large number of molecules of glucose \(\alpha\)-glucose and \(\beta\)-glucose (Anomers). Proteins are complex nitrogeneous polymers of amino acids connected through peptide bonds. The sequence in which amino acids are linked is called Primary structure. Secondary structures are of 2 types \(\alpha\)-helix in globular proteins and \(\beta\)-pleated structure in fibrous proteins involving H-bonds. Tertiary structure has H-bonds, disulphide linkage, ionic bonding and van der Waals' forces. Insulin is hormone for metabolism of glucose, has quarternary structure. Denaturation of protein destroys secondary and tertiary structure, loss of biological activity but primary structure remaining the same.
Enzymes are highly specific, work at specific pH, moderate temperature and catalyse biochemical reactions. Hormones perform specific functions and secreated by endocrine glands. Vitamins are essential for healthy body. A, D, E, K are fat soluble vitamins. Vitamin C and B1, B2, B6 are water soluble. B12 is neither water, nor fat soluble. Nucleic acids are polymer of nucleotides. RNA consist of m-RNA, t-RNA, r-RNA. RNA has Adenine, Cytosine, Uracil and Guanine. It helps in protein synthesis. It cannot replicate. DNA contains deoxyribose, A, C, G and Thymine. It transfers genetic characteristics. DNA has double helix structure and undergoes replication.
(a) Name a disaccharide which on hydrolysis give glucose and galactose.
(b) What type of protein is albumin?
(c) Name one non-reducing sugar.
(d) Which one is complementary base of cytosine in one strand of DNA to that in other strand of DNA?
(e) Which linkage by which nucleotide are joined together between 5' and 3' atoms of pentose sugar?
(f) Which vitamin helps in coagulation of blood?
(g) Which enzyme can dissolve blood clots to prevent heart attack?(a) -
Living system are made up of complex molecules called Biomolecules. Carbohydrate, proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids, lipids, hormones ATP, DNA and RNA play an important role in our daily life. Carbohydrates provide us energy. Protein help in growth and maintenance of body. Nucleic acids, RNA helps in protein synthesis, DNA helps in transfer of genetic characteristics. Fat are source of energy and protect our vital organs.
(a) Why are carbohydrates optically active?
(b) Name two acidic amino acids.
(c) Name a protein which has quarternary structure.
(d) What are products of hydrolysis of fats?
(e) What is role of glycerol in shaving creams?(a) -
Table shows carbohydrates and artificial sweeteners and their relative sweetness. Study the table and answer the questions based on table and related concepts.
Carbohydrate Relative sweetness Lactose 16 Maltose 32 Galactose 32 Glucose 74 Sucrose 100 Fructose 173 Saccharine 500 time than sugar Aspartame 160 times than sugar Alitame 2000 times than sugar Sucralose 650 times than sugar (a) Which is sweetest sugar and why?
(b) What is difference between glucose and fructose?
(c) Why are artificial sweetener better than sugar for diabetic patients?
(d) What is limitation of Alitame?
(e) What happens when glucose is treated with conc. HNO3 ?
(f) What are non-reducing sugar? Select the nonreducing sugar from the table?
(g) Which sugar is present in milk? What are its product of hydrolysis?
(h) Classify the sugars given in table into monosachharides and disachharides.
Glucose, Lactose, Sucrose, Maltose, Fructose, Galactose.
(i) Which artificial sweetener is most suitable for making sweets for diabetic patients.
(j) Which artificial sweetener is added in diet coke and pepsi? What is its limitation?(a)
Case Study
*****************************************
Answers
Biomolecules Case Study Questions With Answer Key Answer Keys
-
(i) (d): \(\alpha \)-D-(+)-glucose and \(\beta \) -D-(+)-glucose differ in configuration at C1 (U., anomeric or glycosidic carbon) and hence are called anomers.
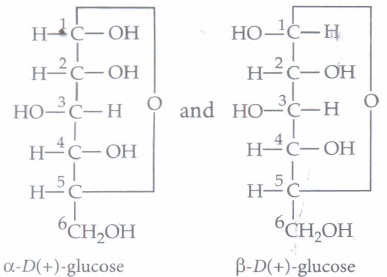
(ii) (b): This structure is an example of pyranose and aldohexose. Here, the carbohydrate's structure is of the \(\beta \) -pyranose form.
(iii) (a) : C-1 is the anomeric carbon.
(iv) (d): Anomers are cyclic monosaccharides or glycosides that are epimers, differing from each other in the configuration at C-1, if they are aldoses or in the configuration at C- 2 if they are ketoses. -
(i) (a): Carboxylic acids are stronger acids than - +NH3, therefore X is the strongest acid. Since -COOH has -I effect which decreases with distance therefore, effect is more pronounced on Z than on Y. As a result Z is more acidic than Y, therefore, overall order of increasing acid strength is X > Z > Y.
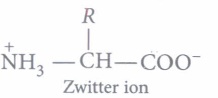
(ii) (d): In aqueous solutions, amino acids mostly exist as zwitter ion or dipolar ion
(iii) (c) : Amino acids are least soluble at their isoelectric points. At a specific pH, called isoelectric point, the positive and negative charges balance each other and the net charge becomes zero. If there is a charge, the amino acid prefers to interact with water, rather than other amino acid molecules, this charge makes it more soluble.
(iv) (c) : Isoelectric point = \(\frac{2.3+9.7}{2}=6\)
-
(i) (b)
(ii) (a)
(iii) (d)
(iv) (d):
-
(i) (a)
(ii) (a)
(iii) (c) : Glucose contains four chiral centres.
(iv) (c) : Pentacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine showing absence of free -CHO group. This cannot be explained by open structure of glucose. -
(i) (c)
(ii) (b)
(c) : Cheese is a denatured protein
(iv) (d) -
(i) (d): DNA occurs in nucleus of the cell while RNA is found mainly in cytoplasm of the cell.
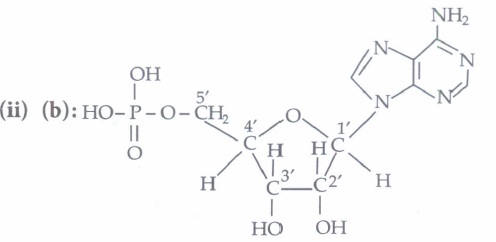
Nucleosides contain only sugar and a base whereas nucleotides contain sugar, base and a phosphate group as well.
(iii) (c): The segment of DNA which acts as the instruction mannual for the synthesis of protein is gene.
(iv) (d): The double helical structure of DNA was proposed by Watson and Crick. -
(i) (d) : All amino acids except glycine are optically active because they contain, asymmetric carbon atom. They exist in both D and L- forms. Most naturally occurring amino acids have L-configuration.
(ii) (b): In a-helix structure, the formation of hydrogen bonds takes place between -co- and -NH groups, whereas in ~-pleated structure, hydrogen bonds are formed between amide groups of two different chains.
(iii) (c) : Out of 20 amino acids, only 10 amino acids can be synthesised by human body.
(iv) (b) -
(i) (a)
(ii) (b):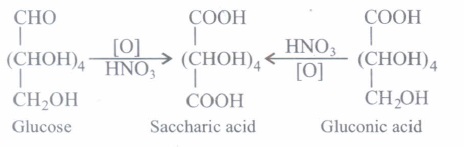
Strong oxidising agents like nitric acid oxidises both the terminal -CHO and -CH2OH groups of glucose to give the dibasic acid, saccharic acid.
(iii) (b)
(iv) (d): If a certain compound gives negative test with ninhydrin and positive test with Benedict's solution then the compound should be a monosaccharide. -
(a) Lactose.
(b) Globular protein.
(c) Sucrose
(d) Guanine
(e) Phosphodiester linkage
(f) Vitamin K.
(g) Streptokinase -
(a) It is because they contain 'Chiral' carbon atoms.
(b) Aspartic acid and Glutamic acid.
(c) Haemoglobin
(d) Glycerol and fatty acids
(e) Glycerol is hygroscopic in nature, therefore, keep the skin moist. -
(a) Fructose is sweetest sugar because it can form the bonds to maximum extent.
(b) Glucose has aldehyde group, where as fructose has keto group.
(c) It is because they do not add calories for diabetic patients.
(d) Its sweetness cannot be controlled.
(e) Saccharic acid is formed
(f) Those sugars which do not give brick red ppt. with Fehling's solution are called non-reducing sugar. Sucrose is non-reducing sugar.
(g) Lactose is present in milk.
Glucose and galactose are its products of hydrolysis.
(h) Glucose, Fructose, Galactose are monosachharides
Lactose, Sucrose, Maltose are disachharides.
(i) Sucralose.
(j) Aspartame. It is unstable at cooking temperature






































